
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321982582
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.23E
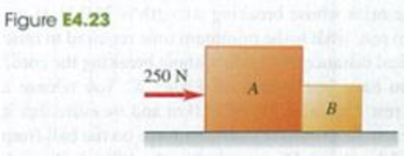
Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal, frictionless surface (Fig. E4.23). Box A has mass 20.0 kg and box B has mass 5.0 kg. A horizontal force of 250 N is exerted on box A. What is the magnitude of the force that box A exerts on box B?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:45
Students have asked these similar questions
Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal, frictionless surface . Box A has mass 20.0 kg and box B has mass 5.0 kg. A horizontal force of 250 N is exerted on box A. What is the magnitude of the force that box A exerts on box B?
Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Box A has mass 20.0 kg and box B has mass 5.0 kg. A horizontal force of 100 N is exerted on box B. What is the magnitude of the force that box B exerts on box A?
A block is on a frictionless table, on earth. The block accelerates at 8.5 m/s2 when a horizontal force is applied to it. The block and table are set up on the moon. The acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the moon is 1.62 m/s2. A horizontal force, equal in magnitude to the weight of the block on earth, is applied to the block when it is on the moon. The acceleration imparted to the block is closest to:
Chapter 4 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Ch. 4.1 - Figure 4.5 shows a force F acting on a crate. With...Ch. 4.2 - In which of the following situations is there zero...Ch. 4.3 - Rank the following situations in order of the...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 4.4TYUCh. 4.5 - You are driving a car on a country road when a...Ch. 4 - Can a body be in equilibrium when only one force...Ch. 4 - A ball thrown straight up has zero velocity at its...Ch. 4 - A helium balloon hovers in midair, neither...Ch. 4 - When you fly in an airplane at night in smooth...Ch. 4 - If the two ends of a rope in equilibrium are...
Ch. 4 - You tie a brick lo the end of a rope and whirl the...Ch. 4 - When a car stops suddenly, the passengers tend to...Ch. 4 - Some people say that the force of inertia (or...Ch. 4 - A passenger in a moving bus with no windows...Ch. 4 - Suppose you chose the fundamental physical...Ch. 4 - Why is the earth only approximately an inertial...Ch. 4 - Does Newtons second law hold true for an observer...Ch. 4 - Some students refer to the quantity ma as the...Ch. 4 - The acceleration of a falling body is measured in...Ch. 4 - You can play catch with a softball in a bus moving...Ch. 4 - Students sometimes say that the force of gravity...Ch. 4 - Why can it hurt your foot more to kick a big rock...Ch. 4 - Its not the fall that hurts you; its the sudden...Ch. 4 - A person can dive into water from a height of 10 m...Ch. 4 - Why are cars designed to crumple in front and back...Ch. 4 - When a string barely strong enough lifts a heavy...Ch. 4 - A large crate is suspended from the end of a...Ch. 4 - Which feels a greater pull due to the earths...Ch. 4 - Why is it incorrect to say that 1.0 kg equals 2.2...Ch. 4 - A horse is hitched to a wagon. Since the wagon...Ch. 4 - True or false? You exert a push P on an object and...Ch. 4 - A large truck and a small compact car have a...Ch. 4 - When a car comes to a stop on a level highway,...Ch. 4 - A small compact car is pushing a large van that...Ch. 4 - Consider a tug-of-war between two people who pull...Ch. 4 - Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal,...Ch. 4 - A manual for student pilots contains this passage:...Ch. 4 - If your hands are wet and no towel is handy, you...Ch. 4 - If you squat down (such as when you examine the...Ch. 4 - When a car is hit from behind, the occupants may...Ch. 4 - In a head-on auto collision, passengers who are...Ch. 4 - In a head-on collision between a compact 1000-kg...Ch. 4 - Suppose you are in a rocket with no windows,...Ch. 4 - Two dogs pull horizontally on ropes attached to a...Ch. 4 - To extricate an SUV stuck in the mud, workmen use...Ch. 4 - BIO Jaw Injury. Due to a jaw injury, a patient...Ch. 4 - A man is dragging a trunk up the loading ramp of a...Ch. 4 - Forces F1 and F2act at a point. The magnitude of...Ch. 4 - An electron (mass = 9.11 1031 kg) leaves one end...Ch. 4 - A 68.5-kg skater moving initially at 2.40 m/s on...Ch. 4 - You walk into an elevator, step onto a scale, and...Ch. 4 - A box rests on a frozen pond, which serves as a...Ch. 4 - A dockworker applies a constant horizontal force...Ch. 4 - A hockey puck with mass 0.160 kg is at rest at the...Ch. 4 - A crate with mass 32.5 kg initially at rest on a...Ch. 4 - A 4.50-kg experimental cart undergoes an...Ch. 4 - A 2.75-kg cat moves in a straight line (the...Ch. 4 - A small 8.00-kg rocket burns fuel that exerts a...Ch. 4 - An astronauts pack weighs 17.5 N when she is on...Ch. 4 - Superman throws a 2400-N boulder at an adversary....Ch. 4 - BIO (a) An ordinary flea has a mass of 210 g. How...Ch. 4 - At the surface of Jupiters moon Io, the...Ch. 4 - A small car of mass 380 kg is pushing a large...Ch. 4 - BIO World-class sprinters can accelerate out of...Ch. 4 - The upward normal force exerted by the floor is...Ch. 4 - Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal,...Ch. 4 - A student of mass 45 kg jumps off a high diving...Ch. 4 - Section 4.6 Free-Body Diagrams 4.25Crates A and B...Ch. 4 - You pull horizontally on block B in Fig. F4.26,...Ch. 4 - A ball is hanging from a long siring that is tied...Ch. 4 - CP A .22-caliber rifle bullet traveling at 350 m/s...Ch. 4 - A chair of mass 12.0 kg is sitting on the...Ch. 4 - A large box containing your new computer sits on...Ch. 4 - CP A 5.60-kg bucket of water is accelerated upward...Ch. 4 - CP You have just landed on Planet X. You release a...Ch. 4 - Two adults and a child want to push a wheeled cart...Ch. 4 - CP An oil tankers engines have broken down, and...Ch. 4 - CP BIO A Standing Vertical Jump. Basketball player...Ch. 4 - CP An advertisement claims that a particular...Ch. 4 - BIO Human Biomechanics. The fastest pitched...Ch. 4 - BIO Human Biomechanics. The fastest served tennis...Ch. 4 - Two crates, one with mass 4.00 kg and the other...Ch. 4 - CP Two blocks connected by a light horizontal rope...Ch. 4 - CALC To study damage to aircraft that collide with...Ch. 4 - CP A 6.50-kg instrument is hanging by a vertical...Ch. 4 - BIO Insect Dynamics. The froghopper (Philaenus...Ch. 4 - A loaded elevator with very worn cables has a...Ch. 4 - CP After an annual checkup, you leave your...Ch. 4 - CP A nail in a pine board stops a 4.9-N hammer...Ch. 4 - CP Jumping to the Ground. A 75.0-kg man steps off...Ch. 4 - The two blocks in Fig. P4.48 are connected by a...Ch. 4 - CP Boxes A and B are connected to each end of a...Ch. 4 - CP Extraterrestrial Physics. You have landed on an...Ch. 4 - CP CALC A mysterious rocket-propelled object of...Ch. 4 - CALC The position of a training helicopter (weight...Ch. 4 - DATA The table gives automobile performance data...Ch. 4 - DATA An 8.00-kg box sits on a level floor. You...Ch. 4 - DATA You are a Starfleet captain going boldly...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.56CPCh. 4 - BIO FORCES ON A DANCER'S BODY. Dancers experience...Ch. 4 - BIO FORCES ON A DANCERS BODY. Dancers experience...Ch. 4 - BIO FORCES ON A DANCER'S BODY. Dancers experience...Ch. 4 - The forces on a dancer can be measured directly...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
A ball rebounds elastically from the floor. What doesthis situation share with the ideas of momentum conservati...
Modern Physics
45. An oil layer floats on 85 cm of water in a tank. The absolute pressure at the bottom of the tank is 112.0 k...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
The high-E string on a guitar is fixed at both ends with length ℓ = 65.0 cm and fundamental frequency f1 = 329....
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the figure here, a box of Cheerios (mass mc = 1.70 kg) and a box of Wheaties (mass mw = 2.60 kg) are accelerated across a horizontal surface by a horizontal force applied to the Cheerios box. The magnitude of the frictional force on the Cheerios box is 2.10 N, and the magnitude of the frictional force on the Wheaties box is 4.60 N. If the magnitude of F is 12.7 N, what is the magnitude of the force on the Wheaties box from the Cheerios box? Number i Unitarrow_forwardThree boxes are lined up so that they are touching each other on a nearly frictionless plane. Box A has a mass of ?A=19.0 kg, box B has a mass of ?B=30.5 kg, and box C has a mass of ?C=53.0 kg. An external force ?⃗ pushes on box A toward the right, and the force that box B exerts on box C has a magnitude of 194 N. Ignore friction. What is the magnitude of the acceleration ? of the boxes?arrow_forwardA student takes the elevator up to the fourth floor to see her favorite physics instructor. She stands on the floor of the elevator, which is horizontal. Both the student and the elevator are solid objects, and they both accelerate upward at 5.35 m/s2. This acceleration only occurs briefly at the beginning of the ride up. Her mass is 88.0 kg. What is the normal force exerted by the floor of the elevator on the student during her brief acceleration? (Assume the direction is upward.)arrow_forward
- A brave but inadequate rugby player is being pushed backward by an opposing player who is exerting a force of 781 N, overcoming the force of friction between the losing player’s feet and the grass.The mass of the losing player plus equipment is 80.1 kg. The losing player is accelerating at 1.22 m/s² backward. What is the magnitude of the force of friction between the losing player’s feet and the grass?To solve this problem, draw a free-body diagram for the losing player. Then write the equation for the net force and acceleration in the horizontal direction, using variables for any unknowns. Finally, solvefor the force of friction, and calculate the magnitude of the force of friction on the losing player.arrow_forwardA 6.00 kg block is in contact with a 4.00 kg block on a horizontal frictionless surface. The 6.00 block is being pushed by a horizontal 20.0 N force. What is the magnitude of the force that the 6.00 kg block exerts on the 4.00 kg block?arrow_forwardQuestion 3. A hockey puck with a mass of 0.5 kg slides horizontally on the frictionless ice of a hockey rink. Two hockey sticks hit the puck simultaneously, exerting two forces F1 and F2. The force F has a magnitude of 5 N and is directed 36.6 degrees below the positive x-axis. F2 has a magnitude of 10 N and is directed 60 degrees above the positive x-axis. Determine the magnitude and direction of the puck's acceleration.arrow_forward
- A lineman is trying to push a training dummy with a force F₁ downward at an angle of 0=39.15°. His coach is pushing horizontally against the dummy in the opposite direction, with a force of magnitude F2 =78.22N. The dummy has a mass of m = 35.71 kg. The lineman exerts a force F₁ = 258.53 N. If the dummy just starts to move in the direction of F1. what is the magnitude of the coefficient of static friction between the dummy and the ground? Retain your answer to two decimal places. F1 F2 μsarrow_forwardA block of mass m is sitting on a block of mass M. The bottom block is sitting on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of static friction between the blocks is μs1, and the coefficient of static friction between the bottom block and the floor is μs2. What is the minimum pull force F on the bottom block so that the blocks begin to move? Given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bottom block and the floor is μk, what is the maximum pull force F so that there is no slipping between the blocks?arrow_forwardChapter 04, Problem 003 GO Two horizontal forces, F, and F,, are acting on a box, but only F, is shown in the drawing. F, The box moves only along the x axis. There is no friction between the box and the surface. Suppose that F = +7.1N and the mass of the box is 3.3 kg. Find the magnitude and direction of F, when the acceleration of the box is (a) +4.7 m/s², (b) -4.7 m/s², and (c) 0 m /s2. can point either to the right or to the left. F, (a) E = (b) F (c) Farrow_forward
- Four blocks with masses m1=5.00kg, m2= 5.10kg, m3= 7.00kg, m4= 7.20kg are pulled on a horizontal, frictionless surface by a 33.0 N force that makes a 34 degree angle with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the tension between m2 and m3 blocks?arrow_forwardAlex is asked to move two boxes of books in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless floor. He decides to move them at the same time by pushing on box A with a horizontal pushing force p =7.5N. Box A has a mass = 10.5 kg and box B has a mass 7.0 kg. The contact force between the two boxes is F and N denotes the normal force. A) What is the acceleration (in m/s to the 2nd) of the two boxes B) What is the force (in N) exerted on mb by ma? C) If Alex were to push from the other side on the 7.0 kg box, how would your answer to part (b) change?arrow_forwardA small car (mass 380 kg) is pushing a large truck ( mass 900 kg) due east on a level road. The car exerts a horizontal force of 1200 N on the truck. What is the magnitude of the force that the truck exerts on the car?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams With Examples; Author: The Physics Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3rZR7FSSidc;License: Standard Youtube License