
Concept explainers
A series of vane shear tests have been performed on a soft clay stratum. The results of these tests are as follows:
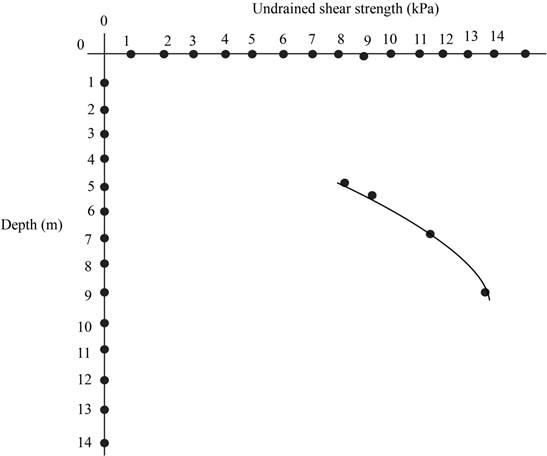
The vane was 60 mm in diameter and 120 mm long. The soil has a liquid limit of 100 and a plastic limit of 30. Compute the undrained shear strength for each test, then develop a plot of undrained shear strength versus depth. This plot should have depth on the vertical axis, with zero at the top of the plot.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 4 Solutions
Foundation Design: Principles and Practices (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
- 8.19 Three routes connect an origin and a destination with performance functions t₁ = 8+ 0.5x1, t2 = 1 + 2x2, and t3 = 3 + 0.75x3, with the x's expressed in thousands of vehicles per hour and the 's expressed in minutes. If the peak-hour traffic demand is 3400 vehicles, determine user-equilibrium traffic flows.arrow_forward8.8 onlyarrow_forward8.4 Consider a Poisson regression model for the number of social/recreational trips generated during a peak-hour period that is estimated by (see Eq. 8.3) BZ = -0.75 +0.025(household size) + 0.008(annual household income, in thousands of dollars) + 0.10(number of nonworking household members). Suppose a household has five members (three of whom work) and an annual income of $100,000. What is the expected number of peak-hour social/recreational trips, and what is the probability that the household will not make a peak-hour social/recreational trip?arrow_forward
- 8.15 An origin-destination pair is connected by a route with a performance function t₁ = 8+ x1, and another with a function t₂ = 1 + 2x2 (with x's in thousands of vehicles per hour and t's in minutes). If the total origin-destination flow is 4000 veh/h, determine user-equilibrium and system-optimal route travel times, total travel time (in vehicle minutes), and route flows.arrow_forward8.13 Consider the situation described in Problem 8.11. If the total number of trips remains constant, determine the amount of amusement floor space that must be added to destination 2 to attract an additional 50 social/recreational trips.arrow_forward5- A basic freeway has 3 lanes in each direction and is on flat terrain. It has a jam density of 190 veh/km and a capacity of 4750 veh/h. The spot speed of 5 cars was collected at the midpoint of a 3.4 km segment of this freeway. Vehicle Speed (km/hr) 1 86 2 89 3 95 4 5 99 100 a) Calculate the space mean speed b) Calculate the free flow speed based on the given information c) A directional weekday peak-hour volume of 4640 vehicles is observed, with 1320 vehicles arriving in the most congested 15-min period. If the traffic stream has 12% large trucks and buses determine the level of service 6- What are the steps that a 4-step model used to predict travel demand on roads network consists of? Briefly describe was sort of information each step provides? 7- The bitumen is a conventional bituminous binder has a penetration index of -1 and = 65°c. T800 pen a) Determine the stiffness modulus of this bitumen if the operating conditions are as follows: temperature of 25°c and loading time of…arrow_forward
- Q) Find the location of centroid for the shaded area shown in Figure below. 20mm 42mm 23mm 30mm 30mm 10mm Xarrow_forwardQuestion 5 (Force Method). Determine the reaction at the supports. Assume A is fixed and B and C are rollers. El is constant. 3 k/ft A 10 ft B 2 k/ft 10 ft Carrow_forwardFind the collapse load (Wu) for the one-end continuous beam shown below. Wu 6 marrow_forward
- 4- As part of a highway interchange project, a ramp will be constructed to allow the vehicles exit the first highway and enter the second highway. The first highway runs north-south and the second one had a right angle to the first one (it runs east-west). Vehicles going to the north can use this exit ramp to enter the second highway as shown in the plan view in the figure below. The design speed in both highways is 100 km/hr. The stationing of the start of the horizontal curve is 40+00. a) Determine the stationing of PI and PT¶ b) The first highway has a vertical grade of +3.5% and the second highway has a grade of - 0.5%. The stationing of the beginning and the end of the crest curve are the same as the horizontal curve. What is the elevation of the end of the vertical curve (PVT) if the elevation of the start point (PVC) is 1500m c) Calculate K for the vertical curve Plan view (horizontal alignment) PT 1 N Profile view (vertical alignment) G1=0.5% PVT PC, 40+00 PVC G1=+3.5%arrow_forward10- A pavement with a thin bituminous surface is going to be constructed with a design traffic of 6*105 ESA. Laboratory testing of the subgrade and pavement materials has given the following CBR values. Design the pavement using the empirical design method. Use the and show how you got the numbers on the graph relevant graph} Subgrade CBR: 5 Granular subbase material: Upper layer CBR> 30 Lower layer CBR = 10 Granular base material CBR >100arrow_forward1- Describe the perception-reaction process in driver's decision making. What are the steps this process consists of and what tasks are included in each step? Why this process should be considered in transportation planning 3- What are the three main parts that can be included in a road cross section? Briefly describe what each part is for? Sketch a typical cross sectionarrow_forward
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning



