
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 38, Problem 3VCQ
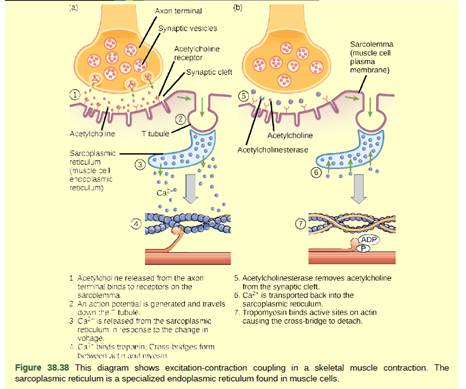
Figure 38.38 The deadly nerve gas Sarin irreversibly inhibits acetycholinesterase. What effect would Sarin have on muscle contraction?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Analyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.
I have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.
13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a
viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then
calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by
both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages.
3 colonies
56
cells
10 μL
10 μL
100 μL
500 με
m
OS
A
B
D
5.0 mL
990 με
990 με
900 με
500 μL
EN
2
100 με
100 μL
118
colonies
12
colonies
Chapter 38 Solutions
Biology 2e
Ch. 38 - Figure 38.19 Which of the following statements...Ch. 38 - Figure 38.37 Which of the following statements...Ch. 38 - Figure 38.38 The deadly nerve gas Sarin...Ch. 38 - The forearm consists of the radius and ulna radius...Ch. 38 - The pectoral girdle consists of the: clavicle and...Ch. 38 - All of the following are groups of vertebrae...Ch. 38 - Which of these is a facial bone? frontal occipital...Ch. 38 - Which of the following is not a true statement...Ch. 38 - The Haversian canal: is arranged as rods or plates...Ch. 38 - The epiphyseal plate: is arranged as rods or...
Ch. 38 - The cells responsible for bone resorption are...Ch. 38 - Compact bone is composed of trabeculae compacted...Ch. 38 - Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become...Ch. 38 - While assembling a skeleton of a new species, a...Ch. 38 - Synchondroses and symphyses are synovial joints...Ch. 38 - The movement of bone away from the midline of the...Ch. 38 - Which of the following is not a characteristic of...Ch. 38 - The elbow is an example of which type of joint?...Ch. 38 - A high ankle sprain iis an injury caused by over...Ch. 38 - In relaxed muscle, the myosin-binding site on...Ch. 38 - The cell membrane of a muscle fiber is called a...Ch. 38 - The muscle relaxes if no new nerve signal arrives....Ch. 38 - The ability of a muscle to generate tension...Ch. 38 - Botulinum toxin causes flaccid paralysis of the...Ch. 38 - What are the major differences between the male...Ch. 38 - What are the major differences between the pelvic...Ch. 38 - Both hydrostatic and exoskeletons can protect...Ch. 38 - Scoliosis is a medical condition where the spine...Ch. 38 - What are the major differences between spongy bone...Ch. 38 - What are the roles of osteoblasts, osteocytes, and...Ch. 38 - Thalidomide was a morning sickness drug given to...Ch. 38 - What movements occur at the hip joint and knees as...Ch. 38 - What movements) occur(s) at the scapulae when you...Ch. 38 - Describe the joints and motions involved in taking...Ch. 38 - How would muscle contractions be affected if ATP...Ch. 38 - What factors contribute to the amount of tension...Ch. 38 - What effect will low blood calcium have on...Ch. 38 - Skeletal muscles can only produce a mechanical...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
CONCEPT QUESTION Review the Chapter Concepts list on p. 62. These all relate to exceptions to the inheritance p...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
You have isolated (1) a streptomycin-resistant mutant (strR) of Chlamydomonas that maps to the chloroplast geno...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
3. Trails that are derived from a common ancestor, like the bones of human arms and bird wings, are said to be_...
Biological Science (6th Edition)
The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the Calvin cycle with A. light energy. B. CO2 and ATP. C. O2 and N...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Describe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward
- 1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forwardwhat measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forward
- You have been hired as a public relations specialist to give invertebrates a good name. After all, they are much more than just creepy crawly bugs! Your first task though is to convince yourself that is true. The best way to do that is to start close to home. Find something in your house that is a product obtained directly from an invertebrate or only due to an invertebrate’s actions. Describe the product, its function and utility, as well as any human manufactured alternatives. Be sure to highlight the advantages of obtaining this directly from nature. Keep in mind, a product can be something you use, wear, eat, or enjoy for its visual appeal.arrow_forwardUse the following tree diagram to answer Questions #8-10. 8) Which of the following two animals are the most closely related based on the tree to the left? a) Pig and camel b) Hippo and pig c) Deer and cow 9) CIRCLE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a hippo and a cow is. 10) Put a SQUARE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a pig and a peccary is.arrow_forwardExplain: Healthy Cell Function Overview→ Briefly describe how a healthy cell usually works: metabolism (ATP production), pH balance, glycogen storage, ion transport, enzymes, etc. Gene Mutation and Genetics Part→ Focus on the autosomal recessive mutation and explain: How gene mutation affects the cell. How autosomal inheritance works. Compare the normal and mutated gene sequences simply. → Talk about possible consequences of a faulty hydrolytic enzyme.arrow_forward
- Can you fill out those termsarrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forwardAn 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College



GCSE PE - ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION - Anatomy and Physiology (Skeletal and Muscular System - 1.5); Author: igpe_complete;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hm_9jQRoO4;License: Standard Youtube License