
Concept explainers
To explain: Label the parts of the flowering plant.
Introduction: Plants are eukaryotic organism and belong to the Plantae kingdom. Plants are autotrophs and can generate their own food by the process of photosynthesis. A plant that generates seeds, flowers, and fruits are called flowering plant and is also referred as an
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
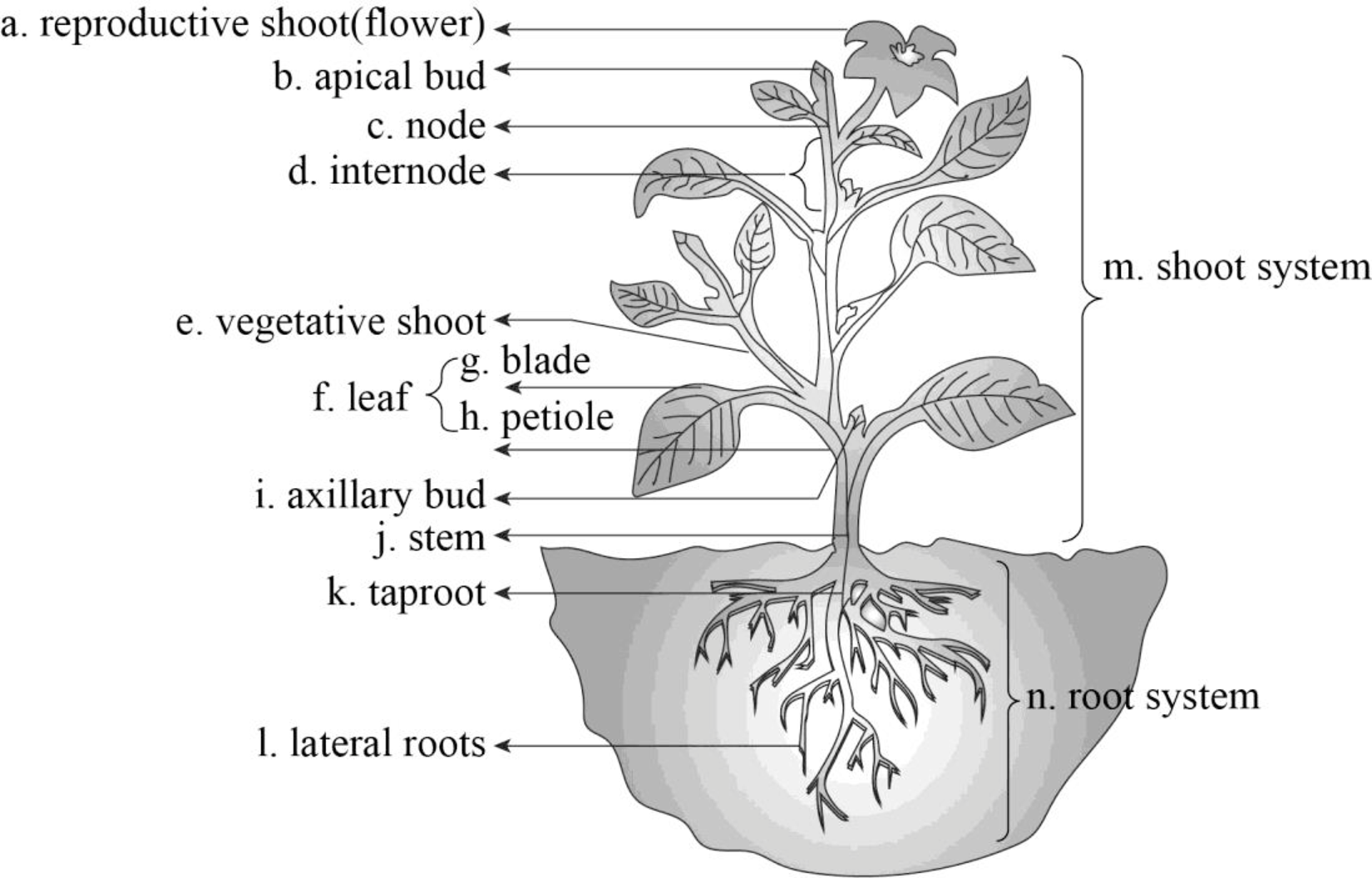
Fig.1: Parts of flowering plants
The organs of plants perform a particular role and it is composed of numerous tissue types. Stems, leaves, and roots are the vascular plant organ. The underground root system of vascular plants attain minerals and water from the soil. An aerial shoot system of leaves and stems is used for absorbing carbon dioxide and light for the process of photosynthesis.
The roots involved in several functions include food storage, absorption, and anchorage. From the primary root, the seed emerges and branches to make a lateral root. Generally, the taproot system is present in tail. The plant anchors by one deep main taproot and it may also involve in nutrient storage.
Alternating nodes are present in the stem. Node is the point where leaves are joined. Internodes are the segment between nodes. The apical bud is the apex of the shoot and it is found at the tip. At the upper angle between the stem and a leaf, the axillary buds are present. It may develop into flowers or lateral branches.
In most plants, the major organ of photosynthesis is leaves. Generally, the leaves consist of stalk or petiole and flattened blade. The petioles are absent in many
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 35 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- What is this?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology A-C components of the question are corresponding to attached image labeled 1. D component of the question is corresponding to attached image labeled 2. For a eukaryotic mRNA, the sequences is as follows where AUGrepresents the start codon, the yellow is the Kozak sequence and (XXX) just represents any codonfor an amino acid (no stop codons here). G-cap and polyA tail are not shown A. How long is the peptide produced?B. What is the function (a sentence) of the UAA highlighted in blue?C. If the sequence highlighted in blue were changed from UAA to UAG, how would that affecttranslation? D. (1) The sequence highlighted in yellow above is moved to a new position indicated below. Howwould that affect translation? (2) How long would be the protein produced from this new mRNA? Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Explain why the cell doesn’t need 61 tRNAs (one for each codon). Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology You discover a disease causing mutation (indicated by the arrow) that alters splicing of its mRNA. This mutation (a base substitution in the splicing sequence) eliminates a 3’ splice site resulting in the inclusion of the second intron (I2) in the final mRNA. We are going to pretend that this intron is short having only 15 nucleotides (most introns are much longer so this is just to make things simple) with the following sequence shown below in bold. The ( ) indicate the reading frames in the exons; the included intron 2 sequences are in bold. A. Would you expected this change to be harmful? ExplainB. If you were to do gene therapy to fix this problem, briefly explain what type of gene therapy youwould use to correct this. Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forward
- Stage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forwardCan you circle a cell in the different stages of mitosis? 1.prophase 2.metaphase 3.anaphase 4.telophase 5.cytokinesisarrow_forwardWhich microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forward
- Select all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that changes in the MC1R gene can lead to: Changes in spots/stripes in lizards, changes in coat coloration in mice, ectopic ear formation in Siberian hamsters, and red hair in humansarrow_forwardPleiotropic genes are genes that (blank) Cause a swapping of organs/structures, are the result of duplicated sets of chromosomes, never produce protein products, and have more than one purpose/functionarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





