Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 7FP
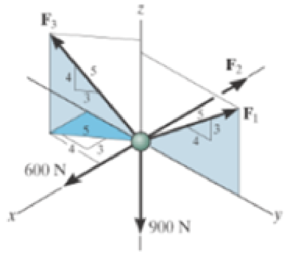
Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so that the particle is held in equilibrium.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Recall that the CWH equation involves two important assumptions. Let us investigate how these
assumptions affect the accuracy of state trajectories under the control inputs optimized in (a) and (b).
(c.1): Discuss the assumptions about the chief and deputy orbits that are necessary for deriving CWH.
PROBLEM 2.50
1.8 m
The concrete post (E-25 GPa and a
=
9.9 x 10°/°C) is reinforced with six
steel bars, each of 22-mm diameter (E, = 200 GPa and a, = 11.7 x 10°/°C).
Determine the normal stresses induced in the steel and in the concrete by a
temperature rise of 35°C.
6c
"
0.391 MPa
240 mm
240 mm
6₁ =
-9.47 MPa
For some viscoelastic polymers that are subjected to stress relaxation tests, the stress decays with
time according to
a(t) = a(0) exp(-4)
(15.10)
where σ(t) and o(0) represent the time-dependent and initial (i.e., time = 0) stresses, respectively, and t and T denote
elapsed time and the relaxation time, respectively; T is a time-independent constant characteristic of the material. A
specimen of a viscoelastic polymer whose stress relaxation obeys Equation 15.10 was suddenly pulled in tension to
a measured strain of 0.5; the stress necessary to maintain this constant strain was measured as a function of time.
Determine E (10) for this material if the initial stress level was 3.5 MPa (500 psi), which dropped to 0.5 MPa (70
psi) after 30 s.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 3.3 - In each case, draw a free-body diagram of the ring...Ch. 3.3 - Write the two equations of equilibrium, Fx = 0 and...Ch. 3.3 - The crate has a weight of 550 lb. Determine the...Ch. 3.3 - The beam has a weight of 700 lb. Determine the...Ch. 3.3 - If the 5-kg block is suspended from the pulley B...Ch. 3.3 - The block has a mass of 5 kg and rests on the...Ch. 3.3 - If the mass of cylinder C is 40 kg, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension in cables AB, BC, and CD,...Ch. 3.3 - The members of a truss are pin connected at joint...Ch. 3.3 - The members of a truss are pin connected at joint...
Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 3.3 - The bearing consists of rollers, symmetrically...Ch. 3.3 - The members of a truss are connected to the gusset...Ch. 3.3 - The gusset plate is subjected to the forces of...Ch. 3.3 - The man attempts to pull down the tree using the...Ch. 3.3 - The cords ABC and BD can each support a maximum...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum force F that can be...Ch. 3.3 - The block has a weight of 20 lb and is being...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum weight W of the block that...Ch. 3.3 - The lift sling is used to hoist a container having...Ch. 3.3 - A nuclear-reactor vessel has a weight of 500(103)...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the stretch in each spring for...Ch. 3.3 - The unstretched length of spring AB is 3 m. If the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the mass of each of the two cylinders if...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the stiffness kT of the single spring...Ch. 3.3 - If the spring DB has an unstretched length of 2 m....Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of DB to hold the...Ch. 3.3 - A vertical force P = 10 lb is applied to the ends...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of spring AC if a...Ch. 3.3 - The springs BA and BC each have a stiffness of 500...Ch. 3.3 - The springs BA and BC each nave a stiffness of 500...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the distances x and y for equilibrium if...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and the distance y...Ch. 3.3 - The 30-kg pipe is supported at A by a system of...Ch. 3.3 - Each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 500 N....Ch. 3.3 - The streetlights A and B are suspended from the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension developed in each cord...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 32PCh. 3.3 - The lamp has a weight of 15 lb and is supported by...Ch. 3.3 - Each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 20 lb....Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 35PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 36PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 38PCh. 3.3 - The ball D has a mass of 20 kg. If a force of F =...Ch. 3.3 - The 200-lb uniform container is suspended by means...Ch. 3.3 - The single elastic cord ABC is used to support the...Ch. 3.3 - A scale is constructed with a 4-ft-long cord and...Ch. 3.3 - The concrete wall panel is hoisted into position...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 2CPCh. 3.3 - Prob. 3CPCh. 3.3 - Prob. 4CPCh. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 10FPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 3.4 - The three cables are used to support the 40-kg...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - If the bucket and its contents have a total weight...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the stretch in each of die two springs...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 47PCh. 3.4 - Determine the tension in the cables in order to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum mass of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable if F = 500 lb.Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 3.4 - Determine the tens on developed in cables AB and...Ch. 3.4 - If the tension developed in each cable cannot...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate that can...Ch. 3.4 - The 25 kg flowerpot is supported at A by the three...Ch. 3.4 - If each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 50 N...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed m the three cables...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in the three...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 60PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 61PCh. 3.4 - If the maximum force in each rod con not exceed...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 63PCh. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 65PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 66PCh. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - The pipe is held in place by the vise. If the bolt...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 3RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 4RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 6RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AB is subjected to a tension of 700 N,...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In an inheritance relationship, the _____ is the general class. a. subclass b. superclass c. slave class d. chi...
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Re-do Practice Program 1, but instead of a struct, use a dass named Node. Your dass should have appropriate mem...
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
T F: A local variable may be accessed by any other procedure in the same Form file.
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
What will the following statement display? print(George, John, Paul, Ringo, sep='@')
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
(Multiples of 2 with an Infinite Loop) Write an application that keeps displaying in the command window the mul...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
What are the steps in chemical machining using photosensitive resists?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the flows in Examples 11.1 and 11.2, calculate the magnitudes of the Δ V2 / 2 terms omitted in B.E., and compare these with the magnitude of the ℱ terms.arrow_forwardCalculate ℛP.M. in Example 11.2.arrow_forwardQuestion 22: The superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical power. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 MPa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an efficiency of 90%. It is requested: Define the Power Plant Schematic Analyze the steam power system considering the steam generator system in the attached figure Determine the electrical power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant Perform an analysis on the power generated and thermal efficiency considering a variation in the steam fractions removed for regeneration ##Data: The steam generator uses biomass from coconut shells to produce 4.5 tons/h of superheated steam; The feedwater returns to the condenser at a temperature of 45°C (point A); Monitoring of the operating conditions in the steam generator indicates that the products of combustion leave the system (point B) at a temperature of 500°C;…arrow_forward
- This is an old practice exam question.arrow_forwardSteam enters the high-pressure turbine of a steam power plant that operates on the ideal reheat Rankine cycle at 700 psia and 900°F and leaves as saturated vapor. Steam is then reheated to 800°F before it expands to a pressure of 1 psia. Heat is transferred to the steam in the boiler at a rate of 6 × 104 Btu/s. Steam is cooled in the condenser by the cooling water from a nearby river, which enters the condenser at 45°F. Use steam tables. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the pressure at which reheating takes place. Use steam tables. Find: The reheat pressure is psia. (P4)Find thermal efficiencyFind m dotarrow_forwardAir at T1 = 24°C, p1 = 1 bar, 50% relative humidity enters an insulated chamber operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/min and mixes with a saturated moist air stream entering at T2 = 7°C, p2 = 1 bar. A single mixed stream exits at T3 = 17°C, p3 = 1 bar. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects Determine mass flow rate of the moist air entering at state 2, in kg/min Determine the relative humidity of the exiting stream. Determine the rate of entropy production, in kJ/min.Karrow_forward
- Air at T1 = 24°C, p1 = 1 bar, 50% relative humidity enters an insulated chamber operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/min and mixes with a saturated moist air stream entering at T2 = 7°C, p2 = 1 bar. A single mixed stream exits at T3 = 17°C, p3 = 1 bar. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects Determine mass flow rate of the moist air entering at state 2, in kg/min Determine the relative humidity of the exiting stream. Determine the rate of entropy production, in kJ/min.Karrow_forwardAir at T1 = 24°C, p1 = 1 bar, 50% relative humidity enters an insulated chamber operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/min and mixes with a saturated moist air stream entering at T2 = 7°C, p2 = 1 bar. A single mixed stream exits at T3 = 17°C, p3 = 1 bar. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects (a) Determine mass flow rate of the moist air entering at state 2, in kg/min (b) Determine the relative humidity of the exiting stream. (c) Determine the rate of entropy production, in kJ/min.Karrow_forwardA simple ideal Brayton cycle operates with air with minimum and maximum temperatures of 27°C and 727°C. It is designed so that the maximum cycle pressure is 2000 kPa and the minimum cycle pressure is 100 kPa. The isentropic efficiencies of the turbine and compressor are 91% and 80%, respectively, and there is a 50 kPa pressure drop across the combustion chamber. Determine the net work produced per unit mass of air each time this cycle is executed and the cycle’s thermal efficiency. Use constant specific heats at room temperature. The properties of air at room temperature are cp = 1.005 kJ/kg·K and k = 1.4. The fluid flow through the cycle is in a clockwise direction from point 1 to 4. Heat Q sub in is given to a component between points 2 and 3 of the cycle. Heat Q sub out is given out by a component between points 1 and 4. An arrow from the turbine labeled as W sub net points to the right. The net work produced per unit mass of air is kJ/kg. The thermal efficiency is %.arrow_forward
- Steam enters the high-pressure turbine of a steam power plant that operates on the ideal reheat Rankine cycle at 700 psia and 900°F and leaves as saturated vapor. Steam is then reheated to 800°F before it expands to a pressure of 1 psia. Heat is transferred to the steam in the boiler at a rate of 6 × 104 Btu/s. Steam is cooled in the condenser by the cooling water from a nearby river, which enters the condenser at 45°F. Use steam tables. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the pressure at which reheating takes place. Use steam tables. The reheat pressure is psia.Find thermal efficieny Find m dotarrow_forwardThis is an old exam practice question.arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure below, moist air at T₁ = 36°C, 1 bar, and 35% relative humidity enters a heat exchanger operating at steady state with a volumetric flow rate of 10 m³/min and is cooled at constant pressure to 22°C. Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, determine: (a) the dew point temperature at the inlet, in °C. (b) the mass flow rate of moist air at the exit, in kg/min. (c) the relative humidity at the exit. (d) the rate of heat transfer from the moist air stream, in kW. (AV)1, T1 P₁ = 1 bar 11 = 35% 120 T₂=22°C P2 = 1 bararrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License