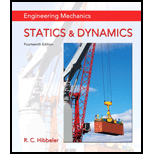
Determine the stretch in each spring for equilibrium of the 2-kg block. The springs are shown in the equilibrium position.
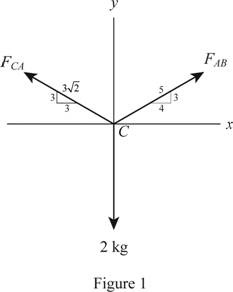
The stretch in each spring for the equilibrium of the block.
Answer to Problem 14P
The stretch in spring AD,
The stretch in spring AC,
The stretch in spring AB,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- The mass of the block (m) is 2 kg.
Assumption:
Consider point E in between the points B and C.
Show the free body diagram of the springs in the equilibrium position as in Figure 1.
Determine the length of the spring AC using the formula.
Here, the length of the point AE is
Determine the length of the spring AB using the formula.
Here, the length of the point BE is
Determine the force in spring AD using the formula.
Here, the mass of the block is m and the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Determine the stretch in spring AD.
Here, the stiffness of the spring AD is
Determine the stretch in the springs AC and AB for equilibrium of the block by applying the equation of equilibrium.
Along the horizontal direction:
Here, the force acting on spring AB is
Along the vertical direction:
Determine the stretch in spring AC.
Here, the stiffness of the spring AC is
Determine the stretch in spring AB.
Here, the stiffness of the spring AB is
Conclusion:
Substitute 3 m for
Substitute 3 m for
Substitute 2 kg for m and
Substitute 19.62 N for
Thus, the stretch in spring AD is
Determine the
Substitute 4 m for
Determine the
Substitute 3m for
Substitute
Determine the
Substitute 3 m for
Determine the
Substitute 3m for
Substitute
Substitute 15.86 N for
Thus, the stretch in spring AC is
Substitute 15.86 N for
Substitute 14.01 N for
Thus, the stretch in spring AB is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
- Problem 1 Consider R has a functional relationship with variables in the form R = K xq xx using show that n ✓ - (OR 1.) = i=1 2 Их Ux2 Ихэ 2 (177)² = ² (1)² + b² (12)² + c² (1)² 2 UR R x2 x3arrow_forward4. Figure 3 shows a crank loaded by a force F = 1000 N and Mx = 40 Nm. a. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to force F. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. b. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to moment Mr. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. Draw a free body diagram of the wall plane showing all the forces, torques, and moments acting there. d. Locate a stress element on the top surface of the shaft at A and calculate all the stress components that act upon this element. e. Determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stresses at this point at A.arrow_forward3. Given a heat treated 6061 aluminum, solid, elliptical column with 200 mm length, 200 N concentric load, and a safety factor of 1.2, design a suitable column if its boundary conditions are fixed-free and the ratio of major to minor axis is 2.5:1. (Use AISC recommended values and round the ellipse dimensions so that both axes are whole millimeters in the correct 2.5:1 ratio.)arrow_forward
- 1. A simply supported shaft is shown in Figure 1 with w₁ = 25 N/cm and M = 20 N cm. Use singularity functions to determine the reactions at the supports. Assume El = 1000 kN cm². Wo M 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 cm Figure 1 - Problem 1arrow_forwardPlease AnswerSteam enters a nozzle at 400°C and 800 kPa with a velocity of 10 m/s and leaves at 375°C and 400 kPa while losing heat at a rate of 26.5 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2, determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit. Use steam tables. The velocity of the steam at the nozzle exit is m/s. The volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit is m3/s.arrow_forward2. A support hook was formed from a rectangular bar. Find the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at sections just above and just below O-B. -210 mm 120 mm 160 mm 400 N B thickness 8 mm = Figure 2 - Problem 2arrow_forward
- Steam flows steadily through a turbine at a rate of 45,000 lbm/h, entering at 1000 psia and 900°F and leaving at 5 psia as saturated vapor. If the power generated by the turbine is 4.1 MW, determine the rate of heat loss from the steam. The enthalpies are h1 = 1448.6 Btu/lbm and h2 = 1130.7 Btu/lbm. The rate of heat loss from the steam is Btu/s.arrow_forwardThe A/D converter wit the specifications listed below is planned to be used in an environment in which the A/D converter temperature may change by ± 10 °C. Estimate the contributions of conversion and quantization errors to the uncertainty in the digital representation of an analog voltage by the converter. FSO N Linearity error Temperature drift error Analog to Digital (A/D) Converter 0-10 V 12 bits ± 3 bits 1 bit/5 °Carrow_forward6-13. A smooth tube in the form of a circle of radius r rotates in its vertical plane with a constant angular velocity w. The position of a particle of mass m that slides inside the tube is given by the relative coordinate p. Find the differential equation for . e О E g ω Figure P6-13arrow_forward
- Problem 2 Consider the power drawn by a resistance load in a DC circuit. The power is calculated as P = VI or P = 1²R. It is given that the normalized uncertainty or % percentage uncertainty in measurements of I, R, and V are the same. Find the uncertainty in P using the two different expressions for power. Is the uncertainty using the two methods the same? If not, WHY, explain?arrow_forwardA piston–cylinder device contains 3 kg of nitrogen initially at 100 kPa and 25°C. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process. The gas constant of N2 is R = 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K. The cv value of N2 at the anticipated average temperature of 350 K is 0.744 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2b). The work done for this process is kJ. The heat transfer for this process is kJ.arrow_forwardI tried solving this one but I have no idea where I went wrong can you please help me out with this?arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
