
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 46P
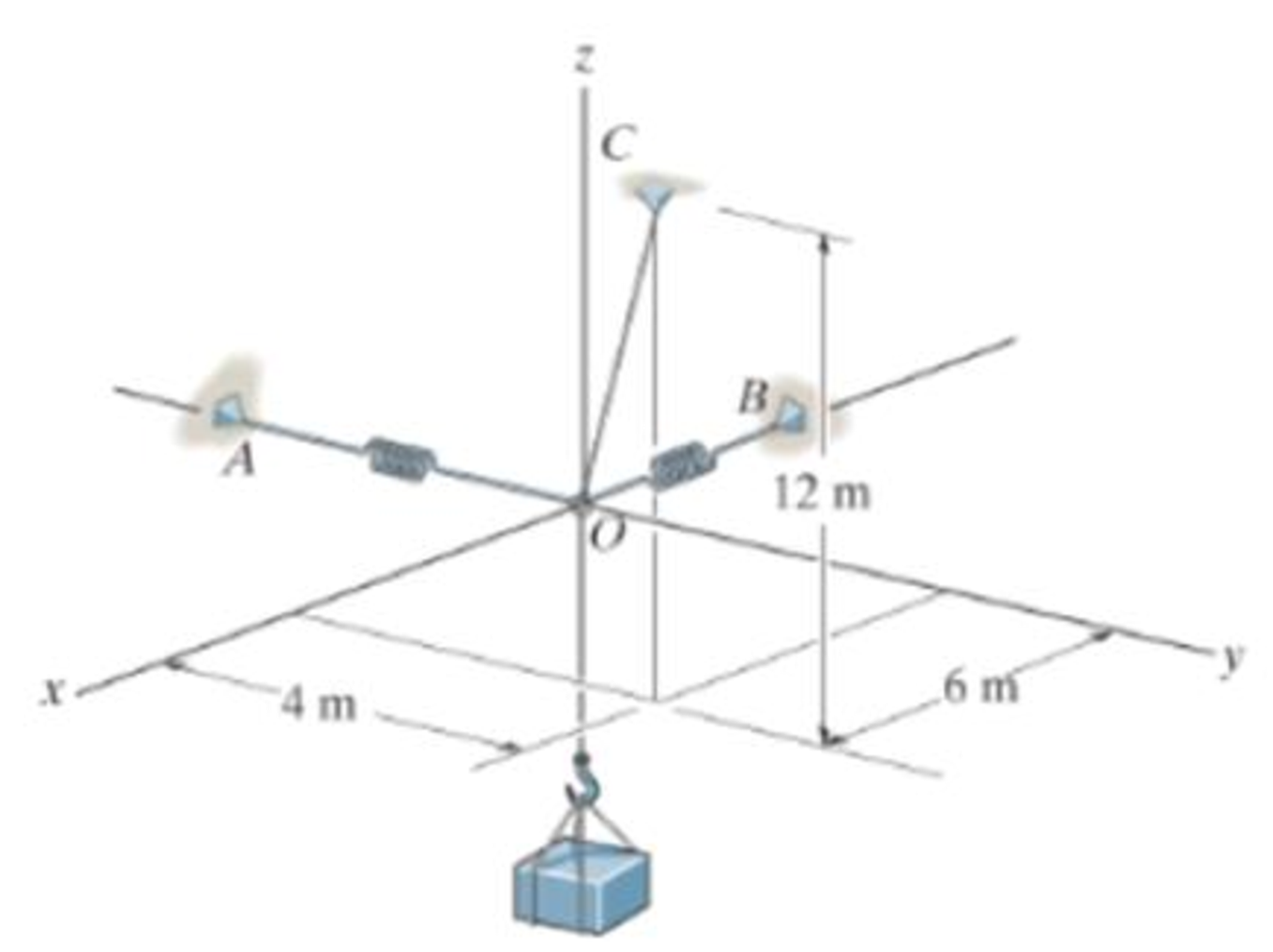
Each spring has on unstretched length of 2 m and a stiffness of k = 300 N/m.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I really don't know how to approach this problem i've tried approaching it with some of the torsional stress equations I know but i'm comming up with awnsers that don't make any sence can you please help me with this?
I tried this problem and don't know what I did wrong or how else I could approach it can you please help me out?
Q3: An engine produce 750 kW power and uses gaseous C12H26 as a fuel
at 25 C; 200% theoretical air is used and air enters at 500 K. The products
of combustion leave at 800 K. The heat loss from the engine is 175 kW.
Determine the fuel consumption for complete combustion.
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 3.3 - In each case, draw a free-body diagram of the ring...Ch. 3.3 - Do not solve.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each supporting cable.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the shortest cable ABC that can be used...Ch. 3.3 - Neglect the size of the pulley.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of the spring.Ch. 3.3 - If the mass of cylinder C is 40 kg, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Also, find the angle .Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitudes of F1 and F2 for...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and its angle for...
Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 3.3 - The bottom one is subjected to a 125-N force at...Ch. 3.3 - If the forces are concurrent at point O, determine...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension force in member C and its...Ch. 3.3 - If the tension in AB is 60 lb, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - The cords ABC and BD can each support a maximum...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum force F that can be...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium and the force...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 3.3 - Determine the force in each of the cables AB and...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 3.3 - The springs are shown in the equilibrium position.Ch. 3.3 - If the block is held in the equilibrium position...Ch. 3.3 - Note that s = 0 when the cylinders are removed.Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3.3 - determine the stiffness of the spring to hold the...Ch. 3.3 - Take k = 180 N/m.Ch. 3.3 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 2 ft,...Ch. 3.3 - Cord AB is 2 ft long. Take k = 50 lb/ft.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the horizontal force F applied to the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the displacement d of the cord from the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the distances x and y for equilibrium if...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and the distance y...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each cord for equilibrium.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest mass of pipe that can be...Ch. 3.3 - If each light has a weight of 50 lb. determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension developed in each cord...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum mass of the lamp that the...Ch. 3.3 - If x = 2 m determine the force F and the sag s for...Ch. 3.3 - If F = 80 N. determine the sag s and distance x...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension in each cord and the angle ...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest weight of the lamp that can...Ch. 3.3 - Also, what is the force in cord AB? Hint: use the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension developed...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3.3 - Take F = 300 N and d = 1 m.Ch. 3.3 - If a force of F = 100 N is applied horizontally to...Ch. 3.3 - If the cable can be attached at either points A...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension in the...Ch. 3.3 - The cord is fixed to a pin at A and passes over...Ch. 3.3 - Establish appropriate dimensions and use an...Ch. 3.3 - If the maximum tension that can be supported by...Ch. 3.3 - If the angle between AB and BC is 30, determine...Ch. 3.3 - If the distance BC is 1.5 m, and AB can support a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - F310. Determine the tension developed in cables...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in these wires.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - If the bucket and its contents have a total weight...Ch. 3.4 - Each spring has on unstretched length of 2 m and a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in the cables in order to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum mass of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable if F = 500 lb.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the greatest force F that can be applied...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tens on developed in cables AB and...Ch. 3.4 - Also, what is the force developed along strut AD?Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate that can...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 3.4 - If each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 50 N...Ch. 3.4 - which has a mass of 15 kg. Take h = 4 m.Ch. 3.4 - Take h = 3.5 m.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each chain for equilibrium....Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If the maximum force in each rod con not exceed...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - If the bolt exerts a force of 50 lb on the pipe in...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the flowerpot that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of the applied vertical...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AB is subjected to a tension of 700 N,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Qu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures. show all work step by step problems formula material sciencearrow_forward(Read Question)arrow_forwardIn figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.arrow_forward
- (Read image)arrow_forward(Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forward
- Problem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forwardProblem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forward
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Ch 2 - 2.2.2 Forced Undamped Oscillation; Author: Benjamin Drew;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Tb7Rx-bCWE;License: Standard youtube license