
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 3.3, Problem 21P
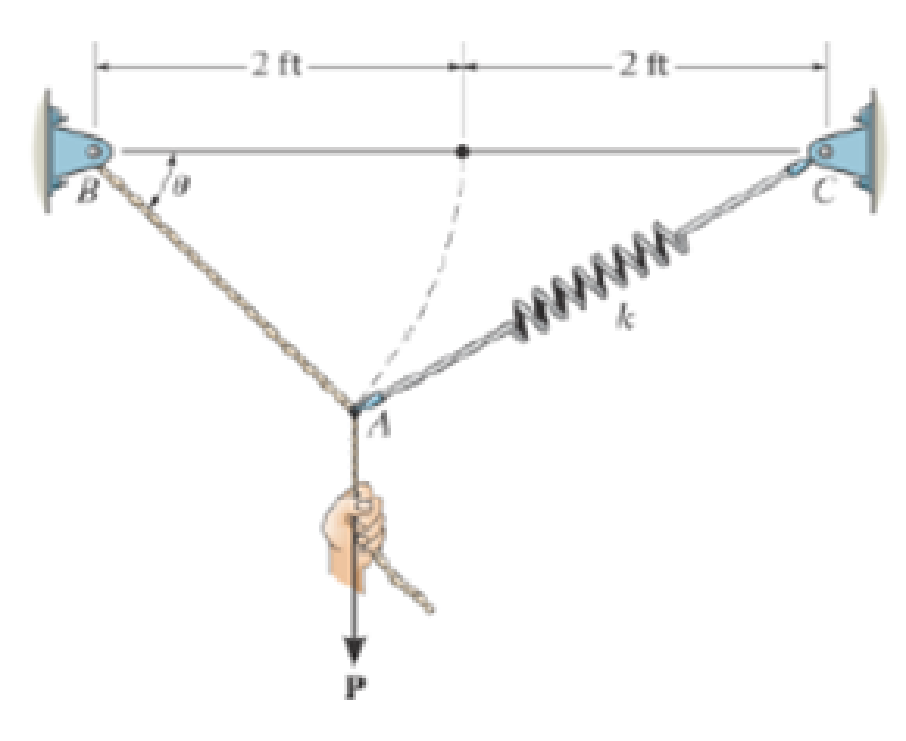
Cord AB is 2 ft long. Take k = 50 lb/ft.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
hand-written solutions only please!
hand-written solutions only please!
hand-written solutions only, please.
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 3.3 - In each case, draw a free-body diagram of the ring...Ch. 3.3 - Do not solve.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each supporting cable.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the shortest cable ABC that can be used...Ch. 3.3 - Neglect the size of the pulley.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of the spring.Ch. 3.3 - If the mass of cylinder C is 40 kg, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Also, find the angle .Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitudes of F1 and F2 for...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and its angle for...
Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 3.3 - The bottom one is subjected to a 125-N force at...Ch. 3.3 - If the forces are concurrent at point O, determine...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension force in member C and its...Ch. 3.3 - If the tension in AB is 60 lb, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - The cords ABC and BD can each support a maximum...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum force F that can be...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium and the force...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 3.3 - Determine the force in each of the cables AB and...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 3.3 - The springs are shown in the equilibrium position.Ch. 3.3 - If the block is held in the equilibrium position...Ch. 3.3 - Note that s = 0 when the cylinders are removed.Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3.3 - determine the stiffness of the spring to hold the...Ch. 3.3 - Take k = 180 N/m.Ch. 3.3 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 2 ft,...Ch. 3.3 - Cord AB is 2 ft long. Take k = 50 lb/ft.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the horizontal force F applied to the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the displacement d of the cord from the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the distances x and y for equilibrium if...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and the distance y...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each cord for equilibrium.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest mass of pipe that can be...Ch. 3.3 - If each light has a weight of 50 lb. determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension developed in each cord...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum mass of the lamp that the...Ch. 3.3 - If x = 2 m determine the force F and the sag s for...Ch. 3.3 - If F = 80 N. determine the sag s and distance x...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension in each cord and the angle ...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest weight of the lamp that can...Ch. 3.3 - Also, what is the force in cord AB? Hint: use the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension developed...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3.3 - Take F = 300 N and d = 1 m.Ch. 3.3 - If a force of F = 100 N is applied horizontally to...Ch. 3.3 - If the cable can be attached at either points A...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension in the...Ch. 3.3 - The cord is fixed to a pin at A and passes over...Ch. 3.3 - Establish appropriate dimensions and use an...Ch. 3.3 - If the maximum tension that can be supported by...Ch. 3.3 - If the angle between AB and BC is 30, determine...Ch. 3.3 - If the distance BC is 1.5 m, and AB can support a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - F310. Determine the tension developed in cables...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in these wires.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - If the bucket and its contents have a total weight...Ch. 3.4 - Each spring has on unstretched length of 2 m and a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in the cables in order to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum mass of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable if F = 500 lb.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the greatest force F that can be applied...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tens on developed in cables AB and...Ch. 3.4 - Also, what is the force developed along strut AD?Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate that can...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 3.4 - If each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 50 N...Ch. 3.4 - which has a mass of 15 kg. Take h = 4 m.Ch. 3.4 - Take h = 3.5 m.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each chain for equilibrium....Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If the maximum force in each rod con not exceed...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - If the bolt exerts a force of 50 lb on the pipe in...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the flowerpot that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of the applied vertical...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AB is subjected to a tension of 700 N,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- hand-written solutions only please!arrow_forwardA prototype automobile is designed to travel at 65 km/hr. A model of this design is tested in a wind tunnel with identical standard sea- level air properties at a 1:5 scale. The measured model drag is 529 N, enforcing dynamic similarity. Determine (a) the drag force on the prototype and (b) the power required to overcome this drag. See the equation Vm m = D V Dm (a) Dp = i (b) Pp = i N hparrow_forwardA new blimp will move at 6 m/s in 20°C air, and we want to predict the drag force. Using a 1: 14-scale model in water at 20°C and measuring a 2500-N drag force on the model, determine (a) the required water velocity, (b) the drag on the prototype blimp and, (c) the power that will be required to propel it through the air. (a) Vm = i (b) Dp = i (c) Pp = i m/s N Warrow_forward
- Drag measurements were taken for a sphere, with a diameter of 5 cm, moving at 3.7 m/s in water at 20°C. The resulting drag on the sphere was 10 N. For a balloon with 1-m diameter rising in air with standard temperature and pressure, determine (a) the velocity if Reynolds number similarity is enforced and (b) the drag force if the drag coefficient in the equation below is the dependent pi term. li ε pVI D 1 = CD = Q μ (a) Vp = i (b) Dp = i m/s Narrow_forwardCalculate the forces in all members of the truss shown using either the method of joints or the method of sectionsarrow_forward20-4-2025 Exam-2-Tribology Q1: What are the assumptions of hydrodynamic lubrication theory: Q2: Explain with sketch the cycle or process of engine lubrication system-pressurized lubrication system Q3: A short bearing is designed to operate with an eccentricity ratio = 0. 7. The journal diameter is 60 mm, and its speed is 1300 r.p.m. The journal is supported by a short hydrodynamic bearing of length L/D = 0. 5, and clearance ratio C/R = 103. The radial load on the bearing is 9800 N. a. Find the Sommerfeld number. b. Find the minimum viscosity of the lubricant for operating at ε = 0.7 c. Select a lubricant if the average bearing operating temperature is 70°c Q4: Two parallel circular disks of 100 mm diameter have a clearance of Imm between them. Under load, the downward velocity of the upper disk is 2 m/s. At the same time, the lower disk is stationary. The clearance is full of SAE 40 oil at a temperature of 60°c. a. Find the load on the upper disk that results in the instantaneous…arrow_forward
- Tribobolgy 15/2022 Monthly Exam. Automobile Eng. Dert 2nd Semster/3rd class Max. Mark: 100% 7. Viscosity of multi-grade oils (a) Reduces with temperature (c) is less sensitive to temperature (b) Increases with temperature (d) None of the above 8. In a hydrodynamic journal bearing if eccentricity ratio = 1, it means (a) Journal/shaft is subjected to no load and the rotational speed is very high. (b) Journal is subjected to no load and the rotational speed is moderate (c) Journal is subjected to very light load and the rotational speed is very high. (d) Journal is subjected to very high load and the rotational speed is negligible. Q4/ The journal speed of a 100mm diameter journal is 2500 rpm. The journal is supported by a short hydrodynamic bearing of length L=0.6D, eccentricity ratio = 0.75 and a clearance ratio C/R=0.001. The radial load on the bearing is 10 kN. The lubricant is SAE 30, and the operating temperature of the lubricant in the bearing is 700C. 1- Assume…arrow_forward1 of 2 Monthly Exam. Automobile Eng. Dert 2nd Semster/3rd class Max. Mark: 100% Q1/A/ Compare between the long and short journal bearings B/ With the help of Stribeck's curve, discuss different regimes of lubrication. C/ Explain the importance of Tribology in the design of different machine elements Q2 /A/ According to the SAE viscosity grading system all engine oils are divided into two classes: monograde and multi-grade. Compare between them? B/What are the differences between grease and Synthetic oils C/ Explain the effect of eccentricity ratio & with respect to hydrodynamic journal bearing. Q3/A/ What are the major factors which affect the selection of lubricants? B/What are the criteria to classify sliding bearings? C/ Answer of the following: 1. According to the SAE viscosity classification, the oil (SAE 40) is lower viscosity than the oil (SAE 20) at the same temperature. (True or False) 2. For a slow speed-highly loaded bearing, used oils of high viscosity; while for high-speed…arrow_forwardThe uniform rods have a mass per unit length of 10kg/m . (Figure 1)If the dashpot has a damping coefficient of c=50N⋅s/m , and the spring has a stiffness of k=600N/m , show that the system is underdamped, and then find the pendulum's period of oscillation.arrow_forward
- 10-50. The principal plane stresses and associated strains in a plane at a point are σ₁ = 30 ksi, σ₂ = -10 ksi, e₁ = 1.14(10-3), €2=-0.655(103). Determine the modulus of elasticity and Poisson's ratio. emps to plum... Wednesday FI a וח 2 Q Search 48 F5 - F6 4+ F7 FB F9 FIO FII F12 & * S 6 7 8 9 ㅁ F2 # *F3 3 $ 4 F4 % W E R T Y ப S ALT D F G H X C V B N J Σ H L ว { P [ ] ALT " DELETE BACKSPACE NUM LOCK T 7 HOME ENTER 4 PAUSE SHIFT CTRL Earrow_forward10−9. The state of strain at the point has components of ϵx = −100(10−6), ϵy = −200(10−6), and γxy=100(10−6). Use the strain transformation equations to determine (a) the in-plane principal strains and (b) the maximum in-plane shear strain and average normal strain. In each case specify the orientation of the element and show how the strains deform the element within the x−y plane.arrow_forwardThe strain gage is placed on the surface of the steel boiler as shown. If it is 0.5 in. long, determine the pressure in the boiler when the gage elongates 0.2(10−3) in. The boiler has a thickness of 0.5 in. and inner diameter of 60 in. Also, determine the maximum x, y in-plane shear strain in the material. Take Est=29(103)ksi, vst=0.3.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY