
Concept explainers
Name the animal shown in the following diagram and indicate the chordate group to which it belongs. Identify the labeled structures and indicate the four chordate characters.
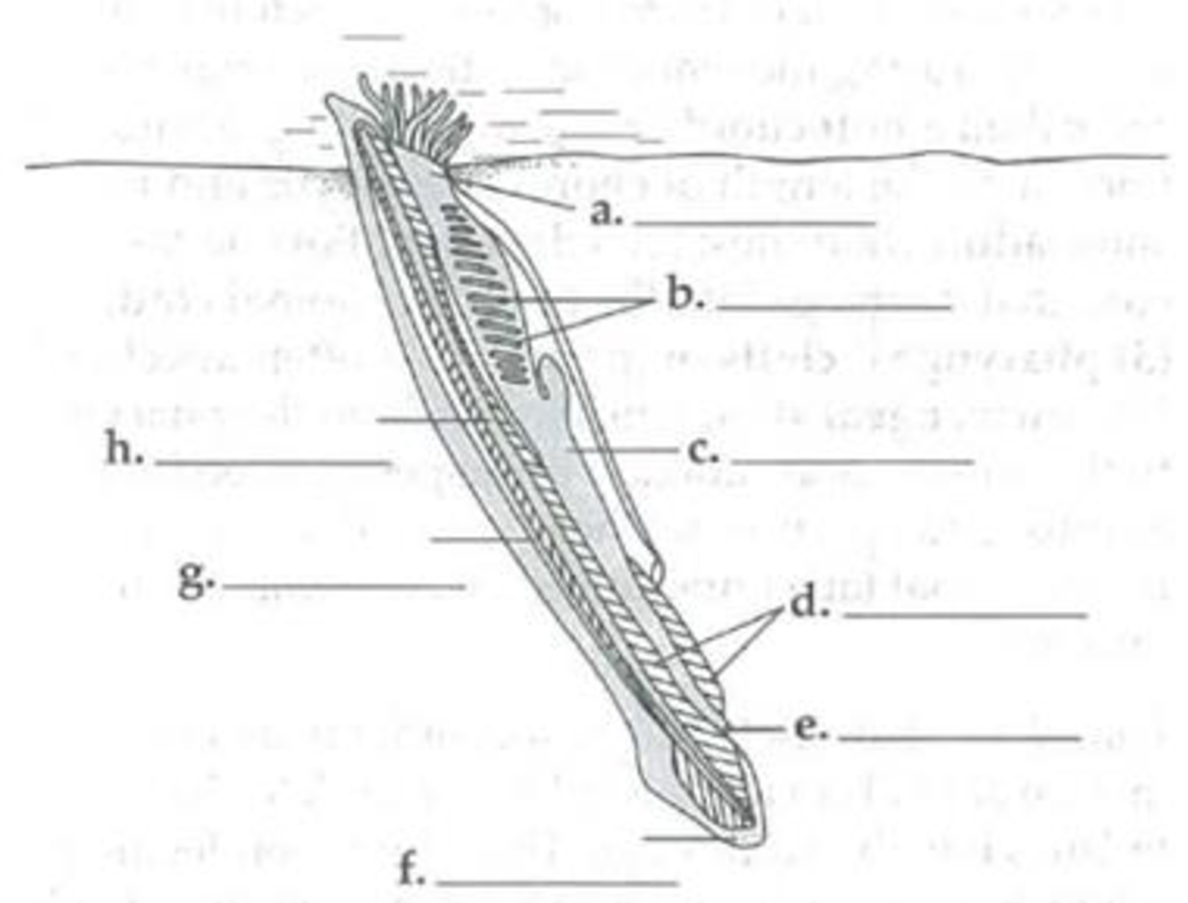
To name: The animals shown in the given diagram, indicate the chordate group to which it belongs, identify the labelled structure, and indicate the four characters of chordate.
Introduction: Deuterostomia is a sub taxon of Bilaterians. It includes chordates and echinoderms. A chordate is an animal belongs to the phylum Chordata. Chordates include urochordates, cephalochordates, and vertebrates.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the labeled structure of lancelet and four characters of chordate.
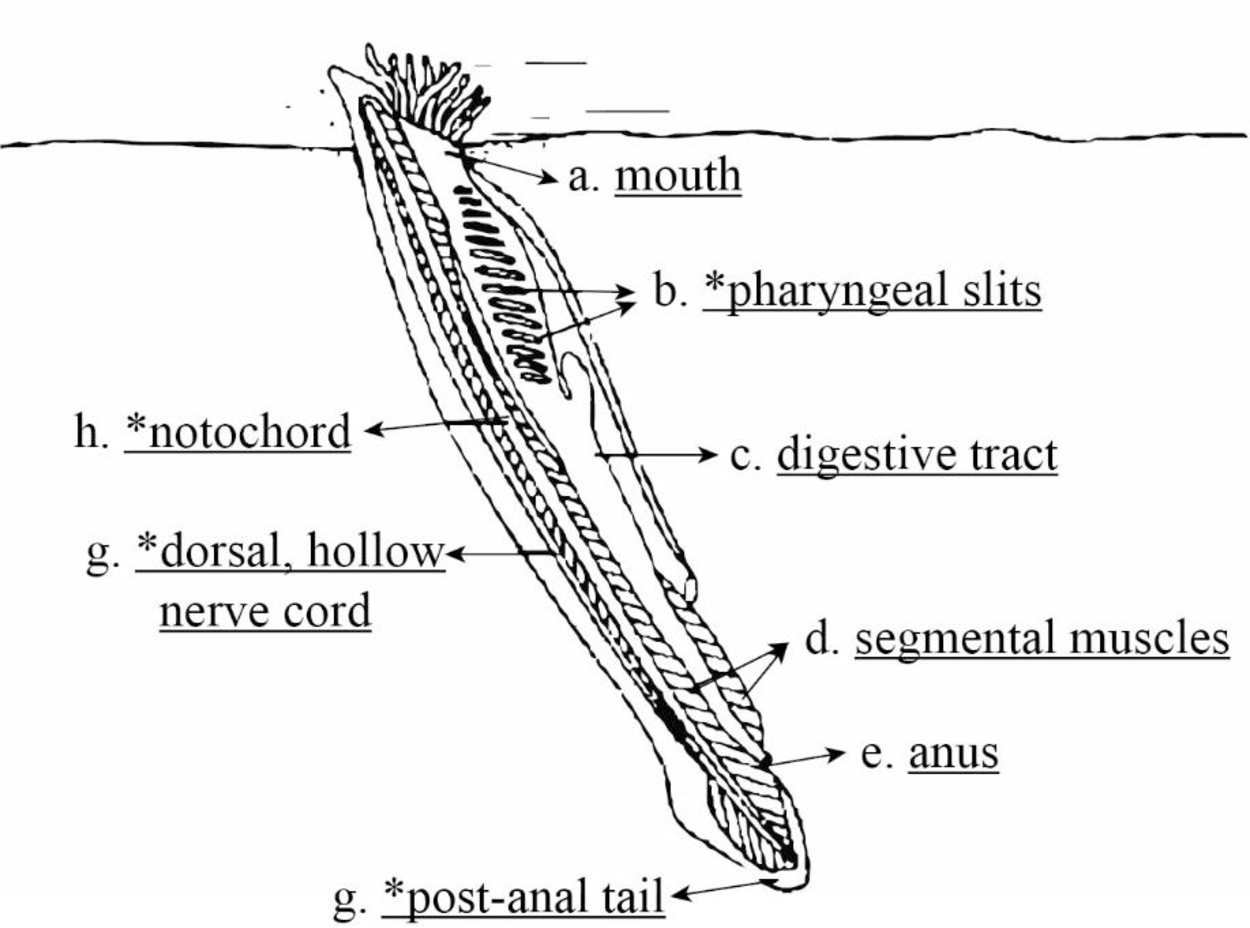
Fig.1: Labeled structure of lancelet and four chordate characters
Explanation of Solution
The animal shown in the given (Fig.1) is lancelet and it belongs to the chordate group of Cephalochordata.
Lancelets are marine animal, which is tiny in nature. It retains complete four characteristics of chordate into the stage of adult. The adult lancelet, which is involved in suspension-feeding burrow backward to the soil and particles of food are filtered by a mucous net, which is produced across the pharyngeal slits. Using serial muscle contractions, the lancelet swims. The notochord is flex by these serial muscle contractions. From the mesoderm, these segments of muscle mature and it is called somites. It is found in all embryos of chordate.
Four chordate characters: In Fig.1, the symbol * indicates the derived characters of chordates. It includes notochord, dorsal, hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.
Notochord: It is a flexible chord and it gives skeletal support beside a length of embryos of chordate and in certain chordate adult.
Dorsal, hollow nerve: It develops into the spinal cord and the brain.
Pharyngeal slits: The pharyngeal grooves or clefts frequently develop into pharyngeal slits. The role of the pharyngeal slit is involved in suspension feeding or portion of head or function as gills.
A muscular, post-anal tail: It contains muscles and skeletal elements.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 34 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Explain in a flowcharts organazing the words down below: genetics Chromosomes Inheritance DNA & Genes Mutations Proteinsarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





