
Concept explainers
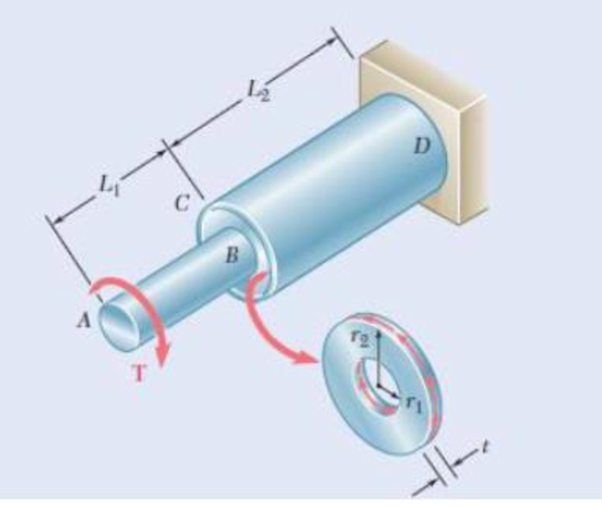
An annular plate of thickness t and modulus G is used to connect shaft AB of radius r1 to tube CD of radius r2. Knowing that a torque T is applied to end A of shaft AB and that end D of tube CD is fixed, (a) determine the magnitude and location of the maximum shearing stress in the annular plate, (b) show that the angle through which end B of the shah rotates with respect to end C of the tube is
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- A 15 cm-OD pipe is buried with its centerline 1.25 m below the surface of the ground [k of soil is 0.35 W/(m K)]. An oil having a density of 800 kg/m³ and a specific heat of 2.1 kJ/(kg K) flows in the pipe at 5.6 L/s. Assuming a ground surface temperature of 5°C and a pipe wall temperature of 95°C, estimate the length of pipe in which the oil temperature decreases by 5.5°C. + Tε = 5ºC Z= 1.25 m D= 15 cm 7p=95°Carrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) 4y+y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 0. 2) y+y=0, y(0) = A, y'(0) = B. 3) "+2y'-8y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=8. 4) y"-2y-3y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=7. 5) y"-ky' =0, y(0)=2, y'(0) =k. 6) y+ky'-2k2y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) y'+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 y+y-17sin(21) y(0)=-1. 9) y-y'-6y=0, y(0)=6. y'(0)=13. 10) y-y=0, 11) y"-4y+4y=0, y(0)=4, y'(0) = 0. y(0) = 2.1, y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) "+7y+12y=21e", y(0)=3.5, y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e", y(0)=0. y'(0) = 0. 15) y+3y+2.25y=91³ +64. y(0)=1, y'(0) = 31.5 16) "-6y+5y= 29 cos(21), y(0)=3.2, y'(0) = 6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=12. 19) y-4y+5y=0, y(0)-1, y'(0) 2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0. y(0)=3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, (0) 3. y(0) 1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, (0)-0, y(0) 1. 24) y+y+1.25y=0, y(0) 1. y'(0) -0.5 25) y+y=2 cos(1). y(0) 2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y=0, (0)-3, y'(0) = 7. 27) y+2y+y=e", y(0)-0. y'(0) = 0. 29) 28) y+2y-3y-10sinh(2),…arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting appreciate your time and effort!. Question:arrow_forward
- 4. Block A and B are two different pieces of wood. Determine the minimum dimension for "a", if the shear stress of the wood is 50Mpa. The thickness of the wood is 30cm. 600N Aarrow_forward1. Determine the reaction force at A. 60 kN 5 B 1 m 1 m- -1 m 4 3 m 30 kN marrow_forwardFind the Laplace Transform of the following functions 1) f() cos(ar) Ans. F(s)=7 2ws 2) f() sin(at) Ans. F(s)= s² + a² 3) f(r)-rcosh(at) Ans. F(s)= 2as 4)(t)=sin(at) Ans. F(s)= 2 5) f(1) = 2te' Ans. F(s)= (S-1) 5+2 6) (1) e cos() Ans. F(s) = (+2)+1 7) (1) (Acostẞr)+ Bsin(Br)) Ans. F(s)- A(s+a)+BB (s+a)+B 8) f()-(-)() Ans. F(s)= 9)(1)(1) Ans. F(s): 10) f(r),()sin() Ans. F(s): 11) 2 k 12) 0 13) 0 70 ㄷ.. a 2a 3a 4a 2 3 4 14) f(1)=1, 0<1<2 15) (1) Ksin(t) 0arrow_forward2. Determine the average normal stress developed in rod AB. The mass is 50kg and the diameter of the rod AB is 8mm. B 8 mmarrow_forward2.64 A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon made from 1.6-mm flat steel plate (E = 200 GPa, v = 0.30). Determine the resulting change in (a) the 50-mm gage length, (b) the width of portion AB of the test coupon, (c) the thickness of portion AB, (d) the cross-sectional area of portion AB. 2.75 kN A 12 mm 50 mm B 2.75 kNarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D\sum Fx=0\sum Fy=0\sum Fz=0\sum Mx=0\sum My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thesectionarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





