
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119459132
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 63P
In Fig. 33-60, light enters a 90° triangular prism at point P with incident angle θ, and then some of it refracts at point Q with an angle of refraction of 90°. (a) What is the index of refraction of the prism in terms of θ? (b) What, numerically, is the maximum value that the index of refraction can have? Does light emerge at Q if the incident angle at P is (c) increased slightly and (d) decreased slightly?
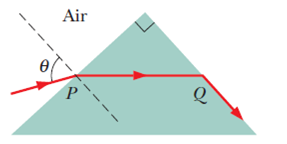
Figure 33-60 Problem 63.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1. A charge of -25 μC is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical volume of radius 11.5 cm.
Determine the electric field due to this charge at a distance of (a) 2 cm, (b) 4.6 cm, and (c) 25 cm from
the center of the sphere.
(a) =
=
(b) E =
(c)Ẻ =
=
NC NC NC
1.
A long silver rod of radius 3.5 cm has a charge of -3.9
ис
on its surface. Here ŕ is a unit vector
ст
directed perpendicularly away from the axis of the rod as shown in the figure.
(a) Find the electric field at a point 5 cm from the center of the rod (an outside point).
E =
N
C
(b) Find the electric field at a point 1.8 cm from the center of the rod (an inside point)
E=0
Think & Prepare
N
C
1. Is there a symmetry in the charge distribution? What kind of symmetry?
2. The problem gives the charge per unit length 1. How do you figure out the surface charge density σ
from a?
1. Determine the electric flux through each surface whose cross-section is shown below.
55
S₂
-29
S5
SA
S3
+ 9
Enter your answer in terms of q and ε
Φ
(a) s₁
(b) s₂
=
-29
(C) Φ
զ
Ερ
(d) SA
=
(e) $5
(f) Sa
$6
=
II
✓
-29
S6
+39
Chapter 33 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
Ch. 33 - Prob. 1QCh. 33 - Prob. 2QCh. 33 - a Figure 33-27 shows light reaching a polarizing...Ch. 33 - Prob. 4QCh. 33 - In the arrangement of Fig. 33-l5a, start with...Ch. 33 - Prob. 6QCh. 33 - Figure 33-30 shows fays of monochromatic Light...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-31 shows the multiple reflections of a...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-32 shows four long horizontal layers AD...Ch. 33 - The leftmost block in Fig. 33-33 depicts total...
Ch. 33 - Prob. 11QCh. 33 - Prob. 12QCh. 33 - Prob. 1PCh. 33 - Prob. 2PCh. 33 - Prob. 3PCh. 33 - About how far apart must you hold your hands for...Ch. 33 - SSM What inductance must be connected to a 17 pF...Ch. 33 - Prob. 6PCh. 33 - Prob. 7PCh. 33 - Prob. 8PCh. 33 - Prob. 9PCh. 33 - Prob. 10PCh. 33 - Prob. 11PCh. 33 - Prob. 12PCh. 33 - Sunlight just outside Earths atmosphere has an...Ch. 33 - Prob. 14PCh. 33 - An airplane flying at a distance of 10 km from a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 16PCh. 33 - Prob. 17PCh. 33 - Prob. 18PCh. 33 - Prob. 19PCh. 33 - Radiation from the Sun reaching Earth just outside...Ch. 33 - ILW What is the radiation pressure 1.5 m away from...Ch. 33 - Prob. 22PCh. 33 - Someone plans to float a small, totally absorbing...Ch. 33 - Prob. 24PCh. 33 - Prob. 25PCh. 33 - Prob. 26PCh. 33 - Prob. 27PCh. 33 - The average intensity of the solar radiation that...Ch. 33 - SSM A small spaceship with a mass of only 1.5 103...Ch. 33 - A small laser emits light at power 5.00 mW and...Ch. 33 - Prob. 31PCh. 33 - Prob. 32PCh. 33 - Prob. 33PCh. 33 - Prob. 34PCh. 33 - Prob. 35PCh. 33 - At a beach the light is generally partially...Ch. 33 - Prob. 37PCh. 33 - Prob. 38PCh. 33 - Prob. 39PCh. 33 - Prob. 40PCh. 33 - A beam of polarized light is sent into a system of...Ch. 33 - Prob. 42PCh. 33 - A beam of partially polarized light can be...Ch. 33 - Prob. 44PCh. 33 - When the rectangular metal tank in Fig. 33-46 is...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-47a, a light ray in an underlying...Ch. 33 - Light in vacuum is incident on the surface of a...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-48a, a light ray in water is incident...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-49 shows light reflecting from two...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-50a, a beam of light in material 1 is...Ch. 33 - GO In Fig. 33-51, light is incident at angle 1 =...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-52a, a beam of light in material 1 is...Ch. 33 - SSM WWW ILW in Fig. 33-53, a ray is incident on...Ch. 33 - Prob. 54PCh. 33 - Prob. 55PCh. 33 - Rainbows from square drops. Suppose that, on some...Ch. 33 - A point source of light is 80.0 cm below the...Ch. 33 - The index of refraction of benzene is 1.8. What is...Ch. 33 - SSM ILW In Fig. 33-57, a ray of light is...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-58, light from ray A refracts from...Ch. 33 - GO In Fig. 33-59, light initially in material 1...Ch. 33 - GO A catfish is 2.00 m below the surface of a...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-60, light enters a 90 triangular prism...Ch. 33 - Suppose the prism of Fig. 33-53 has apex angle =...Ch. 33 - GO Figure 33-61 depicts a simplistic optical...Ch. 33 - Prob. 66PCh. 33 - GO In the ray diagram of Fig. 33-63, where the...Ch. 33 - a At what angle of incidence will the light...Ch. 33 - Prob. 69PCh. 33 - In Fig. 33-64, a light ray in air is incident on a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 71PCh. 33 - An electromagnetic wave with frequency 4.00 1014...Ch. 33 - Prob. 73PCh. 33 - A particle in the solar system is under the...Ch. 33 - SSM In Fig, 33-65, a light ray enters a glass slab...Ch. 33 - Prob. 76PCh. 33 - Rainbow. Figure 33-67 shows a light ray entering...Ch. 33 - The primary rainbow described in Problem 77 is the...Ch. 33 - SSM emerges from the opposite face parallel to its...Ch. 33 - Prob. 80PCh. 33 - Prob. 81PCh. 33 - Prob. 82PCh. 33 - SSM A ray of white light traveling through fused...Ch. 33 - Three polarizing sheets are stacked. The first and...Ch. 33 - In a region of space where gravirational forces...Ch. 33 - An unpolarized beam of light is sent into a stack...Ch. 33 - SSM During a test, a NATO surveillance radar...Ch. 33 - The magnetic component of an electromagnetic wave...Ch. 33 - Calculate the a upper and b lower limit of the...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-71, two light rays pass from air...Ch. 33 - Prob. 91PCh. 33 - In about A D 150, Claudius Ptolemy gave the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 93PCh. 33 - Prob. 94PCh. 33 - Prob. 95PCh. 33 - Prob. 96PCh. 33 - Two polarizing sheets, one directly above the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 98PCh. 33 - Prob. 99PCh. 33 - Prob. 100PCh. 33 - Prob. 101PCh. 33 - Prob. 102PCh. 33 - Prob. 103PCh. 33 - Prob. 104PCh. 33 - Prob. 105PCh. 33 - In Fig. 33-78, where n1 = l.70, n2 = l .50, and n3...Ch. 33 - When red light in vacuum is incident at the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 108PCh. 33 - SSM a Show that Eqs. 33-1 land 33-2 satisfy the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 110P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The data were obtained from a use-dilution test comparing four disinfectants against Salmonella choleraesuis. G...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which of a planets fundamental propert...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
6.1 State the number of electrons that be must be lost by atoms of each of the following to achieve a stable el...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
What are the two types of bone marrow, and what are their functions?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
A 2500Ibm car moving at 25mi/h is accelerated at a constant rate of 15ft/s2 up to a speed of 50mi/h . What are ...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardthe cable may break and cause severe injury. cable is more likely to break as compared to the [1] ds, inclined at angles of 30° and 50° to the vertical rings by way of a scaled diagram. [4] I 30° T₁ 3cm 3.8T2 cm 200 N 50° at it is headed due North and its airspeed indicat 240 km/h. If there is a wind of 100 km/h from We e relative to the Earth? [3]arrow_forwardCan you explain this using nodal analysis With the nodes I have present And then show me how many KCL equations I need to write, I’m thinking 2 since we have 2 dependent sourcesarrow_forward
- The shear leg derrick is used to haul the 200-kg net of fish onto the dock as shown in. Assume the force in each leg acts along its axis. 5.6 m. 4 m- B Part A Determine the compressive force along leg AB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB = Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the compressive force along leg CB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FCB= Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in the winch cable DB. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 2marrow_forwardPart A (Figure 1) shows a bucket suspended from a cable by means of a small pulley at C. If the bucket and its contents have a mass of 10 kg, determine the location of the pulley for equilibrium. The cable is 6 m long. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 4 m B НА x = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback < 1 of 1 T 1 m Units ?arrow_forwardThe particle in is in equilibrium and F4 = 165 lb. Part A Determine the magnitude of F1. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ tvec F₁ = Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the magnitude of F2. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ It vec F2 = Submit Request Answer Part C Determine the magnitude of F3. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ? ? lb lb F₂ 225 lb 135° 45° 30° -60°-arrow_forward
- The 10-lb weight is supported by the cord AC and roller and by the spring that has a stiffness of k = 10 lb/in. and an unstretched length of 12 in. as shown in. Part A Determine the distance d to maintain equilibrium. Express your answer in inches to three significant figures. 節 ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ d = *k J vec 5 t 0 ? d C A in. 12 in. Barrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in . The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F = Value Submit Request Answer Part B 0 ? Units Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? T₂ = Value Units T₁ Carrow_forwardpls help on botharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY