
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119459132
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 9Q
Figure 33-32 shows four long horizontal layers A–D of different materials, with air above and below them. The index of refraction of each material is given. Rays of light are sent into the left end of each layer as shown. In which layer is there the possibility of totally trapping the light in that layer so that, after many reflections, all the light reaches the right end of the layer?
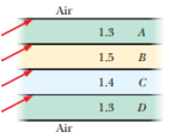
Figure 33-32 Question 9.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram please as well
Chapter 33 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
Ch. 33 - Prob. 1QCh. 33 - Prob. 2QCh. 33 - a Figure 33-27 shows light reaching a polarizing...Ch. 33 - Prob. 4QCh. 33 - In the arrangement of Fig. 33-l5a, start with...Ch. 33 - Prob. 6QCh. 33 - Figure 33-30 shows fays of monochromatic Light...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-31 shows the multiple reflections of a...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-32 shows four long horizontal layers AD...Ch. 33 - The leftmost block in Fig. 33-33 depicts total...
Ch. 33 - Prob. 11QCh. 33 - Prob. 12QCh. 33 - Prob. 1PCh. 33 - Prob. 2PCh. 33 - Prob. 3PCh. 33 - About how far apart must you hold your hands for...Ch. 33 - SSM What inductance must be connected to a 17 pF...Ch. 33 - Prob. 6PCh. 33 - Prob. 7PCh. 33 - Prob. 8PCh. 33 - Prob. 9PCh. 33 - Prob. 10PCh. 33 - Prob. 11PCh. 33 - Prob. 12PCh. 33 - Sunlight just outside Earths atmosphere has an...Ch. 33 - Prob. 14PCh. 33 - An airplane flying at a distance of 10 km from a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 16PCh. 33 - Prob. 17PCh. 33 - Prob. 18PCh. 33 - Prob. 19PCh. 33 - Radiation from the Sun reaching Earth just outside...Ch. 33 - ILW What is the radiation pressure 1.5 m away from...Ch. 33 - Prob. 22PCh. 33 - Someone plans to float a small, totally absorbing...Ch. 33 - Prob. 24PCh. 33 - Prob. 25PCh. 33 - Prob. 26PCh. 33 - Prob. 27PCh. 33 - The average intensity of the solar radiation that...Ch. 33 - SSM A small spaceship with a mass of only 1.5 103...Ch. 33 - A small laser emits light at power 5.00 mW and...Ch. 33 - Prob. 31PCh. 33 - Prob. 32PCh. 33 - Prob. 33PCh. 33 - Prob. 34PCh. 33 - Prob. 35PCh. 33 - At a beach the light is generally partially...Ch. 33 - Prob. 37PCh. 33 - Prob. 38PCh. 33 - Prob. 39PCh. 33 - Prob. 40PCh. 33 - A beam of polarized light is sent into a system of...Ch. 33 - Prob. 42PCh. 33 - A beam of partially polarized light can be...Ch. 33 - Prob. 44PCh. 33 - When the rectangular metal tank in Fig. 33-46 is...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-47a, a light ray in an underlying...Ch. 33 - Light in vacuum is incident on the surface of a...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-48a, a light ray in water is incident...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-49 shows light reflecting from two...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-50a, a beam of light in material 1 is...Ch. 33 - GO In Fig. 33-51, light is incident at angle 1 =...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-52a, a beam of light in material 1 is...Ch. 33 - SSM WWW ILW in Fig. 33-53, a ray is incident on...Ch. 33 - Prob. 54PCh. 33 - Prob. 55PCh. 33 - Rainbows from square drops. Suppose that, on some...Ch. 33 - A point source of light is 80.0 cm below the...Ch. 33 - The index of refraction of benzene is 1.8. What is...Ch. 33 - SSM ILW In Fig. 33-57, a ray of light is...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-58, light from ray A refracts from...Ch. 33 - GO In Fig. 33-59, light initially in material 1...Ch. 33 - GO A catfish is 2.00 m below the surface of a...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-60, light enters a 90 triangular prism...Ch. 33 - Suppose the prism of Fig. 33-53 has apex angle =...Ch. 33 - GO Figure 33-61 depicts a simplistic optical...Ch. 33 - Prob. 66PCh. 33 - GO In the ray diagram of Fig. 33-63, where the...Ch. 33 - a At what angle of incidence will the light...Ch. 33 - Prob. 69PCh. 33 - In Fig. 33-64, a light ray in air is incident on a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 71PCh. 33 - An electromagnetic wave with frequency 4.00 1014...Ch. 33 - Prob. 73PCh. 33 - A particle in the solar system is under the...Ch. 33 - SSM In Fig, 33-65, a light ray enters a glass slab...Ch. 33 - Prob. 76PCh. 33 - Rainbow. Figure 33-67 shows a light ray entering...Ch. 33 - The primary rainbow described in Problem 77 is the...Ch. 33 - SSM emerges from the opposite face parallel to its...Ch. 33 - Prob. 80PCh. 33 - Prob. 81PCh. 33 - Prob. 82PCh. 33 - SSM A ray of white light traveling through fused...Ch. 33 - Three polarizing sheets are stacked. The first and...Ch. 33 - In a region of space where gravirational forces...Ch. 33 - An unpolarized beam of light is sent into a stack...Ch. 33 - SSM During a test, a NATO surveillance radar...Ch. 33 - The magnetic component of an electromagnetic wave...Ch. 33 - Calculate the a upper and b lower limit of the...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-71, two light rays pass from air...Ch. 33 - Prob. 91PCh. 33 - In about A D 150, Claudius Ptolemy gave the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 93PCh. 33 - Prob. 94PCh. 33 - Prob. 95PCh. 33 - Prob. 96PCh. 33 - Two polarizing sheets, one directly above the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 98PCh. 33 - Prob. 99PCh. 33 - Prob. 100PCh. 33 - Prob. 101PCh. 33 - Prob. 102PCh. 33 - Prob. 103PCh. 33 - Prob. 104PCh. 33 - Prob. 105PCh. 33 - In Fig. 33-78, where n1 = l.70, n2 = l .50, and n3...Ch. 33 - When red light in vacuum is incident at the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 108PCh. 33 - SSM a Show that Eqs. 33-1 land 33-2 satisfy the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 110P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Practice Exercise 2
Calculate the pH of a solution containing 0.085 M nitrous acid (HNO2, Ka = 4.5 x 10-4) an...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Modified True/False 9. A giant bacterium that is large enough to be seen without a microscope is Selenomonas.
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
17. For the reaction shown, calculate how many moles of form when each amount of reactant completely reacts.
a...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Where is transitional epithelium found and what is its importance at those sites?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
The bioremediation process shown in the photograph is used to remove benzene and other hydrocarbons from soil c...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY