
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780078028229
Author: Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.3, Problem 3PP
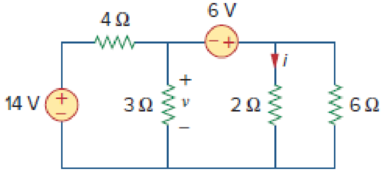
Figure 3.11
For Practice Prob. 3.3.
Find v and i in the circuit of Fig. 3.11.
Answer: −400 mV, 2.8 A.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 1: Two-Force Equilibrium
A 12 kg traffic light is suspended by two cables
attached to a ceiling. Determine the force in Cable 1
(AB) and Cable 2 (AC). In other words, determine the
tension in each cable, assuming the system is in static
equilibrium.
B
If the Z-axis changes, what is the effect
A circularly polarized wave, traveling in the +z-direction, is received by an elliptically
polarized antenna whose reception characteristics near the main lobe are given approx-
imately by
E₁ = (2â, + jâ] f(r. 8. d)
Find the polarization loss factor PLF (dimensionless and in dB) when the incident wave
is
(a) right-hand (CW)
(b) left-hand (CCW)
An elliptically polarized wave traveling in the negative z-direction is received by a circularly polarized
antenna. The vector describing the polarization of the incident wave is given by Ei= 2ax + jay .Find the
polarization loss factor PLF (dimensionless and in dB) when the wave that would be transmitted by the
antenna is (a) right-hand CP (b) left-hand CP.
Medium 1 is a lossless dielectric (ε₁=ε,ε, μ₁=μ₁, σ₁=0)
Medium 2 is a lossless dielectric (ε=&&₂, μ=μ₁, σ₁=0)
[бг Мо о =
= 0]
[2 Mo σ₂ = 0]
E₁ (z) = Ele² + Пe+jB₁²]
E2 (z) = E Te² and
tot
= constant
1. For the case εr1 = 1, &r2= 16, E₁x=1 V/m and a frequency f = 750 MHz determine:
λι
=
n₁ =
22 =
n2=
r =
T=
2. The magnitude |E1 tot (z)| will show an interference pattern in region 1 as:
E˜(z)=E,{1+Te®®]e¯MS =E||{1+Te^^^^\]e=##} | = |E|+Texp(j)
For an incident field E₁x=1 V/m SKETCH the magnitude of E1 tot (z)| and |E20 (z) on the graph
below. Plot the values at 2/4 increments and sketch between. What is the SWR?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Ch. 3.2 - Figure 3.4 For Practice Prob. 3.1. Obtain the node...Ch. 3.2 - Figure 3.6 For Practice Prob. 3.2. Find the...Ch. 3.3 - Figure 3.11 For Practice Prob. 3.3. Find v and i...Ch. 3.3 - Figure 3.14 For Practice Prob. 3.4. Find v1, v2,...Ch. 3.4 - Practice Problem 3.5 Figure 3.19 For Practice...Ch. 3.4 - Practice Problem 3.6 Figure 3.21 For Practice...Ch. 3.5 - Practice Problem 3.7 Figure 3.25 For Practice...Ch. 3.6 - By inspection, obtain the node-voltage equations...Ch. 3.6 - By inspection, obtain the mesh-current equations...Ch. 3.8 - For the circuit in Fig. 3.33, use PSpice to find...
Ch. 3.8 - Use PSpice to determine currents i1, i2, and i3 in...Ch. 3.9 - For the transistor circuit in Fig. 3.42, let =...Ch. 3.9 - The transistor circuit in Fig. 3.45 has = 80 and...Ch. 3 - At node 1 in the circuit of Fig. 3.46, applying...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.46 For Review Questions 3.1 and 3.2 In...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Fig. 3.47, v1 and v2 are...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.47 For Review Questions 3.3 and 3.4....Ch. 3 - The circuit i in the circuit of Fig. 3.48 is:...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.48 For Review Questions 3.5 and 3.6....Ch. 3 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.49, current i1 is: (a)4 A...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.49 For Review Questions 3.7 and 3.8....Ch. 3 - The PSpice part name for a current-controlled...Ch. 3 - Which of the following statements are not true of...Ch. 3 - Using Fig. 3.50, design a problem to help other...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Fig. 3.51, obtain v1 and v2....Ch. 3 - Find the currents I1 through I4 and the voltage vo...Ch. 3 - Given the circuit in Fig. 3.53, calculate the...Ch. 3 - Obtain vo in the circuit of Fig. 3.54. Figure 3.54...Ch. 3 - Solve for V1 in the circuit of Fig. 3.55 using...Ch. 3 - Apply nodal analysis to solve for Vx in the...Ch. 3 - Using nodal analysis, find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Determine Ib in the circuit in Fig. 3.58 using...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10PCh. 3 - Find Vo and the power dissipated in all the...Ch. 3 - Using nodal analysis, determine Vo in the circuit...Ch. 3 - Calculate v1 and v2 in the circuit of Fig. 3.62...Ch. 3 - Using nodal analysis, find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Apply nodal analysis to find io and the power...Ch. 3 - Determine voltages v1 through v3 in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3 - Determine the node voltages in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find v1, v2 and v3 in the...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Fig. 3.69, find v1, v2, and v3...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Fig. 3.70, find v1 and v2 using...Ch. 3 - Determine v1 and v2 in the circuit of Fig. 3.71....Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis and MATLAB to find Vo in the...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis along with MATLAB to determine...Ch. 3 - Calculate the node voltages v1, v2, and v3 in the...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to determine voltages v1, v2,...Ch. 3 - Use MATLAB to find the voltages at nodes a, b, c,...Ch. 3 - Use MATLAB to solve for the node voltages in the...Ch. 3 - Using nodal analysis, find vo and io in the...Ch. 3 - Find the node voltages for the circuit in Fig....Ch. 3 - Obtain the node voltages v1, v2, and v3 in the...Ch. 3 - Which of the circuits in Fig. 3.82 is planar? For...Ch. 3 - Determine which of the circuits in Fig. 3.83 is...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.54 For Prob. 3.5. Rework Prob. 3.5 using...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to obtain ia, ib, and ic in the...Ch. 3 - Using nodal analysis, find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Apply mesh analysis to the circuit in Fig. 3.85...Ch. 3 - Using Fig. 3.50 from Prob. 3.1, design a problem...Ch. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - Apply mesh analysis to find i in Fig. 3.87. Figure...Ch. 3 - Using Fig. 3.88, design a problem to help students...Ch. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - Prob. 45PCh. 3 - Calculate the mesh currents i1 and i2 in Fig....Ch. 3 - Rework Prob. 3.19 using mesh analysis. Use nodal...Ch. 3 - Prob. 48PCh. 3 - Find vo and io in the circuit of Fig. 3.94. Figure...Ch. 3 - Prob. 50PCh. 3 - Apply mesh analysis to find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find i1, i2 and i3 in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 53PCh. 3 - Find the mesh currents i1, i2, and i3 in the...Ch. 3 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.100, solve for I1, I2,...Ch. 3 - Determine v1 and v2 in the circuit of Fig. 3.101....Ch. 3 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.102, find the values of...Ch. 3 - Find i1, i2, and i3 in the circuit of Fig. 3.103....Ch. 3 - Rework Prob. 3.30 using mesh analysis. Using nodal...Ch. 3 - Prob. 60PCh. 3 - Calculate the current gain iois in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Find the mesh currents i1, i2, and i3 in the...Ch. 3 - Find vx and ix in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.107....Ch. 3 - Find vo and io in the circuit of Fig. 3.108.Ch. 3 - Use MATLAB to solve for the mesh currents in the...Ch. 3 - Write a set of mesh equations for the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Obtain the node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Prob. 68PCh. 3 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 3.113, write the...Ch. 3 - Write the node-voltage equations by inspection and...Ch. 3 - Write the mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Prob. 72PCh. 3 - Write the mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - By inspection, obtain the mesh-current equations...Ch. 3 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve Prob. 3.58....Ch. 3 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve Prob. 3.27....Ch. 3 - Solve for V1 and V2 in the circuit of Fig. 3.119...Ch. 3 - Solve Prob. 3.20 using PSpice or MultiSim. 3.20...Ch. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - Find the nodal voltages v1 through v4 in the...Ch. 3 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve the problem in...Ch. 3 - If the Schematics Netlist for a network is as...Ch. 3 - The following program is the Schematics Netlist of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 84PCh. 3 - An audio amplifier with a resistance of 9 ...Ch. 3 - Prob. 86PCh. 3 - For the circuit in Fig. 3.123, find the gain...Ch. 3 - Determine the gain vo/vs of the transistor...Ch. 3 - For the transistor circuit shown in Fig. 3.125,...Ch. 3 - Calculate vs for the transistor in Fig. 3.126...Ch. 3 - Prob. 91PCh. 3 - Prob. 92PCh. 3 - Rework Example 3.11 with hand calculation. In the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 11-2) Now consider that white noise (i.e., noise with a PSD that is constant with frequency) is introduced in the channel of the system described in the previous problem. An ideal low pass filter is used at the receiver input to reduce the noise as much as possible, while transmitting the desired signal. (a) By what factor should the cutoff frequency of the noise reduction filter be reduced in the 16-PAM case, compared to binary? (b) By what factor will the noise power at the decision circuit be reduced in the 16-PAM case? (c) By what factor will the noise amplitude at the decision circuit be reduced in the 16-PAM case? (d) To obtain the same symbol error rate for 16-PAM as for binary, how should the minimum level spacing for 16-PAM compare to binary? (e) If the 16-PAM level spacing is adjusted according to part (d) above, by what factor will the average signal power be increased in the 16-PAM case, compared to binary?arrow_forward11-1) similar to Lathi & Ding, Prob. P.6.7-5 Data at a bit rate Rb must be transmitted using either binary NRZ polar signaling or 16-ary PAM NRZ polar signaling. (a) By what factor will the symbol rate be reduced in the 16-PAM case? (b) By what factor will bandwidth required from the (lowpass) channel be reduced in the 16-PAM case? (c) Assuming the minimum spacing between pulse levels must be the same in both cases, by what factor will the average power be increased in the 16-PAM case? [Hint: take the pulse amplitudes to be ±A in the binary case, and ±A, ±3A, ±5A,..., ±154, and recall that scaling pulse amplitude by a factor k scales the pulse energy by a factor R². Assume that the data is random, so that all 16 levels are equally likely, and that the same pulse shape is used in both cases.] Warning: Solutions to the textbook problem that are posted online are mostly wrong. Work it out for yourself.arrow_forward11-3) similar to Lathi & Ding, Prob. P.6.8-1 Consider the carrier modulator shown in the figure below, which transmits a binary carrier signal. The baseband generator uses polar NRZ signaling with rectangular pulses. The data rate is 8 Mbit/s. (a) If the modulator generates a binary PSK signal, what is the bandwidth of the modulated output? (b) If the modulator generates FSK with the difference fel - fco = 6 MHz (cf. Fig 6.32c), determine the modulated signal bandwidth. Binary data source Baseband signal generator Modulated output Modulator N-E---arrow_forward
- For the circuit shown, find (i) closed-loop voltage gain (ii) Z i of the circuit (iii) f_max. The slew rate is 0.6V/us. ((write your answer in Kilo ohm)) 2Vpp R ww 20 kQ R₁ ww 200 ΚΩ 9+18 V - 18 V 10 kn R₁₂ ΚΩ ((write your answer in KHz))arrow_forwardillustrate the phenomenon of phase reversal in CE amplifier i- When signal current =OA, so IB-8uA ii- When input signal reaches positive peak, so IB=16uA ii- When input signal reaches negative peak, so IB=4uA R₁ www + Vcc = 12V Rc=6kn 16 A 8 μA 4 μА 0 www RE ẞ = 100 VCarrow_forwardIn the circuit shown, find the voltage gain. Given that ẞ = 80 and input resistance Rin=2kQ. SIGNAL +10 V Rc=6kn 4-2 210arrow_forward
- For the transistor amplifier shown, R₁-11kQ, R2=6kQ, Rc=2kQ, RE-3kQ and R₁=2k0. (i) Draw d.c. load line (ii) Determine the DC operating point (iii) Draw a.c. load line. Assume V_BE = 0.7 V. and determine the new operating point + Vcc = 15 V RC Cc Cin R1 wwwwww wwwww R₁₂ RE CE RLarrow_forwardthe first part is the second part write your answer such as: (AND, OR, INVERTER, NAND, NOR) D₁ AK D, R₁ B K First Part? the third part is , and the total are R4 R7 Output R5 R₁ T R6 R3 -UBB Second Part? Third Part? Total?arrow_forwardA multistage amplifier has six stages each of which has a power gain of 40. what is the - Total gain of the amplifier in db ? ii- If the negative feedback of 15db is employed, find the resultant gainarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Thevenin's Theorem; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=veAFVTIpKyM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY