
(a)
The following program will determine the value of int(a) where value of a=10.6.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6
floata=10.6;
//determine and print the value of int(a)
cout<<int(a);
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6, which is floating-point type value. The int(a) will typecast the value of a to integer type so that it will print only integer part only.
Sample Output:

(b)
The following program will determine the value of int(b) where the value of b=13.9.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable b with value 13.9
floatb=13.9;
//determine and print the value of int(b)
cout<<int(b);
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of b is 13.9, which is floating-point type value. The int(b) will typecast the value of a to integer type so that it will print only integer part only.
Sample Output:

(c)
The following program will determine the value of int(c) where the value of c=-3.42.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable c with value -3.42
floatc=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of int(c)
cout<<int(c);
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of c is -3.42, which is floating-point type value. The int(c) will typecast the value of a to integer type so that it will print only integer part only.
Sample Output:
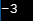
(d)
The following program will determine the value of int(a+b) where the value of a=10.6 and b=13.9.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6 and bwith value 13.9
float a=10.6, b=13.9;
//determine and print the value of int(a+b)
cout<<int(a+b);
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6 and b is 13.9, which is floating-point type value. The int(a+b) will first add the value a and b then typecast the value of its result to an integer type and then print the value using cout statement.
Sample Output:
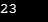
(e)
The following program will determine the value of int(a+b) where the value of a=10.6, b=13.9 and c=-3.42.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6, b with 13.9 and c with -3.42
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of int(a)+b+c
cout<<int(a)+b+c;
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6, b is 13.9, and c is -3.42, which is floating-point type value. The int(a)+b+c will typecast the value of a to an integer type and then add and print the integer value of a, b and c.
Sample Output:

(f)
The following program will determine the value of int(a+b)+c where the value of a=10.6, b=13.9 and c=-3.42.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6, b with 13.9 and c with -3.42
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of int(a+b)+c
cout<<int(a+b)+c;
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6, b is 13.9, and c is -3.42, which is floating-point type value. The int(a+b) will first add the value a and b then typecast the value of its result to an integer type and then add the value of c to it.
Sample Output:
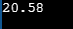
(g)
The following program will determine the value of int(a+b+c) where the value of a=10.6, b=13.9 and c=-3.42.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6, b with 13.9 and c with -3.42
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of int(a+b+c)
cout<<int(a+b+c);
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6, b is 13.9, and c is -3.42, which is floating-point type value. The int(a+b+c) will first add the value of a, b and c then typecast the value of its result to an integer type and print the value using cout statement.
Sample Output:
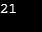
(h)
The following program will determine the value of float(int(a))+b where the value of a=10.6and b=13.9.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6 and b with 13.9
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of float(int(a))+b
cout<<float(int(a))+b ;
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6and b is 13.9, which is floating-point type value. The float(int(a))+bwill first typecast the value of a to an integer type and then typecast this integer value to float and then add value b to it and print the value using cout statement.
Sample Output:

(i)
The following program will determine the value of float(int(a+b)) where the value of a=10.6and b=13.9.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6 and b with 13.9
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of float(int(a+b))
cout<<float(int(a+b)) ;
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6and b is 13.9, which is floating-point type value. The float(int(a+b))will first add the value of a+b and then typecast the value of its result to an integer type and then typecast this integer value to float and print the value using cout statement.
Sample Output:

(j)
The following program will determine the value of abs(a)+abs(b) where the value of a=10.6and b=13.9.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6 and b with 13.9
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of abs(a)+abs(b)
cout<<abs(a)+abs(b) ;
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6and b is 13.9, which is floating-point type value. The abs(a) and abs(b)function are used to get the absolute value of a and b then add this absolute value with each other and print the value using cout statement.
Sample Output:
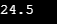
(j)
The following program will determine the value of sqrt(abs(a-b)) where the value of a=10.6and b=13.9.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
Program
//included header file
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
//included namespace
usingnamespacestd;
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable a with value 10.6 and b with 13.9
float a=10.6, b=13.9, c=-3.42;
//determine and print the value of sqrt(abs(a-b))
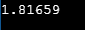
cout<<sqrt(abs(a-b));
//exiting from program
return0;
}
Explanation:
In the above code, the value of a is 10.6and b is 13.9, which is floating-point type value. The abs(a-b)function will determine the absolute value of a-b then the sqrt()function will determine the square root value of this resultand print the value using cout statement.
Sample Output:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
C++ for Engineers and Scientists
- If a UDP datagram is sent from host A, port P to host B, port Q, but at host B there is no process listening to port Q, then B is to send back an ICMP Port Unreachable message to A. Like all ICMP messages, this is addressed to A as a whole, not to port P on A. (a) Give an example of when an application might want to receive such ICMP messages. (b) Find out what an application has to do, on the operating system of your choice, to receive such messages. (c) Why might it not be a good idea to send such messages directly back to the originating port P on A?arrow_forwardDiscuss how business intelligence and data visualization work together to help decision-makers and data users. Provide 2 specific use cases.arrow_forwardThis week we will be building a regression model conceptually for our discussion assignment. Consider your current workplace (or previous/future workplace if not currently working) and answer the following set of questions. Expand where needed to help others understand your thinking: What is the most important factor (variable) that needs to be predicted accurately at work? Why? Justify its selection as your dependent variable.arrow_forward
- According to best practices, you should always make a copy of a config file and add a date to filename before editing? Explain why this should be done and what could be the pitfalls of not doing it.arrow_forwardIn completing this report, you may be required to rely heavily on principles relevant, for example, the Work System, Managerial and Functional Levels, Information and International Systems, and Security. apply Problem Solving Techniques (Think Outside The Box) when completing. should reflect relevance, clarity, and organisation based on research. Your research must be demonstrated by Details from the scenario to support your analysis, Theories from your readings, Three or more scholarly references are required from books, UWIlinc, etc, in-text or narrated citations of at least four (4) references. “Implementation of an Integrated Inventory Management System at Green Fields Manufacturing” Green Fields Manufacturing is a mid-sized company specialising in eco-friendly home and garden products. In recent years, growing demand has exposed the limitations of their fragmented processes and outdated systems. Different departments manage production schedules, raw material requirements, and…arrow_forward1. Create a Book record that implements the Comparable interface, comparing the Book objects by year - title: String > - author: String - year: int Book + compareTo(other Book: Book): int + toString(): String Submit your source code on Canvas (Copy your code to text box or upload.java file) > Comparable 2. Create a main method in Book record. 1) In the main method, create an array of 2 objects of Book with your choice of title, author, and year. 2) Sort the array by year 3) Print the object. Override the toString in Book to match the example output: @Javadoc Declaration Console X Properties Book [Java Application] /Users/kuan/.p2/pool/plugins/org.eclipse.justj.openjdk.hotspo [Book: year=1901, Book: year=2010]arrow_forward
- Q5-The efficiency of a 200 KVA, single phase transformer is 98% when operating at full load 0.8 lagging p.f. the iron losses in the transformer is 2000 watt. Calculate the i) Full load copper losses ii) half load copper losses and efficiency at half load. Ans: 1265.306 watt, 97.186%arrow_forward2. Consider the following pseudocode for partition: function partition (A,L,R) pivotkey = A [R] t = L for i L to R-1 inclusive: if A[i] A[i] t = t + 1 end if end for A [t] A[R] return t end function Suppose we call partition (A,0,5) on A=[10,1,9,2,8,5]. Show the state of the list at the indicated instances. Initial A After i=0 ends After 1 ends After i 2 ends After i = 3 ends After i = 4 ends After final swap 10 19 285 [12 pts]arrow_forward.NET Interactive Solving Sudoku using Grover's Algorithm We will now solve a simple problem using Grover's algorithm, for which we do not necessarily know the solution beforehand. Our problem is a 2x2 binary sudoku, which in our case has two simple rules: •No column may contain the same value twice •No row may contain the same value twice If we assign each square in our sudoku to a variable like so: 1 V V₁ V3 V2 we want our circuit to output a solution to this sudoku. Note that, while this approach of using Grover's algorithm to solve this problem is not practical (you can probably find the solution in your head!), the purpose of this example is to demonstrate the conversion of classical decision problems into oracles for Grover's algorithm. Turning the Problem into a Circuit We want to create an oracle that will help us solve this problem, and we will start by creating a circuit that identifies a correct solution, we simply need to create a classical function on a quantum circuit that…arrow_forward
- using r languagearrow_forward8. Cash RegisterThis exercise assumes you have created the RetailItem class for Programming Exercise 5. Create a CashRegister class that can be used with the RetailItem class. The CashRegister class should be able to internally keep a list of RetailItem objects. The class should have the following methods: A method named purchase_item that accepts a RetailItem object as an argument. Each time the purchase_item method is called, the RetailItem object that is passed as an argument should be added to the list. A method named get_total that returns the total price of all the RetailItem objects stored in the CashRegister object’s internal list. A method named show_items that displays data about the RetailItem objects stored in the CashRegister object’s internal list. A method named clear that should clear the CashRegister object’s internal list. Demonstrate the CashRegister class in a program that allows the user to select several items for purchase. When the user is ready to check out, the…arrow_forward5. RetailItem ClassWrite a class named RetailItem that holds data about an item in a retail store. The class should store the following data in attributes: item description, units in inventory, and price. Once you have written the class, write a program that creates three RetailItem objects and stores the following data in them: Description Units in Inventory PriceItem #1 Jacket 12 59.95Item #2 Designer Jeans 40 34.95Item #3 Shirt 20 24.95arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT- COMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE LProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage




