
(General math) a. Write a C++
b. How do you know the result your program produced is correct?
c. After verifying the output your program produces, modify it to determine the slope of the line connecting the points (2,10) and (12,6).
d. What do you think will happen if you use the points (2,3) and (2,4), which results in a division by zero? How do you think this situation can be handled?
e. If your program doesn’t already do so, change its output to this:
The value of the slope is xxx.xx
The xxx.xx denotes placing the calculated value in a field wide enough for three places to the left of the decimal point and two places to the right of it.
(a)
Program plan: -
Variables
used in the following program are given below: -
- line_slope: -To store the slope of the line
- a1, a2: - To store the coordinates point values of x1 and x2.
- b1, b2: - To store the coordinate point values of y1 and y2.
Formula used: - (b2 − b1)/(a2 − a1)
Program description: -The purpose of the C++ program is to determine the slope of the line connecting two points with the coordinates (3, 7) and (8, 12).
1
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The slope between two points with the coordinates
Program:
//header file
#include <iostream>
//using the namespace
usingnamespacestd;
intmain()
{
//declaring the variables
floatline_slope, a1 =3, a2 =8, b1 =7, b2 =12;
//calculating the slope of the line connecting two points
line_slope=(b2 - b1)/(a2 - a1);
//displaying the slope of the line_slope
cout<<"Slope of a line is: "<<line_slope<<endl;
//return statement
return0;
}
Explanation:
The above code is used to calculate the slope of a line connecting the two points.
Firstly, declaring the variables of float data type. The variable line_slope will store the slope of the line, a1, a2 and b1, b2 is used to store the coordinates point values of x1, x2 and y1, y2.
The slope of a line is calculated by the given formula
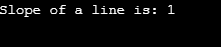
Sample output: -
(b)
To verify the result of the program is correct.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: formula to calculate the slope: -
Slope of the line is 1
Explanation:
Now, calculating the slope of the line by manual calculating to verify the result of the above program.
Since, the slope of the line is 1.
Hence, verified
(c)
To modify the program of exercise by changing the value of coordinates point values.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:formula to calculate the slope: -
a1 = 2, a2 = 12 and b1 = 10, b2 = 6
Program:
//header file
#include <iostream>
//using the namespace
usingnamespacestd;
intmain()
{
//declaring the variables
floatline_slope, a1 =2, a2 =12, b1 =10, b2 =6;
//calculating the slope of the line connecting two points
line_slope=(b2 - b1)/(a2 - a1);
//displaying the slope of the line_slope
cout<<"Slope of a line is: "<<line_slope<<endl;
//return statement
return0;
}
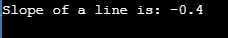
Sample output: -
Explanation:
The slope of a line is calculated by same formula as used in the exercise 1.a
In the above program only the value of the coordinates point has changed.
(d)
To determine the situation while using the points (2, 3) and (2, 4) and the denominator part becomes zero.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:New coordinates point values: - (2, 3) and (2, 4)
Explanation:
While calculating the slope of a line where the coordinates point values are (2, 3) and (2, 4)thanthe values of x1, and x2 are 2 same and the values of y1, and y2 are 3 and 4,here the denominator value is zero as the expression (x2-x1) is equal to zero.
In this case, the value of the slope will be infinite. This situation can be handled by using a conditional statement given below: -
//header file
#include <iostream>
//using the namespace
usingnamespacestd;
intmain()
{
//declaring the variables
floatline_slope, a1 =2, a2 =2, b1 =3, b2 =4;
//calculating the slope of the line connecting two points
line_slope=(b2 - b1)/(a2 - a1);
//displaying the slope of the line_slope
cout<<"Slope of a line is: "<<line_slope<<endl;
//to check when the denominator is equal to zero
if((a2 - a1 ==0))
{
//message
cout<<"The slope of the line is infinite."<<endl;
}
//return statement
return0;
}
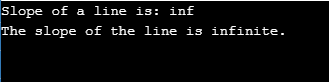
Sample output: -
(e)
To make changes in the above program so that the output is produced in the given format: xxx.xx
cout<<"|"<<setw(5)<<setiosflags(ios::fixed)<<setprecision(2)<<5.267<<"|";
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The format of the output is xxx.xx
Program:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
//using the namespace
//for using the standard I/O
usingnamespacestd;
intmain()
{
//declaring the variables
//as per the requirement
floatline_slope, a1 =12, a2 =7, b1 =8, b2 =3;
//calculating the slope
//by usinf the given formula
line_slope=(b2 - b1)/(a2 - a1);
//displaying the slope and settingthe format of output as xx.xxx
//the width is set to 6 and the number of digits after decimal is //set //to 2
cout<<"The value of the slope is "<<setw(6)<<setiosflags(ios::fixed )<<setprecision(2)<<line_slope<<endl;
//return statement
return0;
}
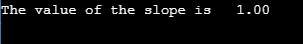
Sample output: -
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
C++ for Engineers and Scientists
- "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
- "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forwardSolve this "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
- "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forwardSpecifications: Part-1Part-1: DescriptionIn this part of the lab you will build a single operation ALU. This ALU will implement a bitwise left rotation. Forthis lab assignment you are not allowed to use Digital's Arithmetic components.IF YOU ARE FOUND USING THEM, YOU WILL RECEIVE A ZERO FOR LAB2!The ALU you will be implementing consists of two 4-bit inputs (named inA and inB) and one 4-bit output (named out). Your ALU must rotate the bits in inA by the amount given by inB (i.e. 0-15).Part-1: User InterfaceYou are provided an interface file lab2_part1.dig; start Part-1 from this file.NOTE: You are not permitted to edit the content inside the dotted lines rectangle. Part-1: ExampleIn the figure above, the input values that we have selected to test are inA = {inA_3, inA_2, inA_1, inA_0} = {0, 1, 0,0} and inB = {inB_3, inB_2, inB_1, inB_0} = {0, 0, 1, 0}. Therefore, we must rotate the bus 0100 bitwise left by00102, or 2 in base 10, to get {0, 0, 0, 1}. Please note that a rotation left is…arrow_forwardSolve this "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
- Solve this "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forwardSolve this "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning

