
Concept explainers
a.
To graph:
The given function using a graphing utility.
a.
Answer to Problem 99E
The graph of our given function would be:
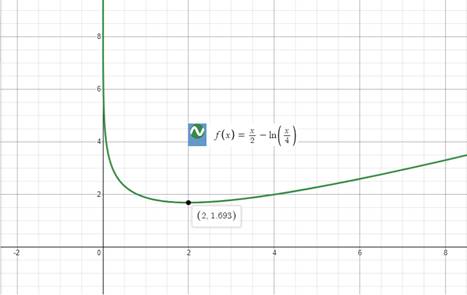
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A function:
Calculation:
Upon graphing the given functionusing a graphing utility, we will get our required graph as shown below:
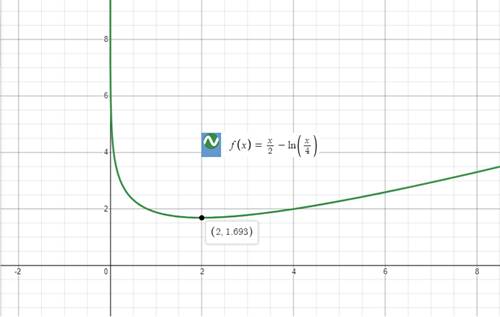
b.
To find:
The domain of the given function.
b.
Answer to Problem 99E
The domain of our given logarithmic function would be
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A function:
Calculation:
We know that logarithmic functions are not defined for negative values. To find domain of our given function, we will set argument of log function greater than 0 as:
Therefore, the domain of our given logarithmic function would be
c.
To find:
Open intervals on which the given function is increasing and decreasing using the graph of function.
c.
Answer to Problem 99E
The function is decreasing on interval
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A function:
Calculation:
Upon looking at graph of our given function, we can see that function is decreasing from 0 to 2 and increasing from 2 to positive infinity.
Therefore, the function is decreasing on interval
d.
To approximate:
The
d.
Answer to Problem 99E
The relative minimum of the given function is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A function:
Calculation:
We can see from our given graph that there is no maximum value for our given function.
We can see that the minimum value of our given function occurs at
Therefore, the relative minimum of the given function is
Chapter 3 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- Evaluate the next integralarrow_forward1. For each of the following, find the critical numbers of f, the intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing, and the relative maximum and minimum values of f. (a) f(x) = x² - 2x²+3 (b) f(x) = (x+1)5-5x-2 (c) f(x) = x2 x-9 2. For each of the following, find the intervals on which f is concave upward or downward and the inflection points of f. (a) f(x) = x - 2x²+3 (b) g(x) = x³- x (c) f(x)=x-6x3 + x-8 3. Find the relative maximum and minimum values of the following functions by using the Second Derivative Test. (a) f(x)=1+3x² - 2x3 (b) g(x) = 2x3 + 3x² - 12x-4arrow_forwardFind the Soultion to the following dy differential equation using Fourier in transforms: = , хуо, ухо according to the terms: lim u(x,y) = 0 x18 lim 4x (x,y) = 0 x14 2 u (x, 0) = =\u(o,y) = -y لوarrow_forward
- Can you solve question 3,4,5 and 6 for this questionarrow_forwardwater at a rate of 2 m³/min. of the water height in this tank? 16) A box with a square base and an open top must have a volume of 256 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the box that will minimize the amount of material used (the surface area). 17) A farmer wishes toarrow_forward#14 Sand pours from a chute and forms a conical pile whose height is always equal to its base diameter. The height o the pile increases at a rate of 5 feet/hour. Find the rate of change of the volume of the sand in the conical pile when the height of the pile is 4 feet.arrow_forward
- (d)(65in(x)-5 cos(x) dx mins by 5x-2x² 3x+1 dx -dx 20 Evaluate each the following indefinite integralsarrow_forward19 Evaluate each the following definite integrals: a) લ b) (+3) 6) (2-2)(+33) dxarrow_forward#11 If a snowball melts so its surface area decreases at a rate of 1cm²/min, find the rate at which the diameter decreases when the diameter is 6 cm.arrow_forward
- Use Deritivitve of the inverse to solve thisarrow_forwardEvaluate the following Limits: e6x-1 Lim +0Sin3x 7x-5x2 2x-1+ Cos 4x +6 c) Lim b) Lim + x³-x2 X-0 1-e' 4x d) Lim 6x²-3 X+0 6x+2x² Find the derivatives of the following functions using the Limit definition of derivativearrow_forward15A cylindrical tank with radius 8 m is being filled with water at a rate of 2 m³/min. What is the rate of change of the water height in this tank? 6)A box with a square base and an open top must box that will minimiarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





