
Concept explainers
Applications.
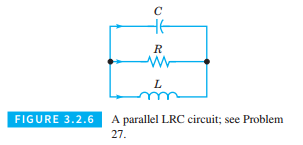
Electric Circuits. The theory of electric circuits, such as that shown in Figure 3.2.6, consisting of inductors, resistors, and capacitors, is based on Kirchhoff’s laws: (1) At any node (or junction), the sum of currents flowing into that node is equal to the sum of currents flowing into that node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of that node, and (2) the net voltage drop around each closed loop is zero. In addition to Kirchhoff’s laws, we also have the relation between the current
Kirchhoff’s laws and the current-voltage relation for each circuit element provide a system of algebraic and differential equations from which the voltage and current throughout the circuit can be determined. Problems 27 through 29 illustrate the procedure just described.
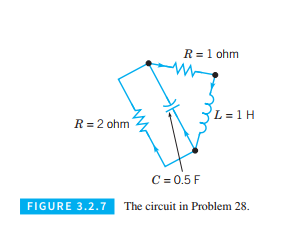
Consider the circuit shown in the Figure 3.2.7. Use the method outlined in problem 27 to show that the current
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS-NEXTGEN WILEYPLUS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics Using The Ti-83/84 Plus Calculator, Books A La Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- How can I prepare for me Unit 3 test in algebra 1? I am in 9th grade.arrow_forwardiid B1 Suppose X1, ..., Xn fx(x), where 2 fx(x) = x exp(−x²/0), 0<< (0 otherwise). (a) Find the maximum likelihood estimator of 0. (b) Show that the MLE is an unbiased estimator of 0. (c) Find the MSE of the MLE. Hint: For parts (b) and (c), you may use integration by parts.arrow_forward2. The size of a claim is modelled by F(a, λ) with a fixed a a maximum likelihood estimate of A given a sample x with a sample mean x = 11 = 121. Give [5 Marks]arrow_forward
- Robbie Bearing Word Problems Angles name: Jocelyn date: 1/18 8K 2. A Delta airplane and an SouthWest airplane take off from an airport at the same time. The bearing from the airport to the Delta plane is 23° and the bearing to the SouthWest plane is 152°. Two hours later the Delta plane is 1,103 miles from the airport and the SouthWest plane is 1,156 miles from the airport. What is the distance between the two planes? What is the bearing from the Delta plane to the SouthWest plane? What is the bearing to the Delta plane from the SouthWest plane? Delta y SW Angles ThreeFourthsMe MATH 2arrow_forwardFind the derivative of the function. m(t) = -4t (6t7 - 1)6arrow_forwardFind the derivative of the function. y= (8x²-6x²+3)4arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning  Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell



