
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781259141089
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 30, Problem 30.30P
An isoprene unit can be thought of as having a head and a tail. The “head” of the isoprene unit is located at the end of the chain nearest the branch point, and the “tail” is located at the end of the carbon chain farthest from the branch point. Most isoprene units are connected together in a “head-to-tail” fashion, as illustrated. For both lycopene (Problem 31.26), and squalene (Figure 31.9), decide which isoprene units are connected in a head-to-tail fashion and which are not.
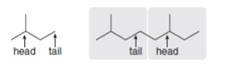
These two isoprene units are
connected in head-tail fashion.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Metal clusters and catalytic processes.
Metal clusters and catalysis.
Q1: Draw a valid Lewis structures for the following molecules. Include appropriate charges and
lone pair electrons. If there is more than one Lewis structure available, draw the best structure.
NH3
Sulfate
Boron tetrahydride.
C3H8 (linear isomer)
OCN
NO3
CH3CN
SO2Cl2
CH3OH2*
Chapter 30 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
Ch. 30 - Problem 31.1
One component of jojoba oil is a wax...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.2PCh. 30 - Problem 31.3
Draw the products formed when...Ch. 30 - Problem 31.4
The main fatty acid component of the...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.5PCh. 30 - Problem 31.6
Draw the structure of a lecithin...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.7PCh. 30 - Problem 31.8
Why are phospholipids, but not...Ch. 30 - Problem 31.9
Explain why regularly ingesting a...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.10P
Ch. 30 - Problem 31.10
Locate the isoprene units in each...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.12PCh. 30 - Problem 31.11
Locate the isoprene units in...Ch. 30 - Problem 31.12
Write a stepwise mechanism for the...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.15PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.16PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.17PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.18PCh. 30 - 31.17 Locate the isoprene units in each...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.20PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.21PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.22PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.23PCh. 30 - 31.22 What is the structure of an optically...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.25PCh. 30 - 31.24 Draw the structure of the following...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.27PCh. 30 - Locate the isoprene units in each compound. a. e....Ch. 30 - Classify each terpene and terpenoid in Problem...Ch. 30 - 31.29 An isoprene unit can be thought of as having...Ch. 30 - 31.30 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the conversion...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.32PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.33PCh. 30 - Draw three-dimensional structures f or each...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.35PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.36PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.37PCh. 30 - 31.38 Draw the products formed when cholesterol is...Ch. 30 - 31.39 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 30 - 31.40 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.41P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the following molecule, indicate the hybridization and shape of the indicated atoms. -z: CH3 CH3 H3C HO: CI: :arrow_forwardQ3: Draw the Lewis structures for nitromethane (CH3NO2) and methyl nitrite (CH3ONO). Draw at least two resonance forms for each. Determine which form for each is the major resonance contributor. Page 1 of 4 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations Q4: Draw the Lewis structures for the cyanate ion (OCN) and the fulminate ion (CNO-). Draw all possible resonance structures for each. Determine which form for each is the major resonance contributor.arrow_forwardMetallic clusters and nanomaterials.arrow_forward
- 55. The photoelectric threshold energy for ytterbium metal is 4.16 × 10-19 J/atom. a. Calculate the wavelength of light that this energy corresponds to (in nm). b. Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does this wavelength fall in? c. Would light of wavelength 490 nm produce a photoelectric effect in ytterbium? Why or why not?arrow_forward14.50 Explain why methyl vinyl ether (CH2=CHOCH 3) is not a reactive dienophile in the Diels-Alder reaction.arrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- 14.49 From what you have learned about the reaction of conjugated dienes in Section 14.10, predict the products of each of the following electrophilic additions. a. H₂O H2SO4 Br2 b. H₂Oarrow_forward14.46 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction. HBr ROOR Br + Brarrow_forwardShow work..don't give Ai generated solution....arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY