
Cost Behavior, High-Low Method, Pricing Decision
Fonseca, Ruiz, and Dunn is a large, local accounting firm located in a southwestern city. Carlos Ruiz, one of the firm’s founders, appreciates the success his firm has enjoyed and wants to give something back to his community. He believes that an inexpensive accounting services clinic could provide basic accounting services for small businesses located in the barrio. He wants to price the services at cost.
Since the clinic is brand new, it has no experience to go on. Carlos decided to operate the clinic for 2 months before determining how much to charge per hour on an ongoing basis. As a temporary measure, the clinic adopted an hourly charge of $25, half the amount charged by Fonseca, Ruiz, and Dunn for professional services.
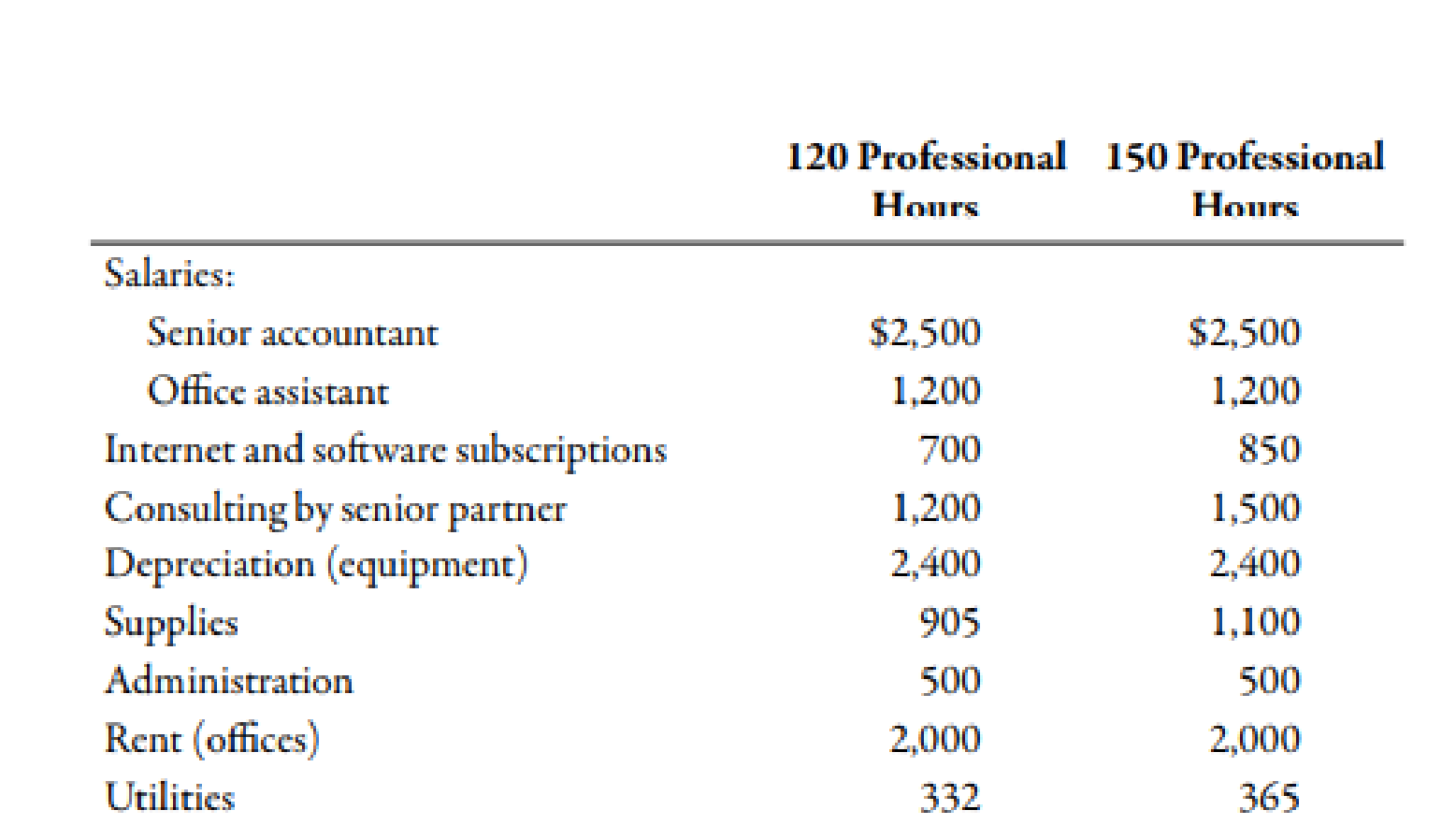
The accounting services clinic opened on January 1. During January, the clinic had 120 hours of professional service. During February, the activity was 150 hours. Costs for these two levels of activity usage are as follows:
Required:
- 1. Classify each cost as fixed, variable, or mixed, using hours of professional service as the activity driver.
- 2. Use the high-low method to separate the mixed costs into their fixed and variable components. (Note: Round variable rates to two decimal places and fixed amounts to the nearest dollar.)
- 3. Luz Mondragon, the chief paraprofessional of the clinic, has estimated that the clinic will average 140 professional hours per month. If the clinic is to be operated as a nonprofit organization, how much will it need to charge per professional hour ? How much of this charge is variable? How much is fixed? (Note: Round answers to two decimal places.)
- 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Suppose the accounting center averages 170 professional hours per month. How much would need to be charged per hour for the center to cover its costs ? Explain why the per-hour charge decreased as the activity output increased. (Note: Round answers to two decimal places.)
1.
Categorize the activities into fixed cost, variable cost or mixed cost.
Explanation of Solution
Cost:
Cost can be defined as the cash and cash equivalent which is incurred against the products or its related services which will benefit the organization in the future. There are two types of costs that are fixed and variable costs. Combination of fixed and variable is referred to as mixed cost.
| Serial Number | Activities | Categorize |
| 1 | Senior accountant | Fixed cost |
| 2 | Office assistant | Fixed cost |
| 3 | Internet and software subscriptions | Mixed cost |
| 4 | Consulting by senior partner | Variable cost |
| 5 | Depreciation | Fixed cost |
| 6 | Supplies | Mixed cost |
| 7 | Administration | Fixed cost |
| 8 | Rent | Fixed cost |
| 9 | Utilities | Mixed cost |
Table (1)
2.
Divide the mixed costs into fixed and variable components with the help of high-low method.
Explanation of Solution
High Low Method:
The method in which, high and low points of data are used to classify the mixed cost into fixed and variable cost known as high low method. This is one among the three costs of separation methods.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of variable rate of internet and software subscriptions:
Substitute $850 for high receiving cost, $700 for low receiving cost, 150 for high professional hours and 120 for low professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, variable rate is $5.00 per hour.
Use the following formula to calculate the fixed cost for a month of internet and software subscriptions:
Substitute $850 for high receiving cost, $5.00 for variable rate and 150 for high professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, fixed cost for a month is $100.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of variable rate of supplies:
Substitute $1,100 for high receiving cost, $905 for low receiving cost, 150 for high professional hours and 120 for low professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, variable rate is $6.5 per hour.
Use the following formula to calculate the fixed cost for a month of supplies:
Substitute $1,100 for high receiving cost, $6.50 for variable rate and 150 for high professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, fixed cost for a month is $125.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of variable rate of utilities:
Substitute $365 for high receiving cost, $332 for low receiving cost, 150 for high professional hours and 120 for low professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, variable rate is $1.10 per hour.
Use the following formula to calculate the fixed cost for a month of utilities:
Substitute $365 for high receiving cost, $1.10 for variable rate and 150 for high professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, fixed cost for a month is $200.
3.
Calculate the value of total cost and charge per hour. Also, calculate the fixed cost and variable cost.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate the value of fixed cost per hour:
Substitute $9,025 for total cost and 140 for professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, the value of fixed cost per hour is $64.46.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of variable cost per hour:
Substitute $5 for variable rate of internet subscriptions, $10 for consulting by senior partner, $6.50 for supplies and 1.10 for utilities in the above formula.
Therefore, the value of variable cost per hour is $22.60.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of total clinic cost:
Substitute $9,025 for fixed cost and $22.60 for variable rate and 140 for professional hours in the above formula.
Therefore, the value of total clinic cost is $12,189.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of charge per hour:
Substitute $12,189 for total clinic cost, 140 for professional hours and $22.60 for variable rate in the above formula.
Therefore, the value of charge per hour is $87.06.
Working Note:
Total Cost is calculated by adding the values of all the activities that is $9,025
4.
Calculate the value of charge per hour when the number of professional hours is 170 hours.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate the value of charge per hour:
Substitute $9,025 for fixed cost, 170 for professional hours and $22.60 for variable rate in the above formula.
Therefore, the value of charge per hour is $75.69.
The charge per hour decreases because fixed cost is divided by the large amount of professional hours.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
- Mit Distributors provided the following inventory-related data for the fiscal year: Purchases: $385,000 Purchase Returns and Allowances: $10,200 Purchase Discounts: $4,300 Freight In: $55,000 Beginning Inventory: $72,000 Ending Inventory: $95,500 What is the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?arrow_forwardanswer ? general accountingarrow_forwardBrightTech Corp. reported the following cost of goods sold (COGS) figures over three years: • 2023: $3,800,000 • 2022: $3,500,000 • 2021: $3,000,000 If 2021 is the base year, what is the percentage increase in COGS from 2021 to 2023?arrow_forward
- Sun Electronics operates a periodic inventory system. At the beginning of 2022, its inventory was $95,750. During the year, inventory purchases totaled $375,000, and its ending inventory was $110,500. What was the cost of goods sold (COGS) for Sun Electronics in 2022?arrow_forwardi want to this question answer of this general accountingarrow_forwardA clothing retailer provides the following financial data for the year. Determine the cost of goods sold (COGS): ⚫Total Sales: $800,000 • Purchases: $500,000 • Sales Returns: $30,000 • Purchases Returns: $40,000 • Opening Stock Value: $60,000 • Closing Stock Value: $70,000 Administrative Expenses: $250,000arrow_forward
- subject : general accounting questionarrow_forwardBrightTech Inc. had stockholders' equity of $1,200,000 at the beginning of June 2023. During the month, the company reported a net income of $300,000 and declared dividends of $175,000. What was BrightTech Inc.. s stockholders' equity at the end of June 2023?arrow_forwardQuestion 3Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. reports the following financialinformation at the end of the current year: Net Sales $100,000 Debtor's turnover ratio (based on net sales) 2 Inventory turnover ratio 1.25 fixed assets turnover ratio 0.8 Debt to assets ratio 0.6 Net profit margin 5% gross profit margin 25% return on investments 2% Use the given information to fill out the templates for incomestatement and balance sheet given below: Income Statement of Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. for the year endingDecember 31, 20XX(in $) Sales 100,000 Cost of goods sold gross profit other expenses earnings before tax tax @ 50% Earnings after tax Balance Sheet of Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. as at December 31, 20XX(in $) Liabilities Amount Assets Amount Equity Net fixed assets long term debt 50,000 Inventory short term debt debtors cash Total Totalarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College




