
EP MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY..-MOD.ACC
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134607894
Author: BAUMAN
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3VI
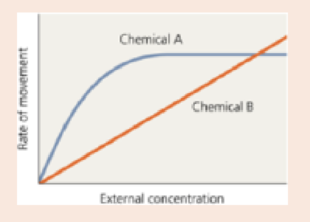
A scientist who is studying passive movement of chemicals across the cytoplasmic membrane of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi measures the rate at which two chemicals diffuse into a cell as a function of external concentration. The results are shown in the following figure. Chemical A diffuses into the cell more rapidly than does B at lower external concentrations, but the rate levels off as the external concentration increases. The rate of diffusion of chemical B continues to increase as the external concentration increases.
- a. How can you explain the differences in the diffusion rates of chemicals A and B?
- b. Why does the diffusion rate of chemical A taper off?
- c. How could the cell increase the diffusion rate of chemical A?
- d. How could the cell increase the diffusion rate of chemical B?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
a. Define diffusion. Is diffusion a passive or an active process? Explain how solute moves in this way.
b. Use your knowledge of diffusion to explain what happened over time when you observed a crystal of methylene blue dropped into a beaker of water. Be sure to use equilibrium in your explanation.
c. Explain your observations over time after a drop of methylene blue and a drop of potassium permanganate were placed in the agar. What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
d. What are tissues? Name the four major types of tissues in the human body.
e. Name the three primary germ layers. Name the primary germ layers from which epithelial tissues and connective tissues develop.
f. List general characteristics that all epithelial tissues have in common.
g. Name the functions of epithelial tissue. Which type of epithelial tissue is found in areas that need protection?
h. Know how to identify simple squamous epithelium, simple cuboidal epithelium, simple columnar…
Bacterial growth depends on many environmental factors, including the temperature of the environment. Since microbes can survive in a certain range of temperatures and will thrive at a temperature, understanding these variables allows for control of their growth. This understanding can be used, for example, to preserve certain foods or to treat infections. This lab simulation will use an instrument called a spectrophotometer. This instrument quantitatively measures the amount of light that is absorbed or transmitted by molecules in solution
a) In your own words give an introduction to the microbial growth and the effect tempature has.
b) In your own words explain the importance of the spectrophotometer in regards to microbial growth.
c) In your own words give a hypothesis on how bacteria will react to different temperatures.
The image below presents the results of an
experiment comparing the effect of Gentamicin and
three concentrations of Acetic acid on Escherichia
coli.
Based on your knowledge about the disk Diffusion
method, and the results of the experiment, what
would be your recommendation on the use of Acetic
acid to control E. coli?
1% acetic acid
5% acetic acid
gentamicin
2% acetic acid
Chapter 3 Solutions
EP MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY..-MOD.ACC
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1TMWCh. 3 - In 1985, an Israeli scientist discovered the...Ch. 3 - Why is a pilus a type of fimbria, but a flagellum...Ch. 3 - Why is the microbe illustrated in Figure 3.2 more...Ch. 3 - The Big Game College sophomore Nadia is a star...Ch. 3 - When the bacterium Escherichia coli is grown in a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6TMWCh. 3 - Why do scientists consider bacterial and archaeal...Ch. 3 - Why did scientists in the 19th and early 20th...Ch. 3 - Why do some scientists consider archaea, which are...
Ch. 3 - Why are eukaryotic glycocalyces covalently bound...Ch. 3 - Many antimicrobial drugs target bacterial cell...Ch. 3 - Colchicine is a drug that inhibits microtubule...Ch. 3 - A cell may allow a large or charged chemical to...Ch. 3 - Which of the following statements concerning...Ch. 3 - A 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules is seen in...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is most associated with...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is not associated with...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is true of Svedbergs? a....Ch. 3 - Which of the following statements is true? a. The...Ch. 3 - Prob. 8MCCh. 3 - Bacterial flagella are ______________. a. anchored...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10MCCh. 3 - A Gram-negative cell is moving uric acid across...Ch. 3 - Gram-positive bacteria _______________. a. have a...Ch. 3 - Endospores ________________. a. are reproductive...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14MCCh. 3 - Dipicolinic acid is an important component of...Ch. 3 - Match the structures on the left with the...Ch. 3 - Match the term on the left with its description on...Ch. 3 - Label the structures of the following prokaryotic...Ch. 3 - Label each type of flagellar arrangement.Ch. 3 - A scientist who is studying passive movement of...Ch. 3 - Describe (or draw) an example of diffusion down a...Ch. 3 - Sketch, name, and describe three flagellar...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3SACh. 3 - The term fluid mosaic has been used in describing...Ch. 3 - A local newspaper writer has contacted you, an...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6SACh. 3 - Compare bacterial cells and algal cells, giving at...Ch. 3 - Contrast a cell of Streptococcus pyogenes (a...Ch. 3 - Differentiate among pili, fimbriae, and cilia,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10SACh. 3 - Prob. 11SACh. 3 - Prob. 12SACh. 3 - What is the function of glycocalyces and fimbriae...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14SACh. 3 - Compare and contrast three types of passive...Ch. 3 - Prob. 16SACh. 3 - Prob. 17SACh. 3 - Prob. 18SACh. 3 - Prob. 1CTCh. 3 - Methylene blue binds to DNA. What structures in a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3CTCh. 3 - Prob. 4CTCh. 3 - A researcher carefully inserts an electrode into...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6CTCh. 3 - An electron micrograph of a newly discovered cell...Ch. 3 - An entry in a recent scientific journal reports...Ch. 3 - Prob. 9CTCh. 3 - Prob. 10CTCh. 3 - Prob. 11CTCh. 3 - Prob. 12CTCh. 3 - Prob. 13CTCh. 3 - Prob. 14CTCh. 3 - Using the following terms, fill in the following...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Bacillis brevis are lysed using a valve-type homogenizer. The extent of disruption depends on the applied pressure and the number of passes through the homogenizer chamber and can be described by the equation, ln(1 − ?) = −????. Is Bacillis brevis a gram-positive or gram-negative bacterial cell? Based on this response, describe the cell wall structure and how it differs from the other type. Develop an equation for calculation of pressure as a function of the number of passes through the homogenizer. What factor(s) did you take into consideration when selecting the number of passes? Escherichia coli cells are lysed with the same homogenization, is this organism gram-positive or gram-negative? What impact does increasing the value of the constant, a, have on the required number of passes at a given pressure? What factors impact the value of a? If fine cell debris after homogenization makes subsequent solid-liquid separation difficult, what would you recommend? Answer as…arrow_forwardWhat are the effects of the different agar concentrations, the temperature, and the dye types on the rate of diffusion? How do these factors mediate in the observed diffusion?arrow_forwarddoes the rate of diffusion correspond with the molecular weight of the dye?arrow_forward
- A) Consider membrane filtration. What is concentration polarization and why does it occur? B) What are the important parameters that affect the diffusivity in/across membranes and what do The they mean physically? C) Consider the Krogh Cylinder model. What is the physical meaning of the critical radiusand why does it occur?arrow_forwardWhy might clinical medicine have an interest in understanding bacterial cell division at the molecular level? Explain why a hyperthermophile would probably not be a human pathogen. Describe four factors that may have an influence on the effectiveness of an antimicrobial treatment. Explain why 70% or 80% alcohol is more effective than 100% alcohol in controlling microorganisms.arrow_forwardIf the generation time of Escherichia coli is 30 minutes, starting with 4 E. coli cells, how many cells can you obtain after 2 hours of growth? A: cellsarrow_forward
- For a lab on diffusion and osmosis, where a egg yolk was placed in a cup water the following question asks Consider a scenario in which the size of an egg yolk remains unchanged after in water soaking for an hour. What are two possible explanations as to why this occurs? What would two reasons be for the yolk to be unchanged after a hour in water?arrow_forwardGram-negative bacteria are surrounded by two membrane bilayers separated by a space termed the periplasm. The periplasm is a multipurpose compartment separate from the cytoplasm. The periplasm has a distinct oxidizing environment that allow certain key protein structural features to be formed. Can you identify an amino acid(s) that would be affected by this oxidizing environment? How would it be affected, and what structural features would be sensitive to this environment? Can you discuss the implications of this from a standpoint of recombinant protein expression?arrow_forwardProteus mirabilis produces the enzyme urease, which converts urea into ammonia. If a patient has a urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by Proteus mirabilis, what signs or symptoms might be observed? Cloudy urine. As the bacteria multiply, the urine becomes progressively cloudier because of the large numbers of cells in suspension. High ammonia content contributes to the strong smell of urine from patients with a UTI. A higher-than-normal urine pH. With large numbers of bacteria producing urease and converting urea into ammonia, the urine pH would be very basic. All of the answers are correct.arrow_forward
- A student designed an experiment to test whether different concentration gradients affect the rate of diffusion through dialysis tubing. Four different solutions (0% NaCl, 1% NaCl, 5% NaCl, and 10% NaCl) were tested under identical conditions. Twenty mL of each solution was placed into separate dialysis tubing that is permeable to Na+, Cl-, and water. Each bag was placed in a separate beaker and covered with distilled water. The concentration of NaCl in the water outside of each bag was measured at 40-second intervals. The graph below shows the results from the 5% bag: Concentration of NaCl Outside of Dialysis Bags Concentration of NaCl (mg/L) 400 320 240 160 80 0 40 80 Time(seconds) 120 5% Solution 160 a. Describe the process of diffusion through the dialysis tubing. b. If you were to design a different experiment testing rates of diffusion, identify experimental procedures. c. Analyze that data in the graph and describe the results. Provide reasoning to justify your answer. d.…arrow_forwardDescribe the cross - section side view of a Gram - negative cell . Clearly state where the following would be located or write the letters in order of appearance from the outside to the inside . If any of these structures are not present , make sure to leave them out . A ) peptidoglycan ; ( B ) periplasm ; ( C ) porin ; ( D ) LPS ; ( E ) teichoic acids ; ( F ) plasma membrane : ( G ) outer membrane : ( H ) nucleoidarrow_forwardIn the diagram below, identify the structures of a cyanobacterial cell based on the following descriptions: a) Outer cellular covering which includes: Mucilaginous layer – outermost layer covering the cell wall; protects the cell from harmful factors of the environment Cell wall – found just below the mucilaginous layer; 2 or 3-layered, the inner layer lies in between the outer wall layer and plasma membrane; the outer layer is made of peptidoglycan Innermost plasma membrane – selectively permeable membrane enclosing the cytoplasm b) Cytoplasm – found below the plasma membrane; the protoplasm which contains structures of different shapes and functions. Lamellae, which contain pigments such as chlorophylls, carotenes, xanthophylls, phycoerythrin and phycocyanin, are located in the peripheral region of cytoplasm. Ribosomes may also be found scattered in the cytoplasm. c) Nucleic material – the nucleoplasm that is centrally located in the cell and contains chromatin in the form…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

The Cell Membrane; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsffT7XIXbA;License: Standard youtube license