
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.73SP
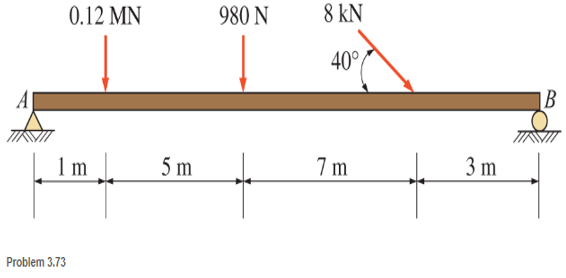
a. Calculate the moments about points A and B due to the nonconcurrent force system shown.
b. Determine the location and direction of the resultant force.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule07:39
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the y-component a force, 100N, acting 45 degrees to the right of the negative y-axis.
Find the x-component the resultant of two forces: A= 100N, acting 30 degrees to left of the negative y-axis, and B=150N, acting 45 degrees below the positive x-axis
Show work clearly
Chapter 3 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 3 - through 3.3 Determine the magnitude, direction,...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Solve Problem 3.1 through 3.3 using the method of...Ch. 3 - Solve Problem 3.1 through 3.3 using the method of...Ch. 3 - through 3.6 Solve Problem 3.1 through 3.3 using...Ch. 3 - The 150-lb force shown is the resultant of two...Ch. 3 - Find the resultant force P exerted on the tree.Ch. 3 - Find the resultant force R exerted on the pole.Ch. 3 - Calculate the resultant force on the screw eye....
Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the coplanar concurrent...Ch. 3 - Use the parallelogram law to find the following...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.13PCh. 3 - Determine the resultant of the coplanar concurrent...Ch. 3 - The resultant of the concurrent force system shown...Ch. 3 - Three force of 900 lb, 1000 lb, and 600 lb are...Ch. 3 - The four forces shown hade parallel lines of...Ch. 3 - Three coplanar concurrent forces act as shown. a....Ch. 3 - Four coplanar concurrent forces act as shown a....Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the four forces of...Ch. 3 - For the concrete wall and footing shown: a....Ch. 3 - Calculate the moment of the 550-lb force about...Ch. 3 - In Problem 3.22 , calculate the moment about point...Ch. 3 - Compute the moment about point A for the linkage...Ch. 3 - Compute the moment of the force F about point A...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant and its location for the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude, sense, and location of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude, sense, and location of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Fresh water is impounded behind a dam to a height...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 3 - A body is subjected to the following three...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the load system shown....Ch. 3 - For the concrete structure shown, determine the...Ch. 3 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 3 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 3 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 3 - 3.49 Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense...Ch. 3 - The resultant and one-component force of a...Ch. 3 - The resultant force of a concurrent force system...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitudes of forces P1 and P2 such...Ch. 3 - The resultant force of a concurrent force system...Ch. 3 - A hockey puck is acted on simultaneously by two...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant force for each of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant force for each of the...Ch. 3 - The resultant of the three concurrent forces shown...Ch. 3 - The transmission tower shown is subjected to a...Ch. 3 - A gravity-type masonry dam, as shown, depends on...Ch. 3 - The transfomer (as shown) must be lifted...Ch. 3 - Refer to the diagram for Problem 3.60 /. Assume...Ch. 3 - The plastic barrel tent anchor of Problem 2.11...Ch. 3 - Calculate the moment of the forces shown with...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the moment (about point A) of the appied...Ch. 3 - The lift force on the wing of an aircraft is...Ch. 3 - A beam is subjected to distributed loads as shown....Ch. 3 - For the concrete gravity wall shown, determine the...Ch. 3 - Fresh water is impounded to a height of 8 ft...Ch. 3 - Plank, 2 in. by 10 in. in cross section and 5 ft...Ch. 3 - a. Compute the moment (about point A) of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the three forces acting...Ch. 3 - a. Calculate the moments about points A and B due...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and F2 shown such...Ch. 3 - Calculate the magnitude, direction, and sense of...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
28. The force on the inside of a cork in a champagne bottle is 10 pound-force [lbf]. If the cylindrical cork ha...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE and state if the members are in tension or compression. Prob. F5-...
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Define a homogeneous material.
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
1.1 What is the difference between an atom and a molecule? A molecule and a crystal?
Manufacturing Engineering & Technology
A particle travels along a straight line with a velocity of v = ( 4t 3t2) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determin...
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
The magnitude of forces F1, F2, and F3 for equilibrium.
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the given loading system, find the equivalent resultant force and couple moment acting at point B. 50 lb/ft 100 lb/ft 50 lb/ft 6 ft 4 ftarrow_forwardPlease solve correctly and cleanarrow_forwardFor the system of forces shown, a. Using the scalar approach, determine the resultant moment about the origin O. Express the answer as a Cartesian vector. Once again, show ALL steps clearly. and show proper figures. b. Next, use the vector approach to obtain resultant moment about the origin O. Express answer as Cartesian vector. Note Further: For each of the scalar and vector, approaches, show clear figures where you mark perpendicular distances and posițion vectors. Solutions with a proper schematic figure : 2 m C FR =7 kN Fp = 5 kN 8. 6 m 2 m 3 m.arrow_forward
- please make it clear and box the answerarrow_forward10 N at 120°, and C = 16 N at 205° Three coplanar forces are given as follows: A = 6 N at 250°, B = Plot the forces in one Argand plane and label properly. Determine the resultant D, where D = A +2(B - C), expressed in both Polar and Cartesian forms.arrow_forwardIn the given problem, the tension in cable BC has a magnitude of 500N. a. Write the tension Tec in cartesian vector form. b. Determine the moment of tension Tec about point A. c. Determine the moment of tension Tec about the axis passing through points and A and D. Hnload 1 m 0.5 m Cile B 2m D 1.5 marrow_forward
- From a single point, five sets of horizontal wires are radiating , viz , the first due north , the 2nd 75o northwest , the third 75 southwest and the fourth 30 southeast . The tension at these 4 sets of wires is 100 N, 60N, 80 N and 120 N, respectively. Find the direction of the fifth wire, its tension and position. Use Varignon’s theorem to find the moment that the force shown in Fig. exerts about point,B.arrow_forwardFind the magnitude and direction of the resultant force if F1 = 100 N at 30 deg N of E and F2 = 80 N at 45 deg N of W.arrow_forwardMoment about a point in 3-D. Force F acts at point C. Determine the momentof force F about point O. Report your answer as a (a) Cartesian vector and (b) in terms of its magnitude and direction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY