
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
Figure 1
Compounds shown in Figure 1 are alcohols that mean acidic proton is bonded to oxygen.
Compound B contains two chlorine atoms which are electron-withdrawing group. Due to
Compound C contains only one chlorine atom which is an electron-withdrawing group Due to
Compound A contains one methyl group which is an electron-donating group. Due to
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
Figure 2
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
Figure 3
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
Figure 4
According to the elemental effect, the acidity increases as the
Compound A contains only chlorine atom which is an electron-withdrawing group. Due to
Compound C contains
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
Figure 5
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
Figure 6
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
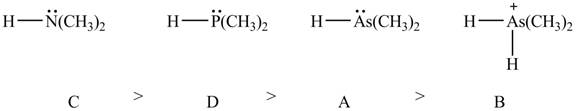
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
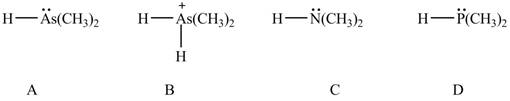
Figure 7
According to the elemental effect, the acidity increases as the atomic number attached to the acidic hydrogen also increases. The element
The atomic number of arsenic is higher than nitrogen and phosphorus. The
The atomic number of phosphorus is higher than nitrogen. The
According to the charge effect, the acidity increases with the presence of positive charge on atom attached to acidic hydrogen. Compound B contains a positive charge. Therefore, compound B is more acidic than compound A.
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
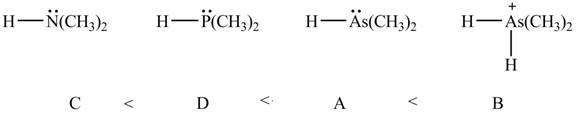
Figure 8
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
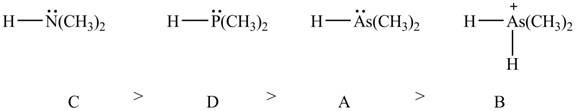
Figure 9
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(d)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
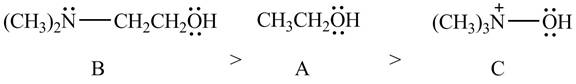
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
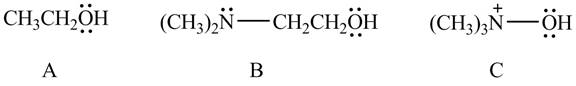
Figure 10
According to the charge effect, the acidity increases with the presence of positive charge on atom attached to acidic hydrogen. Compound C contains a positive charge. Therefore, compound C is more acidic than compound A and B.
Compound B contains only
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
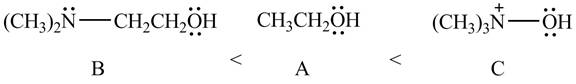
Figure 11
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
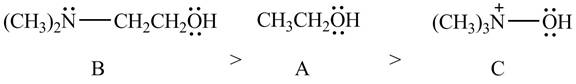
Figure 12
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- At 90ºC the vapor pressure of ortho-xylene is 20 kPa and that of meta-xylene is 18 kPa. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a mixture in which the mole fraction of o-xylene is 0.60?arrow_forwardDraw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forward11. Use the equation below to answer the following questions: 2 Al(s) + 3 Cd(NO3)2 (aq) → 2 Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 Cd(s) a. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction? b. Which species is a spectator ion in this reaction? Define a spectator ion. c. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
