
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the number of
In the Lewis structure, a single bond represents an electron pair in a
Answer to Problem 3.18P
There are sixteen
Explanation of Solution
The line drawing of the given molecule is:
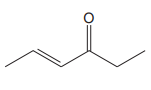
This must be converted to a Lewis structure showing all atoms and lone pairs before the number of bonds of different types and the electrons in nonbonding MOs can be counted.
The Lewis structure of the molecule showing all atoms, bonds and lone pairs can be drawn as:
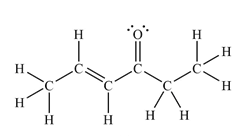
This shows fourteen single bonds, two double bonds, and two lone pairs. Therefore, the molecule contains a total of sixteen
A single bond between two atoms is a
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the number of
In the Lewis structure, a single bond represents an electron pair in a
Answer to Problem 3.18P
There are sixteen
Explanation of Solution
The line drawing of the given molecule is:
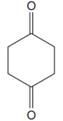
This must be converted to a Lewis structure showing all atoms and lone pairs before the number of bonds of different types and the electrons in nonbonding MOs can be counted.
The Lewis structure of the molecule showing all atoms, bonds and lone pairs can be drawn as:
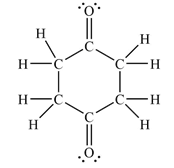
This shows fourteen single bonds, two double bonds, and four lone pairs. Therefore, the molecule contains a total of sixteen
A single bond between two atoms is a
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the number of
In the Lewis structure, a single bond represents an electron pair in a
Answer to Problem 3.18P
There are twelve
Explanation of Solution
The line drawing of the given molecule is:
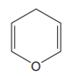
This must be converted to a Lewis structure showing all atoms and lone pairs before the number of bonds of different types and the electrons in nonbonding MOs can be counted.
The Lewis structure of the molecule showing all atoms, bonds and lone pairs can be drawn as:
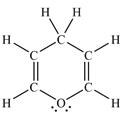
This shows twelve single bonds, two double bonds, and two lone pairs. Therefore, the molecule contains a total of twelve
A single bond between two atoms is a
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the number of
In the Lewis structure, a single bond represents an electron pair in a
Answer to Problem 3.18P
There are nineteen
Explanation of Solution
The line drawing of the given molecule is:
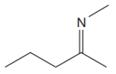
This must be converted to a Lewis structure showing all atoms and lone pairs before the number of bonds of different types and the electrons in nonbonding MOs can be counted.
The Lewis structure of the molecule showing all atoms, bonds and lone pairs can be drawn as:
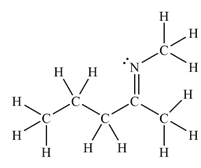
This shows eighteen single bonds, one double bond and one lone pair. Therefore, the molecule contains a total of nineteen
A single bond between two atoms is a
(e)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the number of
In the Lewis structure, a single bond represents an electron pair in a
Answer to Problem 3.18P
There are eleven
Explanation of Solution
The line drawing of the given molecule is:
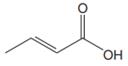
This must be converted to a Lewis structure showing all atoms and lone pairs before the number of bonds of different types and the electrons in nonbonding MOs can be counted.
The Lewis structure of the molecule showing all atoms, bonds and lone pairs can be drawn as:
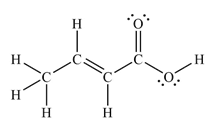
This shows nine single bonds, two double bonds, and four lone pairs. Therefore, the molecule contains a total of eleven
A single bond between two atoms is a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- The 13C NMR signal for which of the indicated carbons will occur at the frequency (most deshielded)? Why is the correct answer E? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation needed to understand the or question.arrow_forwardWhich of the following reagents best achieves the reaction shown below? Why is the correct answer B? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction sequence? Why is the correct answer D? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardThe reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5MgBr) with propanal (CH3CH2CHO)3 followed by hydrolysis yields. A. 2-phenyl-1-propanol B. 1-phenyl-1propanol C. 3-phenyl-2-propanol D. 3-phenyl-1-propanol Why is the correct answer B? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and/or a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction sequence below? Why is the correct answer D? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question. The part that is under the pen in the image is (1) CH3CHO (2) H3O+arrow_forward
- What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ OH HD CH3-CH2-CH-CH3 H A CH3 CH3-CH2-C-O-CH-CH2-CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. ☐ : Jm +arrow_forwardDraw the major product of the following E2 reaction. Make sure you pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Explain why this product is formed using 10 words or less for each. (a) NaH Br acetone TSO, NaH (b) acetonearrow_forward2. Circle the compound that will react SLOWER in an E2 reaction. To get credit for this question, you must EXPLAIN how you got your answer using STRUCTURES and WORDS. Br ** Br...arrow_forward
- 8. 2 20 00 Draw ALL of the possible products for the following reaction CIRCLE the MAJOR product NaOMe MeOHarrow_forwardNAME: 1. Draw the major product of the following E2 reaction. Make sure you pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. To get credit for this question, you must EXPLAIN how you got your answer using STRUCTURES and WORDS. Br NaOCH3 acetone F2 reaction To get credit for thisarrow_forward3. Reactions! Fill in the information missing below. Make sure to pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Br2 CH3OH + 4. Mechanism! Show the complete arrow pushing mechanism, including all steps and intermediates for the following reactions. To get credit for this, you MUST show how ALL bonds are broken and formed, using arrows to show the movement of electrons. H3O+ HOarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

