
Primary Key:
A Primary Key in a
Example:
Students in Universities are assigned a unique registration number.
Therefore, in a STUDENT database table, the attribute “reg_no” acts as primary key.
Foreign Key:
Foreign Key is a column in a relational database table which provides a relation between two tables. It provides a cross reference between tables by pointing to primary key of another table.
Example:
In STUDENT database table, the attribute “reg_no” acts as primary key and in COURSE database table in which the student selects his or her course, the same “reg_no” acts as foreign key for the STUDENT table.
Many to One Relationship:
When more than one record in a database table is associated with only one record in another table, the relationship between the two tables is referred as many to one relationship. It is also represented as M: 1 relationship.
One to Many Relationship:
When one record in a database table is associated with more than one record in another table, the relationship between the two tables is referred as one to many relationship. It is also represented as1: M relationship. This is the opposite of many to one relationship.
One to One Relationship:
When one record in a database table is associated with one record in another table, the relationship between the two tables is referred as one to one relationship. It is also represented as1: 1relationship.
RELATIONAL DIAGRAM:
Relational Diagram is also known as Entity Relational Diagram. It is used to define the conceptual view of the database as viewed by the end user. It is used to depict the database’s main components: entities, relationships and attributes. It describes how data is related to each other.
Explanation of Solution
Given database tables:
Table Name: CHARTER
| CHAR_TRIP | CHAR_DATE | CHAR_PILOT | CHAR_COPILOT | AC_NUMBER | CHAR_DESTINATION | CHAR_DISTANCE | CHAR_HOURS_FLOWN | CHA_HOURS_WAIT | CHAR_FUEL_GALLONS | CHAR_OIL_QTS | CUS_CODE |
| 10001 | 05-Feb-18 | 104 | 2289L | ATL | 936.0 | 5.1 | 2.2 | 354.1 | 1 | 10011 | |
| 10002 | 05-Feb-18 | 101 | 2778V | BNA | 320.0 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 72.6 | 0 | 10016 | |
| 10003 | 05-Feb-18 | 105 | 109 | 4278Y | GNV | 1574.0 | 7.8 | 0.0 | 339.8 | 2 | 10014 |
| 10004 | 06-Feb-18 | 106 | 1484P | STL | 472.0 | 2.9 | 4.9 | 97.2 | 1 | 10019 | |
| 10005 | 06-Feb-18 | 101 | 2289L | ATL | 1023.0 | 5.7 | 3.5 | 397.7 | 2 | 10011 | |
| 10006 | 06-Feb-18 | 109 | 4278Y | STL | 472.0 | 2.6 | 5.2 | 117.1 | 0 | 10017 | |
| 10007 | 06-Feb-18 | 104 | 105 | 2778V | GNV | 1574.0 | 7.9 | 0.0 | 348.4 | 2 | 10012 |
| 10008 | 07-Feb-18 | 106 | 1484P | TYS | 644.0 | 4.1 | 0.0 | 140.6 | 1 | 10014 | |
| 10009 | 07-Feb-18 | 105 | 2289L | GNV | 1574.0 | 6.6 | 23.4 | 459.9 | 0 | 10017 | |
| 10010 | 07-Feb-18 | 109 | 4278Y | ATL | 998.0 | 6.2 | 3.2 | 279.7 | 0 | 10016 | |
| 10011 | 07-Feb-18 | 101 | 104 | 1484P | BNA | 352.0 | 1.9 | 5.3 | 66.4 | 1 | 10012 |
| 10012 | 08-Feb-18 | 101 | 2289L | MOB | 884.0 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 215.1 | 0 | 10010 | |
| 10013 | 08-Feb-18 | 105 | 4278Y | TYS | 644.0 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 174.3 | 1 | 10011 | |
| 10014 | 09-Feb-18 | 106 | 4278V | ATL | 936.0 | 6.1 | 2.1 | 302.6 | 0 | 10017 | |
| 10015 | 09-Feb-18 | 104 | 101 | 2289L | GNV | 1645.0 | 6.7 | 0.0 | 459.5 | 2 | 10016 |
| 10016 | 09-Feb-18 | 109 | 105 | 2778V | MQY | 312.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 67.2 | 0 | 10011 |
| 10017 | 10-Feb-18 | 101 | 1484P | STL | 508.0 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 105.5 | 0 | 10014 | |
| 10018 | 10-Feb-18 | 105 | 104 | 4278Y | TYS | 644.0 | 3.8 | 4.5 | 167.4 | 0 | 10017 |
Table Name: AIRCRAFT
| AC_NUMBER | MODE-CODE | AC_TTAF | AC_TTEL | AC_TTER |
| 1484P | PA23-250 | 1833.1 | 1833.1 | 101.8 |
| 2289L | C-90A | 4243.8 | 768.9 | 1123.4 |
| 2778V | PA31-350 | 7992.9 | 1513.1 | 789.5 |
| 4278Y | PA31-350 | 2147.3 | 622.1 | 243.2 |
Table Name: MODEL
| MOD_CODE | MOD_MANUFACTER | MOD_NAME | MOD_SEATS | MOD_CHG_MILE |
| B200 | Beechcraft | Super KingAir | 10 | 1.93 |
| C-90A | Beechcraft | KingAir | 8 | 2.67 |
| PA23-250 | Piper | Aztec | 6 | 1.93 |
| PA31-350 | Piper | Navajao Chiettan | 10 | 2.35 |
Table Name: PILOT
| EMP_NUM | PIL_LICENSE | PIL_RATINGS | PIL_MED_TYPE | PIL_MED_DATE | PIL_PTI35_DATE |
| 101 | ATP | ATP/SEL/MEL/Instr/CFII | 1 | 20-Jan-18 | 11-Jan-18 |
| 104 | ATP | ATP/SEL/MEL/Instr | 1 | 18-Dec-17 | 17-Jan-18 |
| 105 | COM | COMM/SEL/MEL/Instr/CFI | 2 | 05-Jan-18 | 02-Jan-18 |
| 106 | COM | COMM/SEL/MEL/Instr | 2 | 10-Dec-17 | 02-Feb-18 |
| 109 | COM | ATP/SEL/MEL/SES/Instr/CFII | 1 | 22-Jan-18 | 15-Jan-18 |
Table Name: EMPLOYEE
| EMP_NUM | EMP_TITLE | EMP-LNAME | EMP_FNAME | EMP_INITIAL | EMP_CODE | EMP_HIRE_DATE |
| 100 | Mr. | Kolrnycz | George | D | 15-Jun-62 | 15-Mar-08 |
| 101 | Ms. | Lewis | Rhonda | G | 19-Mar-85 | 25-Apr-06 |
| 102 | Mr. | Vandam | Rhett | 14-Nov-78 | 18-May-13 | |
| 103 | Ms. | Jones | Anne | M | 11-May-94 | 26-Jul-17 |
| 104 | Mr. | Lange | John | P | 12-Jul-91 | 20-Aug-10 |
| 105 | Mr. | Williams | Robert | D | 14-Mar-95 | 19-Jun-17 |
| 106 | Mrs. | Duzak | Jeanine | K | 12-Feb-88 | 13-Mar-18 |
| 107 | Mr. | Deante | George | D | 01-May-95 | 02-Jul-16 |
| 108 | Mr. | Wiesanbach | Paul | R | 14-Feb-86 | 03-Jun-13 |
| 109 | Ms. | Travis | Elizabeth | K | 18-Jun-81 | 14-Feb-16 |
| 110 | Mrs. | Genkazi | Lieghla | W | 19-May-90 | 29-Jun-10 |
Table Name: EMPLOYEE
| CUS_CODE | CUS_LNAME | CUS_FNAME | CUS_INITIAL | CUS_AREACODE | CUS_PHONE | CUS_BALANCE |
| 10010 | Ramas | Alfred | A | 615 | 844-2573 | 0.00 |
| 10011 | Dunne | Leona | K | 713 | 894-1293 | 0.00 |
| 10012 | Smith | Kathy | W | 615 | 894-2285 | 896.54 |
| 10013 | Owolski | Paul | F | 615 | 894-2180 | 1285.19 |
| 10014 | Orlando | Myron | 615 | 222-1672 | 673.21 | |
| 10015 | OBrian | Amy | B | 713 | 442-3381 | 1014.86 |
| 10016 | Brown | James | G | 615 | 297-1228 | 0.00 |
| 10017 | Williams | George | 615 | 290-2556 | 0.00 | |
| 10018 | Fariss | Anne | G | 713 | 382-7185 | 0.00 |
| 10019 | Smith | Olette | K | 615 | 297-3809 | 453.98 |
PRIMARY KEY in the above tables:
For Table Name: CHARTER:
Primary Key: CHAR_TRIP
“CHAR_TRIP” acts as primary key of the table because the attribute “CHAR_TRIP” is a unique ID that is assigned to every individual trip by the charter plane. It also uniquely identifies every other row present in the database table.
For Table Name: AIRCRAFT:
Primary Key: AC_NUMBER
“AC_NUMBER” acts as primary key of the table because the attribute “AC_NUMBER” is a unique number that is assigned to every individual charter plane and is used to distinguish among them. It also uniquely identifies every other row present in the database table.
For Table Name: MODEL:
Primary Key: MOD_CODE
“MOD_CODE” acts as primary key of the table because the attribute “MOC_CODE” is a unique number that is assigned to every individual model of the charter plane and is used to distinguish models among them. It also uniquely identifies every other row present in the database table.
For Table Name: PILOT:
Primary Key: EMP_NUM
“EMP_NUM” acts as primary key of the table because the attribute “EMP_NUM” is a unique number that is assigned to every pilot that flies an aircraft. It also uniquely identifies every other row present in the database table.
For Table Name: EMPLOYEE:
Primary Key: EMP_NUM
“EMP_NUM” acts as primary key of the table because the attribute “EMP_NUM” is a unique number or ID that is assigned to every employee that works in the airline. It also uniquely identifies every other row present in the database table.
For Table Name: CUSTOMER:
Primary Key: CUS_CODE
“CUS_CODE” acts as primary key of the table because the attribute “CUS_CODE” is a unique code that is assigned to every customer that books a flight with the airline. It also uniquely identifies every other row present in the database table.
FOREIGN KEY in the above tables:
For Table Name: CHARTER:
Primary Key: CHAR_PILOT,CHAR_COPILOT,AC_NUMBER,CUS_CODE
“CHAR_PILOT” acts as foreign key of the table because the attribute “CHAR_PILOT” is also present in the table PILOT and it references PILOT and hence it forms a link between the two tables.
“CHAR_COPILOT” acts as foreign key of the table because the attribute “CHAR_COPILOT” is also present in the table PILOT and it references PILOT and hence it forms a link between the two tables.
“AC_NUMBER” acts as foreign key of the table because the attribute “AC_NUMBER” is also present in the table AIRCRAFT and it references AIRCRAFT and hence it forms a link between the two tables.
“CUS_CODE” acts as foreign key of the table because the attribute “CUS_CODE” is also present in the table CUSTOMER and it references CUSTOMER and hence it forms a link between the two tables.
For Table Name: AIRCRAFT:
Foreign Key: MOD_CODE
“MOD_CODE” acts as foreign key of the table because the attribute “MOD_CODE” is also present in the table MODEL and it references MODEL and hence it forms a link between the two tables.
“For Table Name: MODEL:
Foreign Key: None
There is no Foreign Key attribute present in the table because there is no attribute in the table except the primary key which is present in any other database table.
For Table Name: PILOT:
Primary Key: EMP_NUM
“EMP_NUM” acts as foreign key of the table because the attribute “EMP_NUM” is also present in the table EMPLOYEE and it references EMPLOYEE and hence it forms a link between the two tables.
For Table Name: EMPLOYEE:
Foreign Key: None
There is no Foreign Key attribute present in the table because there is no attribute in the table except the primary key which is present in any other database table.
For Table Name: CUSTOMER:
Foreign Key: None
There is no Foreign Key attribute present in the table because there is no attribute in the table except the primary key which is present in any other database table.
Relationship among the tables:
A CUSTOMER requests many CHARTER trips and more than one CHARTER trip can be requested by a single customer. Hence, the relationship between CUSTOMER and CHARTER is one to many or 1: M.
An AIRCRAFT can fly many CHARTER trips but that each CHARTER trip is flown by one AIRCRAFT. Hence, the relationship between AIRCRAFT and CHARTER is one to many or 1: M.
Each AIRCRAFT references a single MODEL but a MODEL references many AIRCRAFT. Hence, the relationship between AIRCRAFT and MODEL is many to one or M: 1.
Many CHARTER trips are flown by a single PILOT and with a single COPILOT but a PILOT can fly only one charter trip at a time. Hence, the relationship between CHARTER and PILOT is many to one or M: 1.
All PILOTS are EMPLOYEES, but not all EMPLOYEES are PILOTS – some are
There is an optional (default) 1:1 relationship between EMPLOYEE and PILOT. It can be represented that EMPLOYEE is the “parent” of PILOT.
Relational Diagram to represent relationship between CHARTER, MODEL, AIRCRAFT, PILOT, EMPLOYEE and CUSTOMER:
The Relational Diagram to represent relationship between CHARTER, MODEL, AIRCRAFT, PILOT, EMPLOYEE and CUSTOMER is shown below:
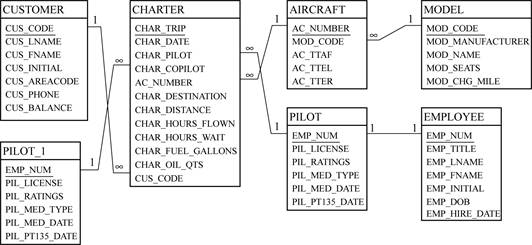
The above relational diagram represents the one to many relationship between CUSTOMER represented as “1” and CHARTER represented as “∞”, one to many relationship between AIRCRAFT represented as “1” and CHARTER represented as “∞” , many to one relationship between AIRCRAFT represented as “∞” and MODEL represented as “1” , many to one relation between CHARTER represented as “∞” and PILOT represented as “1” and an optional one to one relationship between PILOT represented as “1” and EMPLOYEE represented as “1”. A new entity PILOT_1 table is created to split the PILOT table and represent the many to one relationship between CHARTER represented as “∞” and PILOT_1 represented as “1”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Management
 Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr




