To review:
The differences between the properties of water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), and methane (CH4), based on the hydrogen bonding in their structure. The heat of fusion for water, ammonia, and methane is given as 6.01, 5.66, and 0.94 kJ/mol, respectively. Also, determine increase or decrease in the density of ammonia in the form of ice (if generated), as compared to liquid ammonia.
Introduction:
The molecular mass of water, ammonia, and methane is almost equal, and all of them show tetrahedral geometry. The heat of fusion is the highest in water, decreases in ammonia, and is the least in methane. Water has a highly polar structure. The three molecules (water, ammonia, and methane) are sp3 hybridized and are tetrahedral instructure. However, there is a difference in the number of lone pairs in them, leading to an overall different geometry and different physical properties.
Explanation of Solution
Water has two hydrogen atom, shich are covalently bonded to one oxygen atom. The oxygen is sp3 hybridized. Due to the presence of twolone pairs, this molecule has a bent geometry. As a whole, a water molecule is polar and acts as a dipole. The electronegativity of oxygen is more than that of hydrogen, and thus, it bears a partial negative charge, whereas two hydrogen atoms beara partial positive charge. The hydrogen atoms in asingle water molecule are electrondeficient, and thus, tend to be attracted toward the oxygen atom of another water molecule. Thus, hydrogen bonds (intermolecular)act as bridges between neighboringwater molecules. One water molecule can form hydrogen bonds with four otherwater molecules.
The structures of thethreemolecules can be represented as
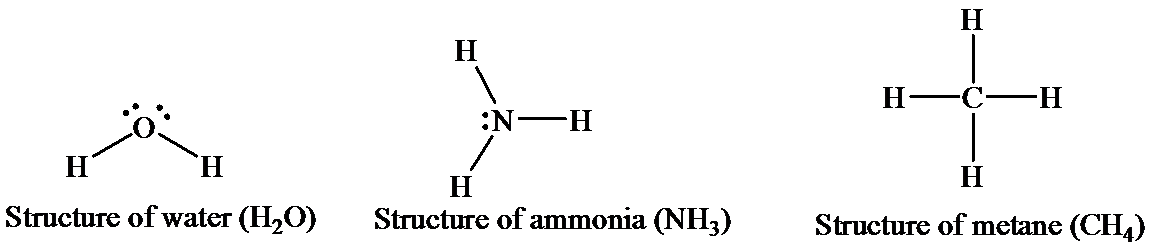
An ammoniamoleculehasonelone pair (unshared electron) ofa nitrogenatom and has a trigonal pyramidal structure. There is limited hydrogen bonding (intramolecular)in case of ammoniaasnitrogen has onlyone lone pair available.
Methane exists in a gaseous statethat has one carbon atom bonded with four hydrogen atoms. The central atom, that is, carbon, forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by the sharing of electrons. This sharing completes the outer shell of both the carbon and the hydrogen atoms. The four hydrogen atoms give an overall tetrahedral shape to the molecule. No hydrogen bonds are involved in methane as there is no highly electronegative element to form a bond with hydrogen.
A hydrogen bondhaslower bond strength thana covalent bond, thus, it is weaker. However, when a largenumber of intermolecular bonds are formed, they are quite strong. This explains the differences in the heat of fusion (energy required to melt ice by breaking bonds) for water, ammonia, and methane. Due to a highernumber of hydrogen bonds, physical propertie, such asmelting point, boiling point, heat capacity, the heat of fusion, surface tensio, nnd heat of vaporization, have higher values in wate, rs compared to that of methane and ammonia.
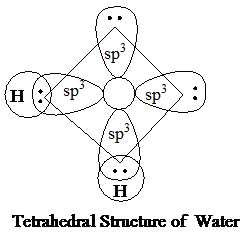


In ammonia, the density of the solid state (ice), if generated, is expected to be more than that of liquid ammonia. This is because the hydrogen bonding between different ammonia molecules will not be as extensive as in case of water insolid state (open cage structure in ice). This is due to limited hydrogen bonding of nitrogen. Thus, as a general case, the solid form of ammonia will beless denser than its liquid form.
Thus, it can be concluded that water, ammonia, and methane molecules are tetrahedral in structure, but differ in their overall geometry and physical properties due to thenumber of lone pairs in them and hydrogen bonding. The heat of fusion is the highest for water moleculesbecauseofstrong intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Also, ammonia ice will not form a cage-like structure (as in water), and thus, its density is expected to be lesser than that of liquid ammonia.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biochemistry, The Molecular Basis of Life, 6th Edition
- H2C CH2 HC-COOO CH2 ܘHO-C-13c-O isocitrate C-S-COA H213c CH2 C-OO 13C-S-COA CH2 C-00 the label will not be present in succinyl CoA C-S-COA succinyl-CoAarrow_forwardA culture of kidneys cells contains all intermediates of the citric acid cycle. It is treated with an irreversible inhibitor of malate dehydrogenase, and then infused withglucose. Fill in the following list to account for the number of energy molecules that are formed from that one molecule of glucose in this situation. (NTP = nucleotidetriphosphate, e.g., ATP or GTP)Net number of NTP:Net number of NADH:Net number of FADH2:arrow_forward16. Which one of the compounds below is the final product of the reaction sequence shown here? OH A B NaOH Zn/Hg aldol condensation heat aq. HCI acetone C 0 D Earrow_forward
- 2. Which one of the following alkenes undergoes the least exothermic hydrogenation upon treatment with H₂/Pd? A B C D Earrow_forward6. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? A) (Z)-3,5,6-trimethyl-3,5-heptadiene B) (E)-2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-heptadiene C) (E)-5-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene D) (Z)-5-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene E) (Z)-2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-heptadienearrow_forwardConsider the reaction shown. CH2OH Ex. CH2 -OH CH2- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate The standard free-energy change (AG) for this reaction is 7.53 kJ mol-¹. Calculate the free-energy change (AG) for this reaction at 298 K when [dihydroxyacetone phosphate] = 0.100 M and [glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate] = 0.00300 M. AG= kJ mol-1arrow_forward
- If the pH of gastric juice is 1.6, what is the amount of energy (AG) required for the transport of hydrogen ions from a cell (internal pH of 7.4) into the stomach lumen? Assume that the membrane potential across this membrane is -70.0 mV and the temperature is 37 °C. AG= kJ mol-1arrow_forwardConsider the fatty acid structure shown. Which of the designations are accurate for this fatty acid? 17:2 (48.11) 18:2(A9.12) cis, cis-A8, A¹¹-octadecadienoate w-6 fatty acid 18:2(A6,9)arrow_forwardClassify the monosaccharides. H-C-OH H. H-C-OH H-C-OH CH₂OH H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH CH₂OH CH₂OH CH₂OH CH₂OH D-erythrose D-ribose D-glyceraldehyde Dihydroxyacetone CH₂OH CH₂OH C=O Answer Bank CH₂OH C=0 HO C-H C=O H-C-OH H-C-OH pentose hexose tetrose H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH aldose triose ketose CH₂OH CH₂OH CH₂OH D-erythrulose D-ribulose D-fructosearrow_forward
- Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrophobic tails. Draw the line-bond structure of cis-A9-hexadecenoate. Clearly show the cis-trans stereochemistry.arrow_forwardThe formation of acetyl-CoA from acetate is an ATP-driven reaction: Acetate + ATP + COA Acetyl CoA+AMP+ PP Calculate AG for this reaction given that the AG for the hydrolysis of acetyl CoA to acetate and CoA is -31.4 kJ mol-1 (-7.5 kcal mol-¹) and that the AG for hydrolysis of ATP to AMP and PP; is -45.6 kJ mol-1 (-10.9 kcal mol-¹). AG reaction kJ mol-1 The PP, formed in the preceding reaction is rapidly hydrolyzed in vivo because of the ubiquity of inorganic pyrophosphatase. The AG for the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate (PP.) is -19.2 KJ mol-¹ (-4.665 kcal mol-¹). Calculate the AG° for the overall reaction, including pyrophosphate hydrolysis. AGO reaction with PP, hydrolysis = What effect does the presence of pyrophosphatase have on the formation of acetyl CoA? It does not affect the overall reaction. It makes the overall reaction even more endergonic. It brings the overall reaction closer to equilibrium. It makes the overall reaction even more exergonic. kJ mol-1arrow_forwardConsider the Haworth projections of ẞ-L-galactose and ẞ-L-glucose shown here. OH CH₂OH OH CH₂OH OH OH OH ОН OH он B-L-galactose B-L-glucose Which terms describe the relationship between these two sugars? epimers enantiomers anomers diastereomersarrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





