
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305389892
Author: Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 11TYK
Discuss Concepts Identify the following structures as a carbohydrate, fatty acid, amino acid, or polypeptide:
a.
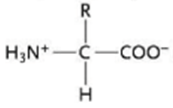 (The R indicates an organic group.)
(The R indicates an organic group.)
b.
c. (glycine)20
d.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(This is a 2-part work, Part 1 is done, only Part 2 is to be worked on at the bottom)Part 1 (Done): Describe the levels of structural hierarchy for the human body, starting with the organismal level and ending with the chemical level. In addition, you should make sure you link each level to the previous level, emphasizing the structural relationships.
The human body is organized into a structural hierarchy that progresses from the macroscopic organismal level down to the microscopic chemical level. Each level builds upon the previous one, creating increasingly complex structures. Below is the hierarchy, from largest to smallest, with explanations linking each level to its predecessor:
1. Organismal Level
The entire living human body.Relationship: All lower levels work together to sustain life at this highest level.
2. Organ System Level
Groups of organs working together to perform major functions.Examples: circulatory, nervous, digestive systems.Relationship: The organismal…
Describe the levels of structural hierarchy for the human body, starting with the organismal level and ending with the chemical level. In addition, you should make sure you link each level to the previous level, emphasizing the structural relationships.
9
S
es
Read the section "Investigating Life: In (Extremely) Cold Blood." Then, drag and drop the terms on the left to complete the concept
map.
Red blood cells
Genes
Icefishes
-have mutated
have colorless
Oxygen
have few
lack
encode
Blood
Cellular
respiration
consists of-
contain
carries
is a
Platelets
White blood
cells
carries
low
amounts
of
Hemoglobin
is necessary for
Plasma
Protein
Reset.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 3.1 - What is the difference between hydrocarbons and...Ch. 3.1 - What is the maximum number of bonds that a carbon...Ch. 3.1 - Do carboxyl groups, amino groups, and phosphate...Ch. 3.1 - What is the difference between a dehydration...Ch. 3.2 - What is the difference between a monosaccharide, a...Ch. 3.3 - What are the three most common lipids in living...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 1SBCh. 3.4 - What is a peptide bond, and what type of reaction...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 3SBCh. 3.5 - What is the monomer of a nucleic acid...
Ch. 3.5 - What are the chemical differences between DNA and...Ch. 3 - Which functional group has a double bond and forms...Ch. 3 - Which of the following characteristics is not...Ch. 3 - Cellulose is to carbohydrate as: a. amino acid is...Ch. 3 - Maltose, sucrose, and lactose differ from one...Ch. 3 - Lipids that are liquid at room temperature: a. are...Ch. 3 - Which of the following statements about steroids...Ch. 3 - The term secondary structure refers to a proteins:...Ch. 3 - The first and major effect in denaturation of...Ch. 3 - In living systems: a. proteins rarely combine with...Ch. 3 - RNA differs from DNA because: a. RNA may contain...Ch. 3 - Discuss Concepts Identify the following structures...Ch. 3 - Discuss Concepts Lipoproteins are relatively...Ch. 3 - Prob. 13TYKCh. 3 - Prob. 14TYKCh. 3 - Prob. 15TYKCh. 3 - Prob. 1ITDCh. 3 - Prob. 2ITDCh. 3 - Prob. 3ITD
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Plating 50 microliters of a sample diluted by a factor of 10-6 produced 91 colonies. What was the originalcell density (CFU/ml) in the sample?arrow_forwardEvery tutor here has got this wrong, don't copy off them.arrow_forwardSuppose that the population from question #1 (data is in table below) is experiencing inbreeding depression (F=.25) (and no longer experiencing natural selection). Calculate the new expected genotype frequencies (f) in this population after one round of inbreeding. Please round to 3 decimal places. Genotype Adh Adh Number of Flies 595 Adh Adh 310 Adhs Adhs 95 Total 1000 fladh Adh- flAdn Adh fAdhs Adharrow_forward
- Which of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why. A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problemsarrow_forwardThis question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardThey got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.arrow_forward
- This question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forwardDon't copy off the other answer if there is anyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College


Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Macromolecules | Classes and Functions; Author: 2 Minute Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5hhrDFo8Vk;License: Standard youtube license