
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The given skeletal structure of amoxicillin needs to be completed.
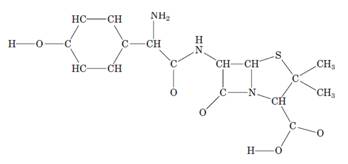
Concept Introduction: Single bond has all sigma bonds; double bond has 1 sigma and 1 pi bond and triple bond has 2 sigma and 1 pi bond. The lone pair of electrons are those electrons which do not take part in bonding. Generally, carbon has zero lone pair, oxygen has 2 lone pairs, sulfur has 2 lone pairs and nitrogen has 1 lone pair of electrons.
(b)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each central atom in the given structure needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Hybridization is defined as mixing of orbital. The geometry of a central atom depends on its hybridization. The shape will be different from geometry if there are lone pair of electrons present on the central atom.
(c)
Interpretation:The bond angles associated with each central atom needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: The bond angles of central atom can be determined from its hybridization and geometry.
(d)
Interpretation:The most polar bond in amoxicillin needs to be detremined.
Concept Introduction: A bond is said to be polar if there is electronegativity difference between the atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:The amoxicilllin needs to be classified as a polar or non-polar molecule.
Concept Introduction: If there are polar bonds present in a molecule then it is considered as a polar molecule.
(f)
Interpretation:Whether amoxicillin expected to possess resonance or not needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Resonance is possessed by a molecule if there is possibility of delocalization of electrons. This can be positive if there is intercation between alternate lone pairs and pi bonds present in a molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- If we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forward
- Give the organic product: O A O B Ос ○ D -NH–CH3 + CH3 CH3 NEN C ? A CH3 CH3 NH- CH3 B CH3 CH3 N=N- C CH3 CH3 N=NNH CH3 D CH3 N=N CH3 NHCH3 LNH CHOarrow_forwardFinish the reaction- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic products: (benzyne) Br ? CH3 + K* :NH, liq NH3 HINT: Two products are formed. Each is a substituted aniline; they are isomers of each other. NH2 II I H₂N. CH3 CH3 III Select one: ○ A. I and II ○ B. I and III O C. I and IV O D. II and III O E. III and IV H₂N CH3 IV CH₂-NH2arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Erase something Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terarrow_forwardQ14. Fill this chart: (please refer to ppt notes/browser to answer these questions) What alcohol is also called wood alcohol? What is the common name of ethanol? Draw the structure of phenol and thiophene? Are bigger chain alcohol like heptanol and octanol are soluble or insoluble in water and explain it ? Are ethers soluble or insoluble in water? What suffix and prefix are used for alcohol while naming alcohol and ether? What the process called when we add water to any alkene to make alcohol? Q16. Draw the diagram of following aromatic compound (practice from previous module) Aniline Phenol Benzoic acid Methyl benzoate Q17. a. Write the oxidation reactions for the 2 propanol. b. Write the oxidation reaction of the ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 11 of 18 (1 point) Question Attempt: 3 of How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box…arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning


