
Concept explainers
Would you expect to find a magnetic field between the capacitor plates in Fig. 29.2? Explain.
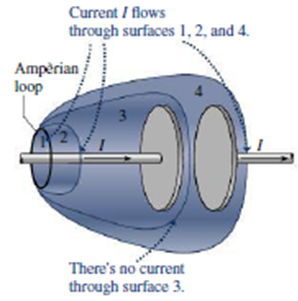
FIGURE 29.2 Four surfaces bounded by the same circular Ampèrian loop. Surface 1 is a flat, circular disk. The others are like soap bubbles in the process of being blown; they’re open at the left end, so if current does pass through a surface, it does so at the right end only.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 29 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





