(a)
Interpretation:
The main product of the mononitration of benzoic acid should be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic
Where,
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring.
The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta direction groups are deactivating groups.
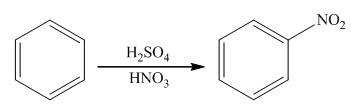
The nitration reaction takes place in the presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. In this reaction, the protonation of nitric acid occurs in order to produce the nitronium ion. The nitronium ion will attach on the benzene ring to form nitrobenzene. The general reaction is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The main product of the monosulphonation of phenol should be predicted.
Concept introduction:
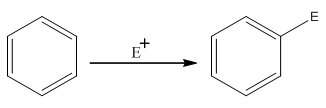
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of benzene. A general electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of benzene can be written as:
Where,
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring.
The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta direction groups are deactivating groups.
The sulfonation takes place in the presence of sulphuric acid. In this reaction, sulfur trioxide is formed that acts as an electrophile. Sulfur trioxide will attach on the benzene ring to form the final product. The general reaction is as follows:
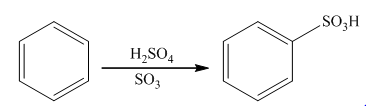
(c)
Interpretation:
The main product of the monobromination of
Concept introduction:
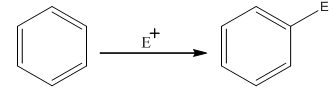
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of benzene. A general electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of benzene can be written as:
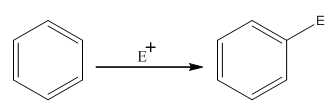
Where,
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring.
The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta direction groups are deactivating groups.
Halogenation is the
The bromination takes place in the presence of Lewis acid and bromine molecule. In this reaction, the bromonium ion is produced that acts as an electrophile. Brominium will attach on the benzene ring to form the final product. The general reaction is as follows:
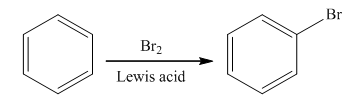
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles And Modern Applications Plus Mastering Chemistry With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- Calculate the reaction quotient for the reaction:NaOH (s) ⇌ Na+ (aq)+ OH- (aq) + 44.4 kJ [Na+] = 4.22 M [OH-] = 6.41 Marrow_forwardGiven the following concentrations for a system, calculate the value for the reaction quotient: Cl2(g)+ CS2(g) ⇌ CCl4(g)+ S2Cl2(g) Cl2 = 31.1 atm CS2 = 91.2 atm CCl4 = 2.12 atm S2Cl2 = 10.4 atmarrow_forwardMatch each chemical or item with the proper disposal or cleanup mwthod, Not all disposal and cleanup methods will be labeled. Metal sheets C, calcium, choroide solutions part A, damp metal pieces Part B, volumetric flask part A. a.Return to correct lables”drying out breaker. Place used items in the drawer.: Rinse with deionized water, dry as best you can, return to instructor. Return used material to the instructor.: Pour down the sink with planty of running water.: f.Pour into aqueous waste container. g.Places used items in garbage.arrow_forward
- Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + NO2-(aq)arrow_forwardWrite the reaction quotient for: Pb2+(aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) ⇌ PbCl2(s)arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium constant expression for the following system at equilibrium: I2 (g) ⇌ 2 I (g)arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

