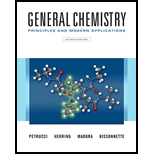
(a)
Interpretation:
The main products of mononitration of chlorobenzene should be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of the
The nitration takes place in the presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. In this reaction, the protonation of nitric acid occurs in order to produce the nitronium ion.
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring. The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta directing groups are deactivating groups.
The different positions with respect to group
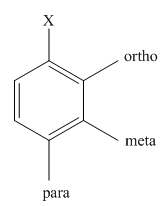
(b)
Interpretation:
The main products of monosulfonation of nitrobenzene should be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of the aromatic compound. Sulphonation is an example of such a reaction.
The sulfonation takes place in the presence of sulphuric acid. In this reaction, sulfur trioxide is formed that acts as an electrophile.
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring. The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta directing groups are deactivating groups.
The different positions with respect to group
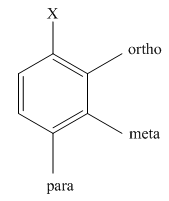
(c)
Interpretation:
The main products of monochlorination of
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of the aromatic compound. Chlorination is an example of such a reaction.
The chlorination takes place in the presence of aluminium chloride. In this reaction, the chloronium ion is produced that acts as an electrophile.
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring. The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta directing groups are deactivating groups.
The different positions with respect to group
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles And Modern Applications Plus Mastering Chemistry With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- Fill-in-the molecules for the oxidation or reduction of the starting alcohol.arrow_forwardName the following carbohydrates give both the systematic and common names. Don't forget to identify the Isomer.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction of XeF4 with H2O? Group of answer choices H2XeF2 H2XeF4 XeO3 H2XeOarrow_forward
- While noble gas exerts the strongest London (dispersion) forces on neighboring atoms? Group of answer choices Xe Ar Kr Nearrow_forwardWhich of the following elements is corrosive to your skin due to that element breaking down C=C bonds? Group of answer choices fluorine iodine bromine chlorinearrow_forwardWhat the best source of sulfide to use on a small scale in the lab? Group of answer choices thiourea H2S NaHS Na2Sarrow_forward
- Which of the following statements about sulfur is FALSE? Group of answer choices H2S is the product of an oxygen-depleted ecosystem. In the acid mine drainage reaction, FeS2 is a product. One allotrope of sulfur has the formula S20. In the environment, bacterial oxidation can convert S2− to elemental S or SO42−.arrow_forwardOf the following choices, which is the best reason that most materials DON'T spontaneously combust even though our atmosphere is about 21% oxygen? Group of answer choices The reduction of O2 in the gas phase (O2 + e− → O2−) is spontaneous. The reduction of O2 in acid solution (O2 + H+ + e− → HO2(aq)) is spontaneous. O2 is not a reactant in combustion. The O2 bond dissociation energy is 494 kJ/mol, leading to a high activation energy for combustion.arrow_forwardplease answer in the scope of the SCH4U course, I am having a hard time understanding, may you show all steps please and thank you! can you also put the final answers in the table so its understandablearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





