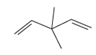
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of carbon atom, total C-C σ bonds and π bonds with 1â—¦,2â—¦,3â—¦ and 4â—¦ carbon atoms should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form same energy and same shape hybrid orbitals which form covalent bond with overlapping of atomic orbitals of other atoms. The number of
1â—¦ orPrimary C atom = C atom which is bonded with one another C atom
2â—¦ orSecondary C atom= C atom which is bonded with two other C atoms
3â—¦ orTertiary C atom= C atom which is bonded with three other C atoms
4â—¦ or Quaternary C atom= C atom which is bonded with four other C atoms
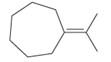
(b)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of carbon atom, total C-C σ bonds and π bonds with 1â—¦, 2â—¦,3â—¦ and 4â—¦ carbon atoms should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form same energy and same shape hybrid orbitals which form covalent bond with overlapping of atomic orbitals of other atoms. The number of chemical bonds formed by the atom always determine type of hybridization. Sigma bonds could only form by hybrid orbitals whereas pi bonds are always formed by overlapping of un-hybrid orbitals hence hybridization is not part of pi bond formation.
1â—¦ or Primary C atom = C atom which is bonded with one another C atom
2â—¦ or Secondary C atom= C atom which is bonded with two other C atoms
3â—¦ or Tertiary C atom= C atom which is bonded with three other C atoms
4â—¦ or Quaternary C atom= C atom which is bonded with four other C atoms
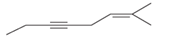
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of carbon atom, total C-C σ bonds and π bonds with 1â—¦, 2â—¦,3â—¦ and 4â—¦ carbon atoms should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form same energy and same shape hybrid orbitals which form covalent bond with overlapping of atomic orbitals of other atoms. The number of chemical bonds formed by the atom always determine type of hybridization. Sigma bonds could only form by hybrid orbitals whereas pi bonds are always formed by overlapping of un-hybrid orbitals hence hybridization is not part of pi bond formation.
1â—¦ or Primary C atom = C atom which is bonded with one another C atom
2â—¦ or Secondary C atom= C atom which is bonded with two other C atoms
3â—¦ or Tertiary C atom= C atom which is bonded with three other C atoms
4â—¦ or Quaternary C atom= C atom which is bonded with four other C atoms
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles And Modern Applications Plus Mastering Chemistry With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- Calculate the reaction quotient for the reaction:NaOH (s) ⇌ Na+ (aq)+ OH- (aq) + 44.4 kJ [Na+] = 4.22 M [OH-] = 6.41 Marrow_forwardGiven the following concentrations for a system, calculate the value for the reaction quotient: Cl2(g)+ CS2(g) ⇌ CCl4(g)+ S2Cl2(g) Cl2 = 31.1 atm CS2 = 91.2 atm CCl4 = 2.12 atm S2Cl2 = 10.4 atmarrow_forwardMatch each chemical or item with the proper disposal or cleanup mwthod, Not all disposal and cleanup methods will be labeled. Metal sheets C, calcium, choroide solutions part A, damp metal pieces Part B, volumetric flask part A. a.Return to correct lables”drying out breaker. Place used items in the drawer.: Rinse with deionized water, dry as best you can, return to instructor. Return used material to the instructor.: Pour down the sink with planty of running water.: f.Pour into aqueous waste container. g.Places used items in garbage.arrow_forward
- Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + NO2-(aq)arrow_forwardWrite the reaction quotient for: Pb2+(aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) ⇌ PbCl2(s)arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium constant expression for the following system at equilibrium: I2 (g) ⇌ 2 I (g)arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





