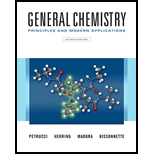
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the following pair of structures is identical molecules, enantiomers or isomers of some other sort:
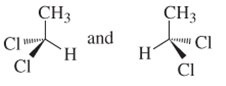
Concept introduction:
Structural or constitutional isomers can be defined as the molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formula. They are molecules in which the bonded atoms have different bonding with each other although the number of molecules is same. Identical molecules are molecules which have same structural formula and same molecular formula.
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are named as R and S configuration. For naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer, the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule is followed.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the following pair of structures is identical molecules, enantiomers or isomers of some other sort:
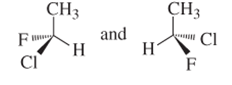
Concept introduction:
Structural or constitutional isomers can be defined as the molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formula. They are molecules in which the bonded atoms have different bonding with each other although the number of molecules is same. Identical molecules are molecules which have same structural formula and same molecular formula.
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are named as R and S configuration. For naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer, the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule is followed.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the following pair of structures is identical molecules, enantiomers or isomers of some other sort:
Concept introduction:
Structural or constitutional isomers can be defined as the molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formula. They are molecules in which the bonded atoms have different bonding with each other although the number of molecules is same. Identical molecules are molecules which have same structural formula and same molecular formula.
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are named as R and S configuration. For naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer, the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule is followed.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the following pair of structures is identical molecules, enantiomers or isomers of some other sort:
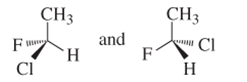
Concept introduction:
Structural or constitutional isomers can be defined as the molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formula. They are molecules in which the bonded atoms have different bonding with each other although the number of molecules is same. Identical molecules are molecules which have same structural formula and same molecular formula.
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are named as R and S configuration. For naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer, the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule is followed.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the following pair of structures is identical molecules, enantiomers or isomers of some other sort:
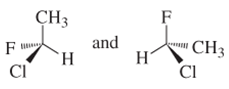
Concept introduction:
Structural or constitutional isomers can be defined as the molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formula. They are molecules in which the bonded atoms have different bonding with each other although the number of molecules is same. Identical molecules are molecules which have same structural formula and same molecular formula.
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are named as R and S configuration. For naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer, the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule is followed.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the following pair of structures is identical molecules, enantiomers or isomers of some other sort:
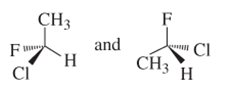
Concept introduction:
Structural or constitutional isomers can be defined as the molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formula. They are molecules in which the bonded atoms have different bonding with each other although the number of molecules is same. Identical molecules are molecules which have same structural formula and same molecular formula.
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are named as R and S configuration. For naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer, the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule is followed.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 26 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles And Modern Applications Plus Mastering Chemistry With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- Y= - 0.039 (14.01) + 0.7949arrow_forwardSuppose 1.76 g of magnesium acetate (Mg (CH3CO2)2) are dissolved in 140. mL of water. Find the composition of the resulting electrolyte solution. In particular, list the chemical symbols (including any charge) of each dissolved ion in the table below. List only one ion per row. mEq Then, calculate the concentration of each ion in dwrite the concentration in the second column of each row. Be sure you round your answers to the L correct number of significant digits. ion Add Row mEq L x 5arrow_forwardA pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows.arrow_forward
- Part II. Identify whether the two protons in blue are homotopic, enantiopic, diasteriotopic, or heterotopic. a) HO b) Bri H HH c) d) H H H Br 0arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardChoose the option that is decreasing from biggest to smallest. Group of answer choices: 100 m, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100000 um, 10000000 nm 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100 m 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100 m 100 m, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100000 um, 10000000 nmarrow_forward
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
