
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.6, Problem 66P
Determine the coordinate direction angles of F1.
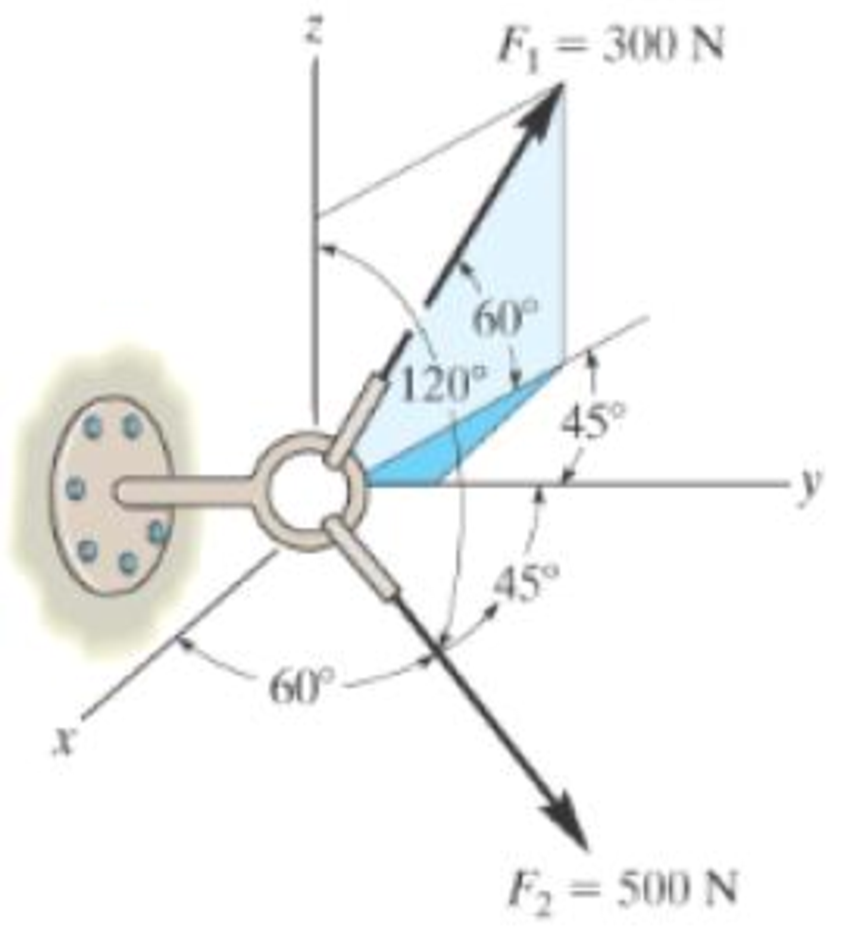
Probs. 2-65/66
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Sketch and describe hatch coamings. Describe structrual requirements to deck plating to compensate discontinuity for corners of a hatch. Show what is done to the deck plating when the decks are cut away and include the supporting members.
An Inclining experiment done on a ship thats 6500 t, a mass of 30t was moved 6.0 m transvesly causing a 30 cm deflection in a 6m pendulum, calculate the transverse meta centre height.
a ship 150 m long and 20.5 m beam floats at a draught of8 m and displaces 19 500 tonne. The TPC is 26.5 and midshipsection area coefficient 0.94. Calculate the block, prismatic andwaterplane area coefficients.
Chapter 2 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 2.3 - Then establish the triangle rule, where FR = F1 +...Ch. 2.3 - Then establish the triangle rule to show FR = FU +...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force....Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve this force into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - along the v axis. Prob. F2-6Ch. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the two components of...Ch. 2.3 - Solve with F = 350 lb. Prob. 2-4/5Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F1 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F2 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force acting on the support is to...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60, determine the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - Also, what is the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve this force into two components acting...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of F and its component...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of F and its direction ....Ch. 2.3 - Determine the required angle (0 45) and the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - What is the component of force acting along member...Ch. 2.3 - Take = 30. Probs. 2-19/20Ch. 2.3 - FR measured counterclockwise from the positive x...Ch. 2.3 - Solve I by first finding the resultant F = F2 + F3...Ch. 2.3 - If F1 = 400 N and F2 = 600 N, determine the angle...Ch. 2.3 - If their lines of action are at an angle apart...Ch. 2.3 - If F1 = 30 lb and F2 = 40 lb, determine the angles...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of FA SO...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction, measured...Ch. 2.3 - What is the minimum magnitude of FR?Ch. 2.3 - directed along the positive x axis, determine the...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the post into its x...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - determine the magnitude of F and its direction ....Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve F1 and F2 into their x and y components.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the gusset plate into...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Express each of the three forces acting on the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the x and y components of F1 and F2....Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation of FB so...Ch. 2.4 - measured counterclockwise from the positive y...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant fore and...Ch. 2.4 - Show that the resultant force is zero. Prob. 2-52Ch. 2.4 - Express F1 and F2 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - What is the magnitude of the resultant force?...Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Set = 30. Probs. 2-56/57Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 59PCh. 2.6 - Show , , . a) F = {50i + 60j 10k} kN b) F = {40i ...Ch. 2.6 - In each case, establish F as a Cartesian vector,...Ch. 2.6 - Set up the calculation used to find the magnitude...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the resultant force acting on the hook....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitudes of the x, y, z components...Ch. 2.6 - If the magnitude of F is 80 N, and = 60 and =...Ch. 2.6 - The component of F in the x-y plane is 7 kN. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Specify the coordinate direction angles of F1 and...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form and...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of F1....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Note that F1 lies in the x-y plane.Ch. 2.6 - If the resultant force FR has a magnitude of 150...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form.Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force as a Cartesian vector.Ch. 2.6 - Determine the resultant of the two forces and...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form and...Ch. 2.6 - If the coordinate direction angles for F1 are 3 =...Ch. 2.6 - If the coordinate direction angles for F1 are 3 =...Ch. 2.6 - If the direction of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.6 - If = 75, determine the magnitudes of F and Fy....Ch. 2.8 - In each case, establish a position vector from...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, express F as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.8 - Express the position vector rAB in Cartesian...Ch. 2.8 - What is the angle ? Prob. F2-20Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 21FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force at...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the resultant force at A. Prob. F2-24Ch. 2.8 - Determine the length of the connecting rod AB by...Ch. 2.8 - Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then...Ch. 2.8 - Express each of the forces in Cartesian vector...Ch. 2.8 - If F = {350i 250j 450k} N and cable AB is 9 m...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 2.8 - If z = 5 m, determine the location +x, +y of point...Ch. 2.8 - Express each of the forces in Cartesian vector...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - Express each force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Represent each force as a Cartesian vector. Probs....Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Express this force as a Cartesian vector acting on...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Represent each force as a Cartesian vector and...Ch. 2.8 - The anticipated loading in two of the struts is...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - If the force in each cable tied to the bin is 70...Ch. 2.8 - Due to symmetry, the tension in the four cables is...Ch. 2.9 - Do not calculate the result. Prob. P2-8Ch. 2.9 - P2.9. In each case, set up the dot product to find...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projected component of the force...Ch. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the components of the force acting...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Express the force F in Cartesian vector form if it...Ch. 2.9 - Express force F in Cartesian vector form if point...Ch. 2.9 - If the force in each chain has a magnitude of 60...Ch. 2.9 - If the resultant force at O has a magnitude of 130...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the length of the chain, and express the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the length of the cable and express the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables. Prob....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the y axis of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of force...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between pipe segments BA and...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angles and made between the axes...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 2.9 - Express this component as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables....Ch. 2.9 - Express the result as a Cartesian vector.Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.9 - Resolve F into components along the u and v axes...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 4RPCh. 2.9 - The cable attach to the tractor at B exerts a...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 6RPCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the edges of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projection of the force F along the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Mass and Weight Scientists measure an objects mass in kilograms and its weight in Newtons. If you know the amou...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Determine the reactions at the supports A and B, then draw the shear and moment diagram. El is constant. Neglec...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
In Exercises 1 through 52, determine the output produced by the lines of code. DimintRate,doublingTimeAsDecimal...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
What is the disadvantage of having too many features in a language?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
For the circuit shown, use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and i1.
How much power is delivered to the c...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
This statement can cause other program statements to execute only under certain conditions. 1. Conditional 2. D...
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A vessel loads 680 t fuel between forward and aft deep tanks. centre of gravity of forward tank is 24m forward of ships COG. centre to centre between tanks is 42 m. how much in each tank to keep trim the samearrow_forwardBeam of a vessel is 11% its length. Cw =0.72. When floating in SW of relative denisity 1.03, TPC is 0.35t greater than in freshwater. Find the length of the shiparrow_forwardAn inclining experiment was carried out on a ship of 4000tonne displacement, when masses of 6 tonne were moved transverselythrough 13.5 m. The deflections of a 7.5 m pendulurnwere 81, 78, 85, 83, 79, 82, 84 and 80 mm respectively.Caiculate the metacentric height.arrow_forward
- A ship of 10 000 tonne displacement has a waterplanearea of 1300 m2. The ship loads in water of 1.010 t/m3 andmoves into water of 1.026 t/m3. Find the change in meandraughtarrow_forwardA ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water.arrow_forwardA ship has 300 tonne of cargo in the hold, 24 m forward ofmidships. The displacement of the vessel is 6000 tonne and its centre of gravity is 1.2 m forward of midships.Find the new position of the centre of gravity if this cargo ismoved to an after hold, 40 m from midshipsarrow_forward
- Sketch and describe how ships are supported in dry dock. When and where does the greatest amount of stresses occur?arrow_forwardSketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspendedarrow_forwardA ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.arrow_forward
- A steamer has waterplane area 1680m2 recorded in water with relative denisty 1.013. Displacement = 1200 t, calculate difference in draught in salwater reltive denisity 1.025.arrow_forwardrelative velocity 11.72 m/s is correct, need help finding the angle pleasearrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the two automobiles 2 s after A has passed through the intersection.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License