
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168000
Author: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 4PE
A flat minor is neither converging nor diverging. To prove this, consider two rays originating from the same point and diverging at an angle θ. Show that after striking a plane mirror, the angle between their directions remains θ.
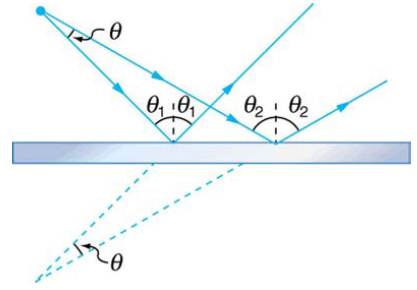
Figure 25.52 A flat mirror neither converges nor diverges light rays. Two rays continue to diverge at the same angle after reflection.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank you
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V)
ammeter
I =
Chapter 25 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 25 - Using the law of reflection, explain how powder...Ch. 25 - Diffusion by reflection from a rough surface is...Ch. 25 - Why is the index of refraction always greater than...Ch. 25 - Does the fact that the light flash from lightning...Ch. 25 - Will light change direction toward or away from...Ch. 25 - Explain why an object in water always appears to...Ch. 25 - Explain why a person’s legs appeal very short when...Ch. 25 - Why is the front surface of a thermometer curved...Ch. 25 - Suppose light were incident from air onto a...Ch. 25 - A ring with a colorless gemstone is dropped into...
Ch. 25 - A high-quality diamond may be quite clear and...Ch. 25 - Is it possible that total internal reflection...Ch. 25 - The most common type at mirage is an illusion that...Ch. 25 - It can he argued that a flat piece of glass, such...Ch. 25 - You can often see a reflection when looking at a...Ch. 25 - When you focus a camera, you adjust the distance...Ch. 25 - A thin lens has two focal points, one on either...Ch. 25 - Will the focal length of a lens change when it is...Ch. 25 - What are the differences between teal and virtual...Ch. 25 - Can you see a virtual image? Can you photograph...Ch. 25 - Is it necessary to project a real image onto a...Ch. 25 - At what distance is an image always locatedat do,...Ch. 25 - Under what circumstances will an image be located...Ch. 25 - What is meant by a negative magnification? What is...Ch. 25 - Can a case 1 image be larger than the object even...Ch. 25 - Figure 25.49 shows a light bulb between two...Ch. 25 - Devise an arrangement of mirrors allowing you to...Ch. 25 - If you wish to see your entire body in a flat...Ch. 25 - It can be argued than a flat mirror has an in?nite...Ch. 25 - Why are diverging mirrors often used for rear-view...Ch. 25 - Suppose a man stands in front of a mirror as shown...Ch. 25 - Show that when light reflects from two mirrors...Ch. 25 - Light shows staged with lasers use moving mirrors...Ch. 25 - A flat minor is neither converging nor diverging....Ch. 25 - What is the speed of light in water? In glycerine?Ch. 25 - What is the speed of light in air? In crown glass?Ch. 25 - Calculate the index of refraction for a medium in...Ch. 25 - In what substance in Table 25.1 is the speed of...Ch. 25 - There was a major collision of an asteroid with...Ch. 25 - A scuba diver training in a pool looks at his...Ch. 25 - Components of some computers communicate with each...Ch. 25 - (a) Using information in Figure 25.53, find the...Ch. 25 - Suppose you have an unknown clear substance...Ch. 25 - On the Moon’s surface, lunar astronauts placed a...Ch. 25 - Suppose Figure 25.54 represents a ray of light...Ch. 25 - Figure 25.54 shows a ray of light passing from one...Ch. 25 - Unreasonable Results Suppose light travels from...Ch. 25 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider sunlight...Ch. 25 - Unreasonable Results Light traveling from water to...Ch. 25 - Verify that the critical angle for light going...Ch. 25 - (a) At the end of Example 25.4, it was stated that...Ch. 25 - An optical fiber uses flint glass clad with crown...Ch. 25 - At what minimum angle will you get total internal...Ch. 25 - Suppose you are using total internal reflection to...Ch. 25 - You can determine me index of refraction of a...Ch. 25 - A ray of light, emitted beneath the surface of an...Ch. 25 - A light ray entering an optical fiber surrounded...Ch. 25 - (a) What is me ratio of the speed of red light to...Ch. 25 - A beam of white light goes from air into water at...Ch. 25 - By how much do the critical angles for red (660...Ch. 25 - (a) A narrow beam of light containing yellow (580...Ch. 25 - A parallel beam of light containing orange (610...Ch. 25 - A ray of 610 nm light goes from air into fused...Ch. 25 - A narrow beam of light containing red (660 nm) and...Ch. 25 - A narrow beam of white light enters a prism made...Ch. 25 - What is the power in diopters at a camera lens...Ch. 25 - Your camera's zoom lens has an adjustable focal...Ch. 25 - What is the focal length of 1.75 D reading glasses...Ch. 25 - You note that your prescription for new eyeglasses...Ch. 25 - How far from the lens must the film in a camera...Ch. 25 - A certain slide projector has a 100 mm focal...Ch. 25 - A doctor examines a mole with a 15.0 cm focal...Ch. 25 - How far from a piece of paper must you hold your...Ch. 25 - A camera with a 50.0 mm focal length lens is being...Ch. 25 - A camera lens used for taking close-up photographs...Ch. 25 - Suppose your 50.00 mm local length camera lens is...Ch. 25 - (a) What is the focal length of a magnifying glass...Ch. 25 - What magnification will be produced by a lens of...Ch. 25 - In Example 25.7, the magnification of a book held...Ch. 25 - Suppose a 200 mm focal length telephoto lens is...Ch. 25 - A camera with a 100 mm focal length lens is used...Ch. 25 - Combine thin lens equations to show that the...Ch. 25 - What is the focal length of a makeup mirror that...Ch. 25 - Some telephoto cameras use a mirror rather than a...Ch. 25 - (a) Calculate the focal length of the mirror...Ch. 25 - Find the magnification of the heater element in...Ch. 25 - What is the focal length of a makeup mirror that...Ch. 25 - A shopper standing 3.00 m from a convex security...Ch. 25 - An object 1.50 cm high is held 3.00 cm from a...Ch. 25 - Ray tracing for a flat mirror shows that the image...Ch. 25 - Show that for a flat mirror hi= ho, knowing that...Ch. 25 - Use the law of reflection to prove that the focal...Ch. 25 - Referring to the electric room heater considered...Ch. 25 - Consider a 250-W heat lamp fixed to the ceiling in...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Police Captain Jeffers has suffered a myocardial infarction. a. Explain to his (nonmedically oriented) family w...
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Mendel crossed peas having round green seeds with peas having wrinkled yellow seeds. All F1 plants had seeds th...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B. Column ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Define histology.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
What percentage of Earths land surface do glaciers presently cover? ____________
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forward
- A long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forward
- Explain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forward
- For each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY