
Concept explainers
Draw the products formed in the crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
(a)
Interpretation: The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
Concept introduction: The crossed aldol reaction takes place between the two different carbonyl compounds that is between two different aldehydes or two different ketones or one aldehyde and one ketone. The crossed aldol reaction takes place only if the carbonyl compound contains an acidic
Answer to Problem 24.8P
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction is shown below.
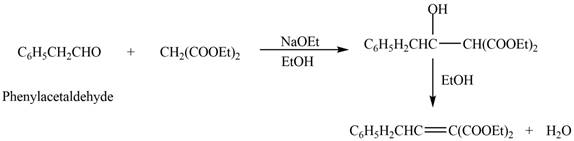
Figure 1
In this crossed aldol reaction, phenylacetaldehyde reacts with
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
(b)
Interpretation: The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
Concept introduction: The crossed aldol reaction takes place between the two different carbonyl compounds that is between two different aldehydes or two different ketones or one aldehyde and one ketone. The crossed aldol reaction takes place only if the carbonyl compound contains an acidic
Answer to Problem 24.8P
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction is shown below.
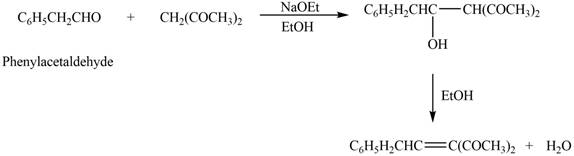
Figure 2
In this crossed aldol reaction, phenylacetaldehyde reacts with
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
(c)
Interpretation: The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
Concept introduction: The crossed aldol reaction takes place between the two different carbonyl compounds that is between two different aldehydes or two different ketones or one aldehyde and one ketone. The crossed aldol reaction takes place only if the carbonyl compound contains an acidic
Answer to Problem 24.8P
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
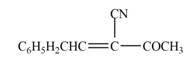
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction is shown below.
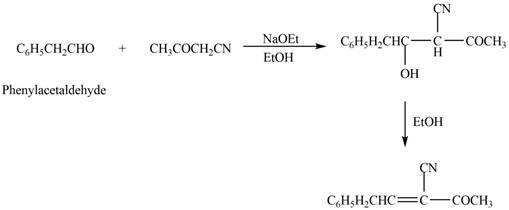
Figure 3
In this crossed aldol reaction, phenylacetaldehyde reacts with
The product that is formed in the given crossed aldol reaction of phenylacetaldehyde
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- please help with synthesisarrow_forward10. Stereochemistry. Assign R/S stereochemistry for the chiral center indicated on the following compound. In order to recieve full credit, you MUST SHOW YOUR WORK! H₂N CI OH CI カー 11. () Stereochemistry. Draw all possible stereoisomers of the following compound. Assign R/S configurations for all stereoisomers and indicate the relationship between each as enantiomer, diastereomer, or meso. NH2 H HNH, -18arrow_forwardb) 8. Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur Please explain your rational using 10 words or less not likely to occur • The double bond is still in the Same position + Likely to oc occur WHY? -3 H3C Brave Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less. CI 2 -cobs ?? MUST INDICATE H -2 -2 Br EQ Cl OR AT Br H& most stable WHY? - 4arrow_forward
- CH 12 Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided. NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below -4 NOT HOH OH 3 Conformer A: Br OH A Samo Br H 04 Br H H3 CH₂ H anti stagere Br CH clipsed H Brott H IV H MISSING 2 -2 B C D E F X 6 Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY: 13. (1 structure LOWEST ENERGY: Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry when applicable. a) ८८ 2 "Br {t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa Parent name (noname) 4 Bromo Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane # -2 -2arrow_forwardin the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





