
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305116399
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 24.68CP
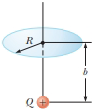
A particle with charge Q is located on the axis of a circle of radius R at a distance b from the plane of the circle (Fig. P23.48). Show that if one-fourth of the electric flux from the charge passes through the circle, then
Figure P23.48
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve and answer the problem correctly please. Be sure to give explanations on each step and write neatly please. Thank you!!
In the figures, the masses are hung from an elevator ceiling. Assume the velocity of the elevator is constant. Find the tensions in
the ropes (in N) for each case. Note that 0₁ = 35.0°, 0₂ = 55.0°, 03 = 60.0°, m₁ = 3.00 kg, and m2 = 7.00 kg. (Due to the
nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values-including answers submitted in WebAssign-in your calculations.)
(a)
Τι
WY NY MY
T3
e₁
T₁
=
N
=
N
=
N
(b)
18
Τι
=
Τι
T3
=
|| || ||
=
T
T
Ts
m₂
N
N
N
02
T₂
T3
m₁
You are working with a movie director and investigating a scene with a cowboy sliding off a tree limb and falling onto the saddle of
a moving horse. The distance of the fall is several meters, and the calculation shows a high probability of injury to the cowboy
from the stunt. Let's look at a simpler situation. Suppose the director asks you to have the cowboy step off a platform 2.55 m off
the ground and land on his feet on the ground. The cowboy keeps his legs straight as he falls, but then bends at the knees as
soon as he touches the ground. This allows the center of mass of his body to move through a distance of 0.660 m before his body
comes to rest. (Center of mass will be formally defined in Linear Momentum and Collisions.) You assume this motion to be under
constant acceleration of the center of mass of his body. To assess the degree of danger to the cowboy in this stunt, you wish to
calculate the average force upward on his body from the ground, as a multiple of the cowboy's…
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Ch. 24 - Suppose a point charge is located at the center of...Ch. 24 - If the net flux through a gaussian surface is...Ch. 24 - A cubical gaussian surface surrounds a long,...Ch. 24 - A coaxial cable consists of a long, straight...Ch. 24 - In which of the following contexts ran Gausss law...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge q is located inside a...Ch. 24 - Charges of 3.00 nC, -2.00 nC, -7.00 nC, and 1.00...Ch. 24 - A large, metallic, spherical shell has no net...Ch. 24 - Two solid spheres, both of radius 5 cm. carry...Ch. 24 - A uniform electric field of 1.00 N/C is set up by...
Ch. 24 - A solid insulating sphere of radius 5 cm carries...Ch. 24 - A cubical gaussian surface is bisected by a large...Ch. 24 - Rank the electric fluxes through each gaussian...Ch. 24 - Consider an electric field that is uniform in...Ch. 24 - A cubical surface surrounds a point charge q...Ch. 24 - A uniform electric field exists in a region of...Ch. 24 - If the total charge inside a closed surface is...Ch. 24 - Explain why the electric flux through a closed...Ch. 24 - If more electric field lines leave a gaussian...Ch. 24 - A person is placed in a large, hollow, metallic...Ch. 24 - Consider two identical conducting spheres whose...Ch. 24 - A common demonstration involves charging a rubber...Ch. 24 - On the basis of the repulsive nature of the force...Ch. 24 - The Sun is lower in the sky during the winter than...Ch. 24 - A flat surface of area 3.20 m2 is rotated in a...Ch. 24 - A vertical electric field of magnitude 2.00 104...Ch. 24 - A 40.0-cm-diameter circular loop is rotated in a...Ch. 24 - Consider a closed triangular box resting within a...Ch. 24 - An electric field of magnitude 3.50 kN/C is...Ch. 24 - A nonuniform electric field is given by the...Ch. 24 - An uncharged, nonconducting, hollow sphere of...Ch. 24 - Find the net electric flux through the spherical...Ch. 24 - The following charges are located inside a...Ch. 24 - The electric field everywhere on the surface of a...Ch. 24 - Four closed surfaces, S1 through S4 together with...Ch. 24 - A charge of 170 C is at the center of a cube of...Ch. 24 - In the air over a particular region at an altitude...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge of 12.0 C is placed at the...Ch. 24 - (a) Find the net electric flux through the cube...Ch. 24 - (a) A panicle with charge q is located a distance...Ch. 24 - An infinitely long line charge having a uniform...Ch. 24 - Find the net electric flux through (a) the closed...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q = 5.00 C is located at...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q is located at the center...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q is located a small...Ch. 24 - Figure P23.23 represents the top view of a cubic...Ch. 24 - In nuclear fission, a nucleus of uranium-238,...Ch. 24 - The charge per unit length on a long, straight...Ch. 24 - A 10.0-g piece of Styrofoam carries a net charge...Ch. 24 - Determine the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 24 - A large, flat, horizontal sheet of charge has a...Ch. 24 - Suppose you fill two rubber balloons with air,...Ch. 24 - Consider a thin, spherical shell of radius 14.0 cm...Ch. 24 - A nonconducting wall carries charge with a uniform...Ch. 24 - A uniformly charged, straight filament 7.00 m in...Ch. 24 - Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each...Ch. 24 - Consider a long, cylindrical charge distribution...Ch. 24 - A cylindrical shell of radius 7.00 cm and length...Ch. 24 - A solid sphere of radius 40.0 cm has a total...Ch. 24 - Review. A particle with a charge of 60.0 nC is...Ch. 24 - A long, straight metal rod has a radius of 5.00 cm...Ch. 24 - Why is the following situation impossible? A solid...Ch. 24 - A solid metallic sphere of radius a carries total...Ch. 24 - A positively charged panicle is at a distance R/2...Ch. 24 - A very large, thin, flat plate of aluminum of area...Ch. 24 - In a certain region of space, the electric field...Ch. 24 - Two identical conducting spheres each having a...Ch. 24 - A square plate of copper with 50.0-cm sides has no...Ch. 24 - A long, straight wire is surrounded by a hollow...Ch. 24 - A thin, square, conducting plate 50.0 cm on a side...Ch. 24 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 2.00 cm has a...Ch. 24 - Consider a plane surface in a uniform electric...Ch. 24 - Find the electric flux through the plane surface...Ch. 24 - A hollow, metallic, spherical shell has exterior...Ch. 24 - A sphere of radius R = 1.00 m surrounds a particle...Ch. 24 - A sphere of radius R surrounds a particle with...Ch. 24 - A very large conducting plate lying in the xy...Ch. 24 - A solid, insulating sphere of radius a has a...Ch. 24 - A solid insulating sphere of radius a = 5.00 cm...Ch. 24 - Two infinite, nonconducting sheets of charge are...Ch. 24 - For the configuration shown in Figure P24.45,...Ch. 24 - An insulating solid sphere of radius a has a...Ch. 24 - A uniformly charged spherical shell with positive...Ch. 24 - An insulating solid sphere of radius a has a...Ch. 24 - A slab of insulating material has a nonuniform...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.62CPCh. 24 - A dosed surface with dimensions a = b= 0.400 111...Ch. 24 - A sphere of radius 2a is made of a nonconducting...Ch. 24 - A spherically symmetric charge distribution has a...Ch. 24 - A solid insulating sphere of radius R has a...Ch. 24 - An infinitely long insulating cylinder of radius R...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q is located on the axis of...Ch. 24 - Review. A slab of insulating material (infinite in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A box of mass m = 2.00 kg is released from rest at the top of an inclined plane as seen in the figure. The box starts out at height h =0.200 m above the top of the table, the table height is H = 2.00 m, and 0 = 41.0°. H m (a) What is the acceleration (in m/s²) of the box while it slides down the incline? m/s² (b) What is the speed (in m/s) of the box when it leaves the incline? m/s (c) At what horizontal distance (in m) from the end of the table will the box hit the ground? m (d) How long (in s) from when the box is released does it hit the ground? S (e) Does the box's mass affect any of your above answers? Yes Noarrow_forward(a) A sphere made of rubber has a density of 0.940 g/cm³ and a radius of 7.00 cm. It falls through air of density 1.20 kg/m³ and has a drag coefficient of 0.500. What is its terminal speed (in m/s)? m/s (b) From what height (in m) would the sphere have to be dropped to reach this speed if it fell without air resistance? marrow_forwardThe systems shown below are in equilibrium. If the spring scales are calibrated in newtons, what do they read? Ignore the masses of the pulleys and strings and assume the pulleys and the incline are frictionless. (Let m = 2.19 kg and € = 29.0°.) scale in (a) N N scale in (b) scale in (c) N scale in (d) N a C m m m m m b d m Ꮎarrow_forward
- An elevator car has two equal masses attached to the ceiling as shown. (Assume m = 3.10 kg.) m m T₁ T2 (a) The elevator ascends with an acceleration of magnitude 2.00 m/s². What are the tensions in the two strings? (Enter your answers in N.) = N T₁ Τι = N (b) The maximum tension the strings can withstand is 78.8 N. What is the maximum acceleration of the elevator so that a string does not break? (Enter the magnitude in m/s².) m/s²arrow_forward(a) At what speed (in m/s) will a proton move in a circular path of the same radius as an electron that travels at 7.85 x 100 m/s perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic field at an altitude where the field strength is 1.20 x 10-5 T? 4.27e3 m/s (b) What would the radius (in m) of the path be if the proton had the same speed as the electron? 7.85e6 x m (c) What would the radius (in m) be if the proton had the same kinetic energy as the electron? 195.38 x m (d) What would the radius (in m) be if the proton had the same momentum as the electron? 3.7205 marrow_forward! Required information The block shown is made of a magnesium alloy, for which E = 45 GPa and v = 0.35. Know that σx = -185 MPa. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 25 mm B D 40 mm 100 mm Determine the magnitude of Oy for which the change in the height of the block will be zero. The magnitude of Oy is MPa.arrow_forward
- The rigid bar ABC is supported by two links, AD and BE, of uniform 37.5 × 6-mm rectangular cross section and made of a mild steel that is assumed to be elastoplastic with E = 200 GPa and σy= 250 MPa. The magnitude of the force Q applied at B is gradually increased from zero to 265 kN and a = 0.640 m. 1.7 m 1 m D A B 2.64 m E Determine the value of the normal stress in each link. The value of the normal stress in link AD is The value of the normal stress in link BE is 250 MPa. MPa.arrow_forwardTwo tempered-steel bars, each 16 in. thick, are bonded to a ½ -in. mild-steel bar. This composite bar is subjected as shown to a centric axial load of magnitude P. Both steels are elastoplastic with E= 29 × 106 psi and with yield strengths equal to 100 ksi and 50 ksi, respectively, for the tempered and mild steel. The load P is gradually increased from zero until the deformation of the bar reaches a maximum value dm = 0.04 in. and then decreased back to zero. Take L = 15 in. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 2.0 in. in. 3 in. 3 16 in. Determine the maximum stress in the tempered-steel bars. The maximum stress in the tempered-steel bars is ksi.arrow_forwardAmmonia enters the compressor of an industrial refrigeration plant at 2 bar, -10°C with a mass flow rate of 15 kg/min and is compressed to 12 bar, 140°C. Heat transfer from the compressor to its surroundings occurs at a rate of 6 kW. For steady-state operation, calculate, (a) the power input to the compressor, in kW, Answer (b) the entropy production rate, in kW/K, for a control volume encompassing the compressor and its immediate surroundings such that heat transfer occurs at 300 K.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardShown to the right is a block of mass m=5.71kgm=5.71kg on a ramp that makes an angle θ=24.1∘θ=24.1∘ with the horizontal. This block is being pushed by a horizontal force, F=229NF=229N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the two surfaces is μ=0.51μ=0.51. Enter an expression for the acceleration of the block up the ramp using variables from the problem statement together with gg for the acceleration due to gravity. a=arrow_forwardIf the density and atomic mass of copper are respectively 8.80 x 103 kg/m³ and 63.5 kg/kmol (note that 1 kmol = 1,000 mol), and copper has one free electron per copper atom, determine the following. (a) the drift speed of the electrons in a 10 gauge copper wire (2.588 mm in diameter) carrying a 13.5 A current 1.988-4 See if you can obtain an expression for the drift speed of electrons in a copper wire in terms of the current in the wire, the diameter of the wire, the molecular weight and mass density of copper, Avogadro's number, and the charge on an electron. m/s (b) the Hall voltage if a 2.68 T field is applied perpendicular to the wire 3.34e-6 x Can you start with basic equations for the electric and magnetic forces acting on the electrons moving through the wire and obtain a relationship between the magnitude of the electric and magnetic field and the drift speed of the electrons? How is the magnitude of the electric field related to the Hall voltage and the diameter of the wire? Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY