
Concept explainers
Name the following compounds:
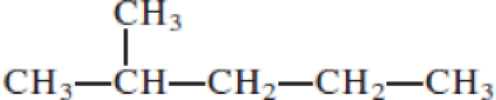
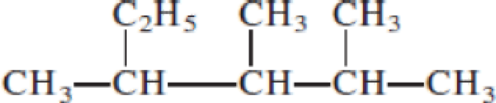
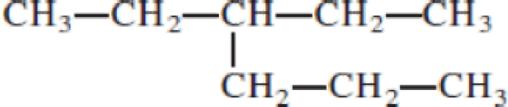
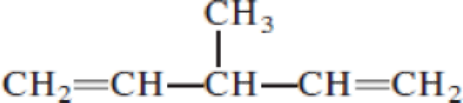
- (a) CH3─C≡C─CH2─CH3
a)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
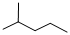
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
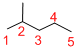
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENTANE. The Suffix ‘ane’ represents the structure contains only single bonds.
Predict substituents and its location:
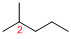
At each Carbon of 2 one methyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituents, then prefix ‘2-methyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 2-methylpentane.
b)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
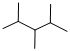
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
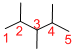
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENTANE. The Suffix ‘ane’ represents the structure contains only single bonds.
Predict substituents and its location:
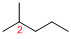
At each Carbon of 2, 3, and 4 one methyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing three identical substituents, then prefix ‘2,3,4-trimethyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 2,3,4-trimethylpentane.
c)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hyphen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
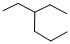
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
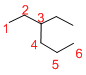
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains six carbons and the parent name is HEXANE. The Suffix ‘ane’ represents the structure contains only single bonds.
Predict substituents and its location:

At each Carbon of 3 one ethyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituent, then prefix ‘3-ethyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 3-ethylhexane.
d)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name by replacing ‘ane’ to ‘ene’. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hyphen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
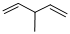
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
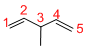
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is 1,4-PENTDIENE. The Suffix ‘diene’ represents the structure contains two double bonds at C-1 and C-4.
Predict substituents and its location:
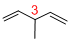
At each Carbon of 3 one methyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituent, then prefix ‘3-methyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 3-methyl-1,4-pentadiene.
e)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name by replacing ‘ane’ to ‘yne’. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:

Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
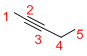
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENT-2-YNE. The Suffix ‘2-yne’ represents the structure contains one triple bond at C-2.
Predict substituents and its location:
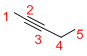
No substituents present and no prefix can be written. Hence, the name is,
IUPAC name: Pent-2-yne.
f)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature for alkene:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the double bond should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name by replacing ‘ane’ to ‘ene’. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Geometric isomers of Alkenes:
Cis-isomer: When two particular atoms (group of atoms) are adjacent to each other, the alkene is known as cis-isomer.
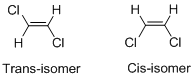
Trans-isomer: When two particular atoms (group of atoms) are across from each other, the alkene is known as cis-isomer.
Explanation of Solution
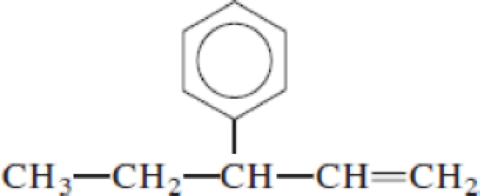
Given structure:
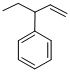
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
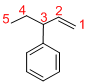
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENT-1-ENE. The Suffix ‘1-ene’ represents the structure contains one double bond at C-1.
Predict substituents and its location:

At each Carbon of 3 one phenyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituent, then prefix ‘3-phenyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 3-phenylpent-1-ene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Chemistry
- Which region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forwardPredict the product of the following reactions: O 0= excess Х Кон ОН H+ H+ Iarrow_forwardHow many chiral centers/stereocenters are there in the following molecule? 1 2 3 4arrow_forward
- Which of these correspond to the molecule: 2,5-dimethylheptanearrow_forwardGiven the following data, determine the order of the reaction with respect to H2. H2(g) + 21Cl(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) Experiment [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (M/s) 1 250 325 0.266 2 250 81 0.0665 3 50 325 0.266arrow_forwardWhich one of the following molecules is chiral? H- NH₂ H3C དང་།་ OH H HO H₂N HO- -H CHO -OH H HO- OH H- -H CH₂OH OHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





