
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether B vitamin thiamin is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(a)
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
None of the given processes includes B vitamin thiamin as a cofactor. B vitamin thiamin is needed as a cofactor in the conversion of pyruvate to
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin thiamin is encountered in the form of thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP) in the carbohydrate metabolism. TPP in not involved in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lactate fermentation, and glycogenolysis. Hence, none of the given processes includes vitamin thiamin as a cofactor.
Pyruvate is converted to
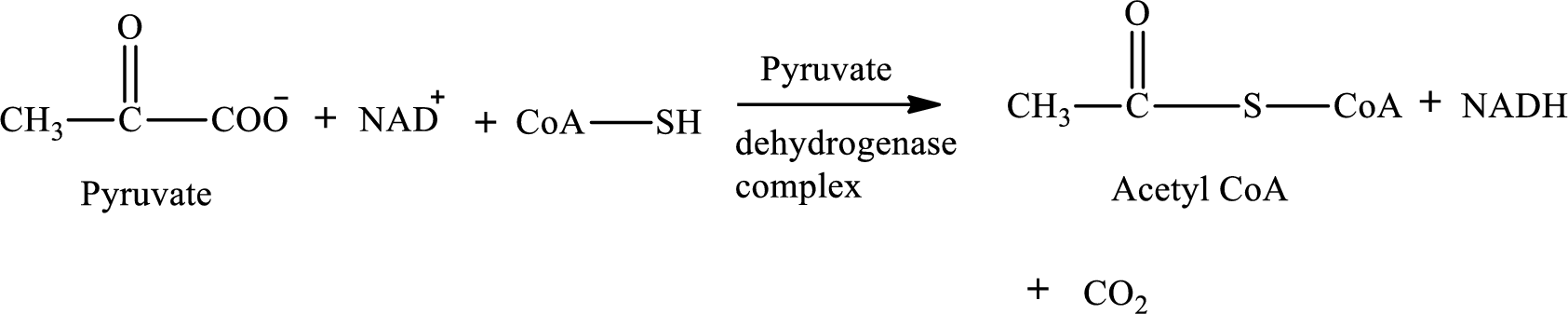
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains three different enzymes. Each enzyme contains numerous subunits. The overall reaction requires FAD,
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate B vitamin riboflavin is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(b)
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
None of the given processes includes vitamin riboflavin as a cofactor. B vitamin riboflavin is needed as a cofactor in the citric acid cycle.
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin riboflavin is encountered in the form of FAD(Flavin adenine dinucleotide) in the carbohydrate metabolism. FAD in not involved in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lactate fermentation, and glycogenolysis. Hence, none of the given processes includes B vitamin riboflavin as a cofactor.
The citric acid cycle is the third stage of the biochemical energy production process. The cycle includes the reactions in which the acetyl part of acetyl CoA is oxidized and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether B vitamin pantothenic acid is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(c)
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
None of the given processes includes B vitamin pantothenic acid as a cofactor. B vitamin pantothenic acid is needed as a cofactor in the conversion of pyruvate to
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin pantothenic acid is encountered in the form of
Pyruvate is converted to
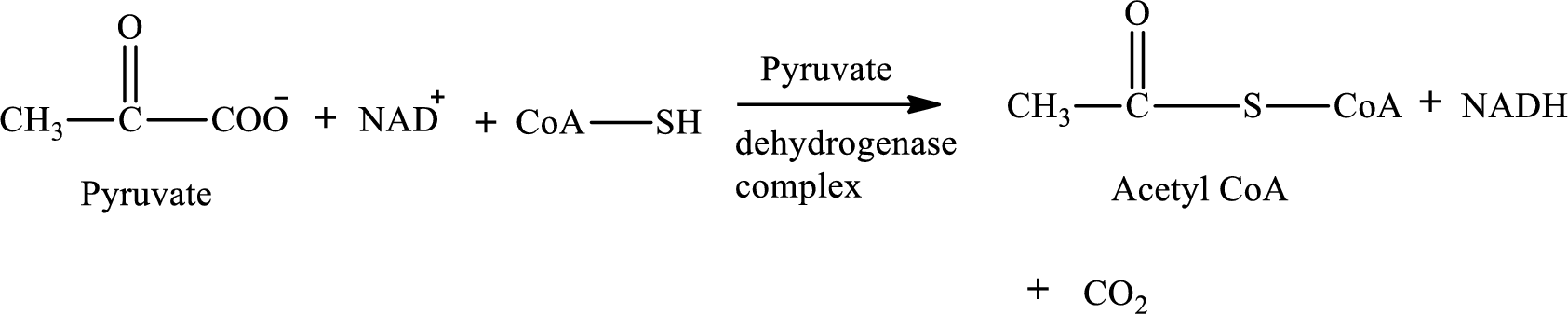
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains three different enzymes. Each enzyme contains numerous subunits. The overall reaction requires FAD,
(d)
Interpretation: To indicate
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Explain in a flowcharts organazing the words down below: genetics Chromosomes Inheritance DNA & Genes Mutations Proteinsarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forward
- Nutritional Sciences: From Fundamentals to Food, ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337486415Author:McGuirePublisher:Cengage
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





