
Concept explainers
a)
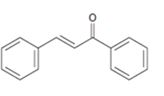
Interpretation:
The structure of the
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule to give an aldol. The aldol dehydrates on heating to yield α, β-unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
To show:
The structure of the aldehydes or ketones that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction.
b)
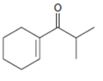
Interpretation:
The structure of the aldehydes or ketones that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule to give an aldol. The aldol dehydrates on heating to yield α, β-unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
To show:
The structure of the aldehydes or ketones that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction.
c)
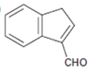
Interpretation:
The structure of the aldehydes or ketones that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo a base catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction in aldol condensation. In this reaction two molecules of the reactant combine by forming a bond between α-carbon of one molecule and the carbonyl carbon within the same molecule or of the second molecule to give an aldol. The aldol dehydrates on heating to yield α, β-unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
To show:
The structure of the aldehyde that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction.
d)
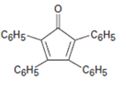
Interpretation:
The structure of the aldehydes or ketones that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Mixed aldol condensation leads to a single product if i)one of the carbonyl partners contains no α hydrogen atoms but contains an unhindered carbonyl group and ii) if one of the carbonyl partners are much more acidic than the other and thus forms an enolate anion in preference to other.
To show:
The structure of the aldehydes or ketones that should be used as a starting material to synthesize the compound given in an aldol reaction.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 23 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Is (CH3)3NHBr an acidic or basic salt? What happens when dissolved in aqueous solution? Doesn't it lose a Br-? Does it interact with the water? Please advise.arrow_forward© Macmilla Finish resonance structure 3 Select Draw Templates More C H N 0 H H S Erase Which structure is the most stable (lowest energy) resonance contributor? The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and sulfur. All structures are equal in stability. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on sulfur and carbon. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and carbon. Q2Qarrow_forwardThree pure compounds are formed when 1.00 g samples of element x combine with, respectively, 0.472 g, 0.630 g, and 0.789 g of element z. The first compound has the formula x2Z3. find the empricial formula of the other two compoundsarrow_forward
- Draw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forwardIn reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

