
Concept explainers
a)
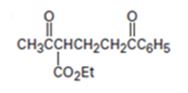
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
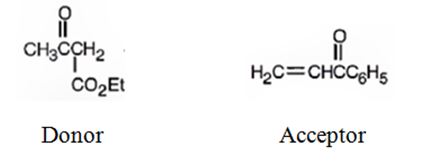
Explanation of Solution
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylacetoacetate (nucleophilic donor) and phenyl vinyl ketone (electrophilic acceptor).
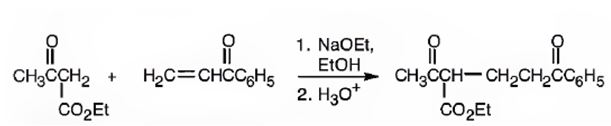
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
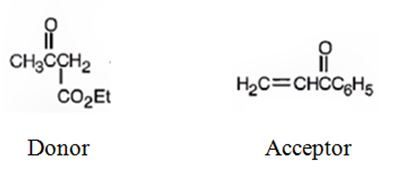
b)
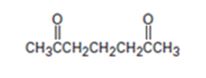
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylacetoacetate (nucleophilic donor) and methyl vinyl ketone (electrophilic acceptor).
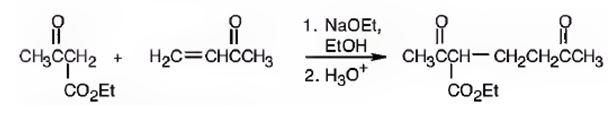
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

c)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
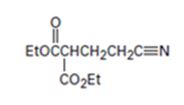
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylacetoacetate (nucleophilic donor) and vinyl nitrile (electrophilic acceptor).
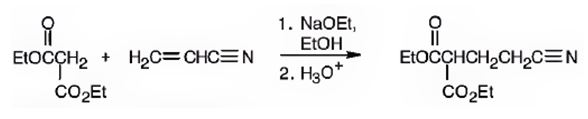
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

d)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
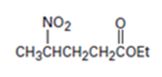
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between nitro ethane (nucleophilic donor) and ethylacrylate (electrophilic acceptor).
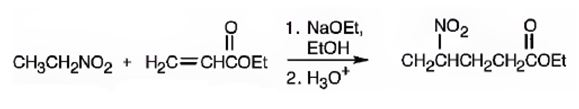
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
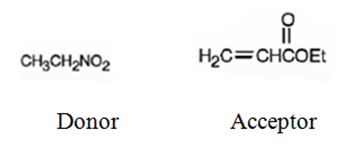
e)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
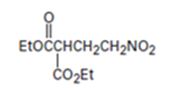
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylsuccinate (nucleophilic donor) and nitro ethene (electrophilic acceptor).
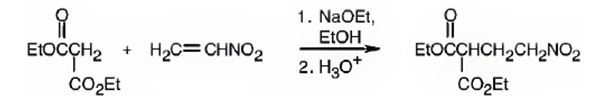
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

f)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
Explanation of Solution
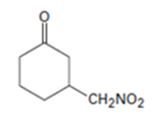
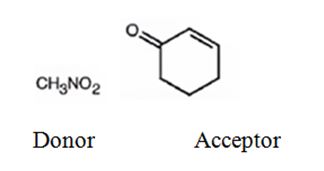
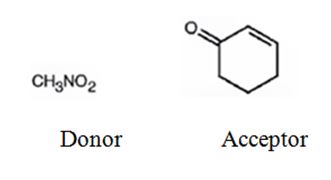
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between nitro methane (nucleophilic donor) and 2-cyclopentenone (electrophilic acceptor).
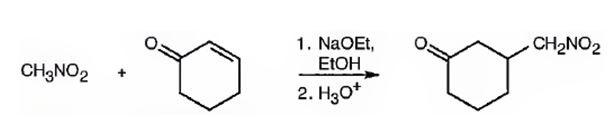
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Highlight the chirality (or stereogenic) center(s) in the given compound. A compound may have one or more stereogenic centers. OH OH OH OH OH OHarrow_forwardUsing wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration. NH H Br X टेarrow_forwardProvide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forward
- Please draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardGiven a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


