
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134042282
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 34P
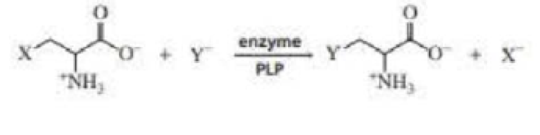
In addition to the reaction mentioned in Section 23.5. PLP can catalyze β-substitution reactions. Propose a mechanism for the following PLP-catalyzed β-substitution reaction:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$
Indicate characteristics of oxodec acid.
What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 23.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 23.1 - Prob. 3PCh. 23.2 - How many conjugated double bonds are there in a....Ch. 23.2 - Instead of adding to the 4a position and...Ch. 23.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 23.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 23.3 - Acetolactate synthase is another TPP-requiring...Ch. 23.3 - Acetolactate synthase transfers the acyl group of...Ch. 23.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 23.5 - Which compound is more easily decarboxylated?
Ch. 23.5 - Prob. 14PCh. 23.5 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 23.5 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 23.5 - The enzyme that catalyzes the C C bond cleavage...Ch. 23.5 - Propose a mechanism for the ,-elimination reaction...Ch. 23.6 - Ethanolamine ammonia lyase, a coenzyme...Ch. 23.6 - Prob. 20PCh. 23.7 - How do the structure of tetrahydrofolate and...Ch. 23.7 - What is the source of the methyl group in...Ch. 23.8 - Thiols such as ethanethiol and propanethiol can be...Ch. 23 - How does the metal ion in carboxypeptidase A...Ch. 23 - Prob. 24PCh. 23 - Prob. 25PCh. 23 - For each of the following reactions, name both the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 27PCh. 23 - When transaminated, the three branched-chain amino...Ch. 23 - What acyl groups have we seen transferred by...Ch. 23 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 23 - Draw the products of the following reaction, where...Ch. 23 - When UMP is dissolved in T2O, exchange of T for H...Ch. 23 - Dehydratase is a PLP-requiring enzyme that...Ch. 23 - In addition to the reaction mentioned in Section...Ch. 23 - PLP can catalyze both ,-elimination reactions...Ch. 23 - The glycine cleavage system is a group of four...Ch. 23 - Prob. 37PCh. 23 - FADH2 reduces , -unsaturated thioesters to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
DIGESTER-35 | VITAMINS AND THEIR RELATED COENZYMES| GPAT | NIPER | PHARMACIST| DI; Author: GPAT DISCUSSION CENTER;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CGrdNYmho0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY