
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a.![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 1](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image001.jpg) f.
f.![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 2](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image002.jpg)
b.![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 3](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image003.jpg) g.
g.![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 4](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image004.jpg)
c.
![]()
d.![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 6](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image006.jpg) i.
i. ![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 7](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image007.jpg)
e. ![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 8](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image008.jpg) j.
j.![Chapter 23, Problem 23.52P, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. a.f. b.g. c. CH3CH2CH2CO2Et[2]CH3CH2I[1]LDAh. , example 9](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9780073402772/Chapter-23/images/02772-23-23.52p-question-digital_image009.jpg)
(a)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The various organic reactions form different organic products with the help of the variety of reagents. Some of the organic compounds are formed by the characteristic action of the various functional groups present in them.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
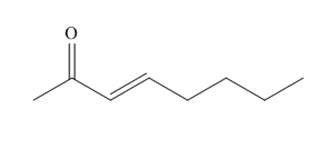
Explanation of Solution
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown below.
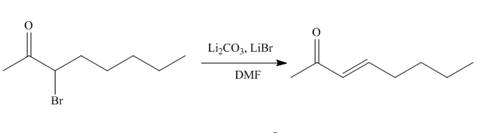
Figure 1
The above reaction takes place between a brominated compound and
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The various organic reactions form different organic products with the help of the variety of reagents. Some of the organic compounds are formed by the characteristic action of the various functional groups present in them.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
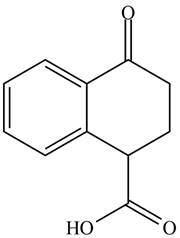
Explanation of Solution
Decarboxylation occurs when a carboxyl group is attached to alpha carbon of another carbonyl group. It removes the carboxylic group from the alpha carbon of the carbonyl group. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
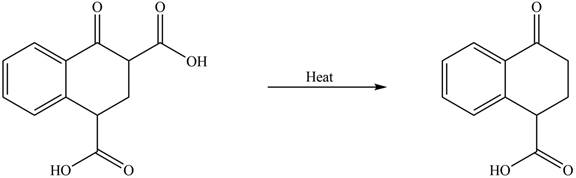
Figure 2
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is a sterically hindered strong base. In an unsymmetrical ketone, it abstracts hydrogen from least substituted carbon to form kinetic product.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
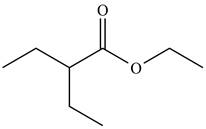
Explanation of Solution
LDA abstracts a proton from the alpha carbon of ethylbutanoate to form enolate. This enolate ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks on electrophilic centre of iodoethane and forms
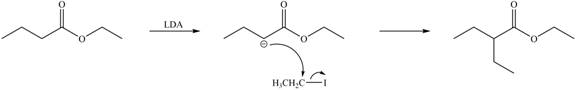
Figure 3
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkyl amines are formed by the reaction of alkyl halides with amines. This reaction is known as alkylation of amines.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
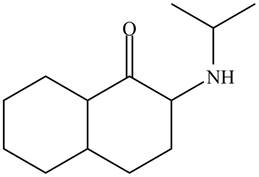
Explanation of Solution
In the first step,
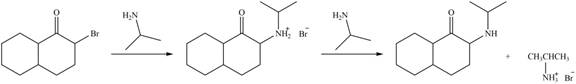
Figure 4
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is a sterically hindered strong base. In an unsymmetrical ketone, it abstracts hydrogen from least substituted carbon to form kinetic product.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
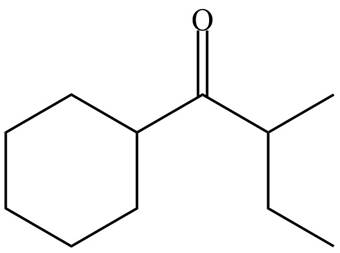
Explanation of Solution
LDA abstracts a proton from the less hindered alpha carbon of
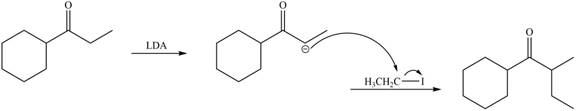
Figure 5
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Monobromo product is formed by the reaction of carbonyl compounds with bromine in the presence of acetic acid and further treatment of monobromo with base yield alkenes.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
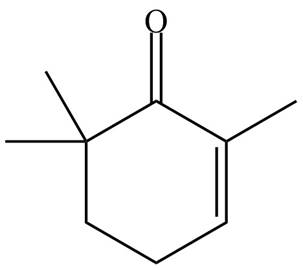
Explanation of Solution
Monobromo product is formed by the reaction of
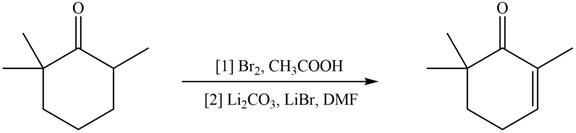
Figure 6
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Haloform is produced by the halogenation of a methyl ketone in the presence of a base. This reaction is also known as haloform reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
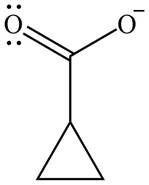
Explanation of Solution
The enolate ion reacts with iodine and form
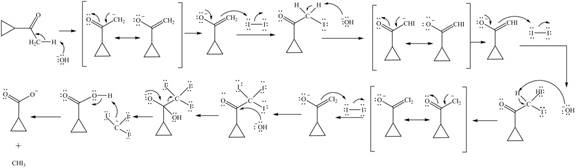
Figure 7
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Sodium hydride is a strong base. It abstracts a proton and forms carbanion. This carbanion acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophilic centre of alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
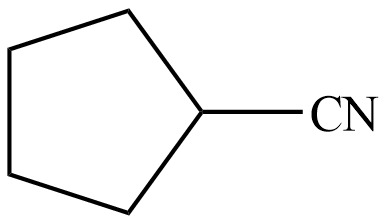
Sodium hydride abstracts a proton from the carbon which is attached to cyanide and forms secondary carbanion. The next step is intra molecular cyclization. Now this carbanion acts as nucleophile and attack to the carbon (electrophile) which is directly attach to the electronegative atom i.e. chlorine. The corresponding chemical reaction of given organic compound with a strong base is shown below
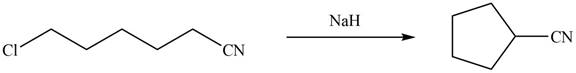
Figure 8
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is cyclopentanecarbonitrile.
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Bromination is a type of radical substitution reaction. It is highly specific reaction. In this reaction, an alkyl halide is formed by the replacement of hydrogen atom from highly substituted carbon by
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
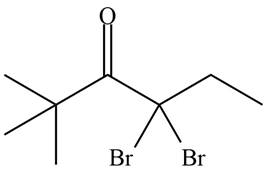
Explanation of Solution
An alkyl halide is formed by the replacement of hydrogen atom from highly substituted carbon by
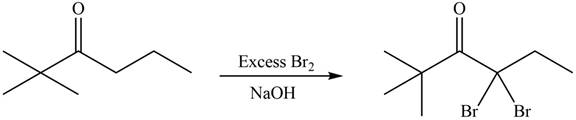
Figure 9
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The various organic reactions form different organic products with the help of the variety of reagents. Some of the organic compounds are formed by the characteristic action of the various functional groups present in them.
Answer to Problem 23.52P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
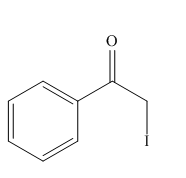
Explanation of Solution
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
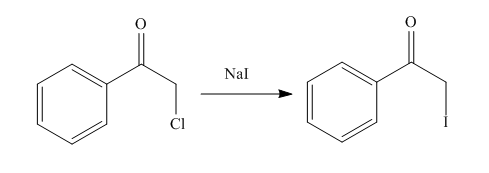
Figure 10
In the above reaction, chlorinated compound reacts with sodium iodide that results in the replacement of chlorine atom by iodine atom.
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Complete the mechanismarrow_forwardV Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
