
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553292
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 22P
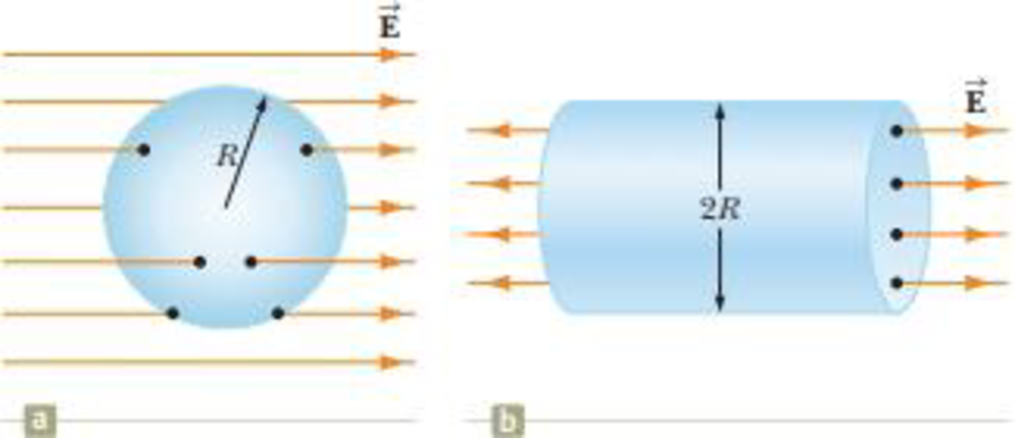
Find the net electric flux through (a) the closed spherical surface in a uniform electric field shown in Figure P23.22a and (b) the closed cylindrical surface shown in Figure P23.22b. (c) What can you conclude about the charges, if any, inside the cylindrical surface?
Figure P23.22
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
Question 01
A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling
together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure
rolling motion Question 02
A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more
down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal
Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration
b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same
acceleration
Question 03
i)
Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit
A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads
seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate
ii)
The angular acceleration
iii)
The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel
Question 04
in 20
Question B3
Consider the following FLRW spacetime:
t2
ds² = -dt² +
(dx²
+ dy²+ dz²),
t2
where t is a constant.
a)
State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat.
[2 marks]
b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function
of time t, starting at t = 0.
[3 marks]
c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy
B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect
to galaxy A.
d) The Friedmann equations are
2
k
8πG
а
4πG
+
a²
(p+3p).
3
a
3
[5 marks]
Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the
FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page.
[5 marks]
e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i)
radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv)
none of the previous. Justify your answer.
f)
[5 marks]
A conformally…
SECTION B
Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B
[Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.]
Question B1
Consider the line element
where w is a constant.
ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx²,
a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric.
[2 marks]
b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.]
[10 marks]
c)
Write down the geodesic equations.
[5 marks]
d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion.
[4 marks]
e)
Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics.
[4 marks]
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 23.2 - Suppose a point charge is located at the center of...Ch. 23.3 - If the net flux through a gaussian surface is...Ch. 23 - A negatively charged rod of finite length carries...Ch. 23 - A positively charged disk has a uniform charge per...Ch. 23 - A uniformly charged ring of radius 10.0 cm has a...Ch. 23 - The electric field along the axis of a uniformly...Ch. 23 - Example 23.3 derives the exact expression for the...Ch. 23 - A uniformly charged rod of length L and total...Ch. 23 - A continuous line of charge lies along the x axis,...Ch. 23 - A thin rod of length and uniform charge per unit...
Ch. 23 - (a) Consider a uniformly charged, thin-walled,...Ch. 23 - A vertical electric field of magnitude 2.00 104...Ch. 23 - A flat surface of area 3.20 m2 is rotated in a...Ch. 23 - A nonuniform electric field is given by the...Ch. 23 - An uncharged, nonconducting, hollow sphere of...Ch. 23 - Find the net electric flux through the spherical...Ch. 23 - Four closed surfaces, S1 through S4 together with...Ch. 23 - A charge of 170 C is at the center of a cube of...Ch. 23 - (a) Find the net electric flux through the cube...Ch. 23 - A particle with charge of 12.0 C is placed at the...Ch. 23 - A particle with charge Q = 5.00 C is located at...Ch. 23 - Prob. 20PCh. 23 - Prob. 21PCh. 23 - Find the net electric flux through (a) the closed...Ch. 23 - Figure P23.23 represents the top view of a cubic...Ch. 23 - Determine the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 23 - Prob. 25PCh. 23 - Prob. 26PCh. 23 - A large, flat, horizontal sheet of charge has a...Ch. 23 - A nonconducting wall carries charge with a uniform...Ch. 23 - A uniformly charged, straight filament 7.00 m in...Ch. 23 - You are working on a laboratory device that...Ch. 23 - Consider a long, cylindrical charge distribution...Ch. 23 - Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each...Ch. 23 - A solid sphere of radius 40.0 cm has a total...Ch. 23 - A cylindrical shell of radius 7.00 cm and length...Ch. 23 - You are working for the summer at a research...Ch. 23 - You are working for the summer at a research...Ch. 23 - Find the electric flux through the plane surface...Ch. 23 - Prob. 38APCh. 23 - Prob. 39APCh. 23 - Show that the maximum magnitude Emax of the...Ch. 23 - A line of positive charge is formed into a...Ch. 23 - Prob. 42APCh. 23 - A sphere of radius R = 1.00 m surrounds a particle...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R surrounds a particle with...Ch. 23 - A slab of insulating material has a nonuniform...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius 2a is made of a nonconducting...Ch. 23 - Prob. 47CPCh. 23 - Prob. 48CPCh. 23 - Review. A slab of insulating material (infinite in...Ch. 23 - Identical thin rods of length 2a carry equal...Ch. 23 - A solid insulating sphere of radius R has a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
More than one choice may apply. Using the terms listed below, fill in the blank with the proper term. anterior ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Identify each of the following reproductive barriers as prezygotic or postzygotic. a. One lilac species lives o...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
What process causes the Mediterranean intermediate Water MIW to become more dense than water in the adjacent At...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
4.1 Write the symbols for the following elements.
a. copper
b. platinum
c. calcium
d. manganese
e. Iron
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
- Checkpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forwardWhat is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY