
(a)
Interpretation: For a given set of compounds,
Concept Introduction: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions.
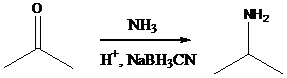
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with primary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce secondary amines.
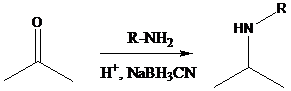
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with secondary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce tertiary amines.
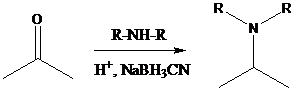
There are two ways to get the starting compounds in either left or right side cleavage of all C−N bonds. After the cleavage, retrosynthetic analysis of the starting materials is done. If both aldehyde/ketone and amine starting materials are decided, reductive amination is followed in both the ways by placing the suitable reagents.
(b)
Interpretation: For a given set of compounds, amines are to be prepared via two different methods of reductive amination
Concept Introduction: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions. Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primary amines.
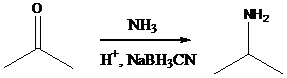
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with primary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce secondary amines.
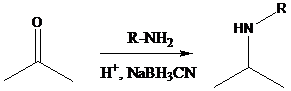
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with secondary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce tertiary amines.
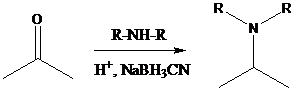
There are two ways to get the starting compounds in either left or right side cleavage of all C−N bonds. After the cleavage, retrosynthetic analysis of the starting materials is done. If both aldehyde/ketone and amine starting materials are decided, reductive amination is followed in both the ways by placing the suitable reagents.
(c)
Interpretation: For a given set of compounds, amines are to be prepared via two different methods of reductive amination
Concept Introduction: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions. Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primary amines.
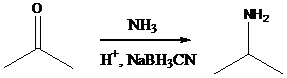
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with primary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce secondary amines.
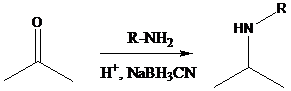
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with secondary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce tertiary amines.
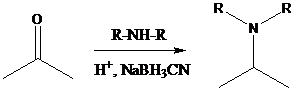
There are two ways to get the starting compounds in either left or right side cleavage of all C−N bonds. After the cleavage, retrosynthetic analysis of the starting materials is done. If both aldehyde/ketone and amine starting materials are decided, reductive amination is followed in both the ways by placing the suitable reagents.
(d)
Interpretation: For a given set of compounds, amines are to be prepared via two different methods of reductive amination
Concept Introduction: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions. Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primary amines.
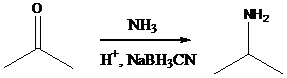
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with primary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce secondary amines.
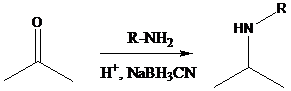
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with secondary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce tertiary amines.
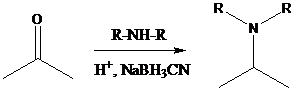
There are two ways to get the starting compounds in either left or right side cleavage of all C−N bonds. After the cleavage, retrosynthetic analysis of the starting materials is done. If both aldehyde/ketone and amine starting materials are decided, reductive amination is followed in both the ways by placing the suitable reagents.
(e)
Interpretation: For a given set of compounds, amines are to be prepared via two different methods of reductive amination
Concept Introduction: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions. Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primary amines.
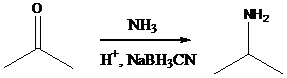
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with primary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce secondary amines.
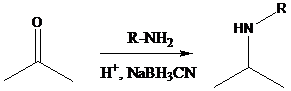
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with secondary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce tertiary amines.
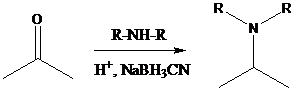
There are two ways to get the starting compounds in either left or right side cleavage of all C−N bonds. After the cleavage, retrosynthetic analysis of the starting materials is done. If both aldehyde/ketone and amine starting materials are decided, reductive amination is followed in both the ways by placing the suitable reagents.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1 TERM ACCESS
- CHEM2323 Problem 2-26 Tt O PS CH02 Name: Use the curved-arrow formalism to show how the electrons flow in the resonance form on the left to give the one on the right. (Draw all lone pairs first) (a) NH2 NH2 + (b) Problem 2-27 Double bonds can also act like Lewis bases, sharing their electrons with Lewis acids. Use curved arrows to show how each of the following double bonds will react with H-Cl and draw the resulting carbocation. (a) H2C=CH2 (b) (c) Problem 2-28 Identify the most electronegative element in each of the following molecules: (a) CH2FCI F Problem 2-29 (b) FCH2CH2CH2Br (c) HOCH2CH2NH2 (d) CH3OCH2Li F 0 0 Use the electronegativity table in Figure 2.3 to predict which bond in the following pairs is more polar and indicate the direction of bond polarity for each compound. (a) H3C-Cl or Cl-CI (b) H3C-H or H-CI (c) HO-CH3 or (CH3)3Si-CH3 (d) H3C-Li or Li-OHarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- at 32.0 °C? What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.46 M aqueous solution of urea [(NH2), CO] at 3 Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardReagan is doing an atomic absorption experiment that requires a set of zinc standards in the 0.4-1.6 ppm range. A 1000 ppm Zn solution was prepared by dissolving the necessary amount of solid Zn(NO3)2 in water. The standards can be prepared by diluting the 1000 ppm Zn solution. Table 1 shows one possible set of serial dilutions (stepwise dilution of a solution) that Reagan could perform to make the necessary standards. Solution A was prepared by diluting 5.00 ml of the 1000 ppm Zn standard to 50.00 ml. Solutions C-E are called "calibration standards" because they will be used to calibrate the atomic absorption spectrometer. a. Compare the solution concentrations expressed as ppm Zn and ppm Zn(NO3)2. Compare the concentrations expressed as M Zn and M Zn(NO3)2 - Which units allow easy conversion between chemical species (e.g. Zn and Zn(NO3)2)? - Which units express concentrations in numbers with easily expressed magnitudes? - Suppose you have an analyte for which you don't know the molar…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





