
(a)
Interpretation: The structures of 2 and 3, an acid-catalyzed mechanism for the conversion of 3 to 4 and the reasons for the equilibrium favor enamine 4 over imine 3 have to be found for the given reactions.
Concept Introduction:
An azide is converted into an
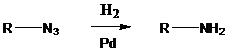
To find: Draw the structures of 2 and 3
Do hydrogenation on an azide
(b)
Interpretation: The structures of 2 and 3, an acid-catalyzed mechanism for the conversion of 3 to 4 and the reasons for the equilibrium favor enamine 4 over imine 3 have to be found for the given reactions.
Concept Introduction:
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the reaction of an

To find: Provide an acid-catalyzed mechanism for the conversion of 3 to 4
Do protonation for imine

(c)
Interpretation: The structures of 2 and 3, an acid-catalyzed mechanism for the conversion of 3 to 4 and the reasons for the equilibrium favor enamine 4 over imine 3 have to be found for the given reactions.
Concept Introduction:
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine followed by loss of H2O. The word "enamine" is derived from the affix en-, used as the suffix of alkene, and the root amine. This can be compared with enol, which is a functional group containing both alkene (en-) and alcohol (-ol). Enamines are considered to be nitrogen analogs of enols. If one of the nitrogen substituents is a hydrogen atom, H, it is the tautomeric form of an imine. This usually will rearrange to the imine; however there are several exceptions (such as aniline). The enamine-imine tautomerism may be considered analogous to the keto-enol tautomerism. In both cases, a hydrogen atom switches its location between the heteroatom (oxygen or nitrogen) and the second carbon atom. Enamines are both good nucleophiles and good bases.

To find: Get the reasons for the equilibrium favor enamine 4 over imine 3
Explain the conjugation

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1 TERM ACCESS
- Reagan is doing an atomic absorption experiment that requires a set of zinc standards in the 0.4-1.6 ppm range. A 1000 ppm Zn solution was prepared by dissolving the necessary amount of solid Zn(NO3)2 in water. The standards can be prepared by diluting the 1000 ppm Zn solution. Table 1 shows one possible set of serial dilutions (stepwise dilution of a solution) that Reagan could perform to make the necessary standards. Solution A was prepared by diluting 5.00 ml of the 1000 ppm Zn standard to 50.00 ml. Solutions C-E are called "calibration standards" because they will be used to calibrate the atomic absorption spectrometer. a. Compare the solution concentrations expressed as ppm Zn and ppm Zn(NO3)2. Compare the concentrations expressed as M Zn and M Zn(NO3)2 - Which units allow easy conversion between chemical species (e.g. Zn and Zn(NO3)2)? - Which units express concentrations in numbers with easily expressed magnitudes? - Suppose you have an analyte for which you don't know the molar…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardHow will you prepare the following buffers? 2.5 L of 1.5M buffer, pH = 10.5 from NH4Cl and NH3arrow_forward
- How will you prepare the following buffers? 2.5 L of 1.5M buffer, pH = 10.5 from NH4Cl and NH3arrow_forwardCH₂O and 22 NMR Solvent: CDCl3 IR Solvent: neat 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 15 [ اند 6,5 9.8 3.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.8 3.0 2.0 1.0 9.8 200 100arrow_forwardprotons. Calculate the mass (in grams) of H3AsO4 (MW=141.9416) needed to produce 3.125 x 1026arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





