
CHEMISTRY:MOLECULAR NATURE (LL)W/ACCESS
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781119497325
Author: JESPERSEN
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 5PE
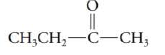
Oxidation of an alcohol gave the following product. What was the formula of the original alcohol? (Hint: How many hydrogens are removed from the alcohol carbon by oxidation?)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(ME EX1) Prblm #9/10
Can you explain in detail (step by step) I'm so confused with these problems. For turmber 13 can u turn them into lewis dot structures so I can better understand because, and then as well explain the resonance structure part. Thanks for the help.
Problems 19 and 20: (ME EX1) Can you please explain the following in detail? I'm having trouble understanding them. Both problems are difficult for me to explain in detail, so please include the drawings and answers.
(ME EX1) Prblm #4-11 Can you please help me and explain these I'm very confused in detail please. Prblm number 9 I don't understand at all (its soo confusing to me and redraw it so I can better depict it).
Chapter 22 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:MOLECULAR NATURE (LL)W/ACCESS
Ch. 22 - Prob. 1PECh. 22 - Prob. 2PECh. 22 - Prob. 3PECh. 22 - Practice Exercise 22.4
Write the IUPAC names of...Ch. 22 - Oxidation of an alcohol gave the following...Ch. 22 - Prob. 6PECh. 22 - Prob. 7PECh. 22 - Prob. 8PECh. 22 - Prob. 9PECh. 22 - Prob. 10PE
Ch. 22 - Complete the following equation by drawing...Ch. 22 - Prob. 12PECh. 22 - Prob. 13PECh. 22 - Prob. 14PECh. 22 - Prob. 15PECh. 22 - Label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions of...Ch. 22 - Draw a ribose ring and a deoxyribose ring. What is...Ch. 22 - Practice Exercise 22.18
Which base pairs match in...Ch. 22 - Prob. 1RQCh. 22 - Prob. 2RQCh. 22 - Prob. 3RQCh. 22 - Prob. 4RQCh. 22 - Prob. 5RQCh. 22 - Prob. 6RQCh. 22 - Prob. 7RQCh. 22 - Which of the following compounds has the higher...Ch. 22 - In general terms, why do functional groups impart...Ch. 22 - Prob. 10RQCh. 22 - What is the difference between geometric isomers...Ch. 22 - Prob. 12RQCh. 22 - No number is needed to identify the location of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 14RQCh. 22 - Prob. 15RQCh. 22 - Prob. 16RQCh. 22 - 22.17 In general terms, why doesn't benzene...Ch. 22 - Prob. 18RQCh. 22 - 22.19 Explain why is more soluble in water than ....Ch. 22 - Prob. 20RQCh. 22 - Prob. 21RQCh. 22 - Why do aldehydes and ketones have boiling points...Ch. 22 - Acetic acid boils at 118C, higher even than...Ch. 22 - Methyl ethanoate has many more atoms than its...Ch. 22 - Prob. 25RQCh. 22 - 22.26 Write condensed structures of the following...Ch. 22 - 3-Butanol is not a proper name, but a structure...Ch. 22 - Prob. 28RQCh. 22 - Prob. 29RQCh. 22 - Prob. 30RQCh. 22 - Prob. 31RQCh. 22 - Prob. 32RQCh. 22 - Amines, RNH2, do not have boiling points as high...Ch. 22 - A monofunctional organic nitrogen compound...Ch. 22 - Prob. 35RQCh. 22 - Prob. 36RQCh. 22 - Prob. 37RQCh. 22 - Write the products that can be expected to form in...Ch. 22 - Prob. 39RQCh. 22 - Prob. 40RQCh. 22 - 22.41 What do we mean by the term polymer...Ch. 22 - Prob. 42RQCh. 22 - Prob. 43RQCh. 22 - Prob. 44RQCh. 22 - Prob. 45RQCh. 22 - Prob. 46RQCh. 22 - Prob. 47RQCh. 22 - Prob. 48RQCh. 22 - Prob. 49RQCh. 22 - Prob. 50RQCh. 22 - Prob. 51RQCh. 22 - Prob. 52RQCh. 22 - Prob. 53RQCh. 22 - Prob. 54RQCh. 22 - Prob. 55RQCh. 22 - Prob. 56RQCh. 22 - Prob. 57RQCh. 22 - Prob. 58RQCh. 22 - What are the three fundamental needs for...Ch. 22 - Prob. 60RQCh. 22 - Prob. 61RQCh. 22 - Prob. 62RQCh. 22 - Name the compounds that form when sucrose is...Ch. 22 - Prob. 64RQCh. 22 - Prob. 65RQCh. 22 - Prob. 66RQCh. 22 - Prob. 67RQCh. 22 - 22.68 What function is served by glycogen in the...Ch. 22 - How are lipids defined?Ch. 22 - Why are lipids more soluble than carbohydrates in...Ch. 22 - 22.71 Cholesterol is not an ester, yet it is...Ch. 22 - A product such as corn oil is advertised as...Ch. 22 - Is it likely that the following compound could be...Ch. 22 - Describe the specific ways in which the monomers...Ch. 22 - What is the peptide bond? How is it similar to the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 76RQCh. 22 - Prob. 77RQCh. 22 - Why is a distinction made between the terms...Ch. 22 - Prob. 79RQCh. 22 - What kind of substance makes up most enzymes?Ch. 22 - Prob. 81RQCh. 22 - Prob. 82RQCh. 22 - Prob. 83RQCh. 22 - 22.84 How are the two DNA strands in a double...Ch. 22 - In what ways do DNA and RNA differ structurally.Ch. 22 - 22.86 Which base pairs with
Ch. 22 - The process of transcription begins with which...Ch. 22 - The process of translation begins with which...Ch. 22 - Prob. 89RQCh. 22 - 22.90 Write full (expanded) structures for each of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 91RQCh. 22 - Prob. 92RQCh. 22 - Prob. 93RQCh. 22 - Prob. 94RQCh. 22 - Prob. 95RQCh. 22 - Prob. 96RQCh. 22 - Prob. 97RQCh. 22 - Prob. 98RQCh. 22 - Prob. 99RQCh. 22 - Prob. 100RQCh. 22 - Prob. 101RQCh. 22 - 22.102 Write the structures of the cis and tram...Ch. 22 - 22.103 Write the structures of the products that...Ch. 22 - Prob. 104RQCh. 22 - 22.105 Repeat Problem 22.103 using...Ch. 22 - Repeat Problem 22.104 using cyclohexene. The...Ch. 22 - Prob. 107RQCh. 22 - Predict the products of the reaction of benzene...Ch. 22 - Prob. 109RQCh. 22 - Prob. 110RQCh. 22 - Prob. 111RQCh. 22 - Prob. 112RQCh. 22 - Prob. 113RQCh. 22 - Write the structure of the product of the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 115RQCh. 22 - Prob. 116RQCh. 22 - Prob. 117RQCh. 22 - Prob. 118RQCh. 22 - Prob. 119RQCh. 22 - Prob. 120RQCh. 22 - Prob. 121RQCh. 22 - Write the structures of the products that form in...Ch. 22 - Prob. 123RQCh. 22 - Prob. 124RQCh. 22 - Prob. 125RQCh. 22 - Prob. 126RQCh. 22 - Prob. 127RQCh. 22 - Prob. 128RQCh. 22 - 22.129 Write the structure of a triacylglycerol...Ch. 22 - 22.130 Write the structures of the products of the...Ch. 22 - Write the structure of the triacylglycerol that...Ch. 22 - *22.132 If the compound in Problem 22.130 is...Ch. 22 - *22.133 What parts of glyccrophospholipid...Ch. 22 - *22.134 In general terms, describe the structure...Ch. 22 - Prob. 135RQCh. 22 - What is the structure of the tripeptide that could...Ch. 22 - 22.137 What are the structures of the two...Ch. 22 - Prob. 138RQCh. 22 - Prob. 139RQCh. 22 - Prob. 140RQCh. 22 - Prob. 141RQCh. 22 - 22.142 Suggest a reason why trimethylamine, , has...Ch. 22 - Prob. 143RQCh. 22 - How many tripeptides can be made from three...Ch. 22 - Prob. 145RQCh. 22 - Prob. 146RQCh. 22 - Estimate the number of kilojoules of heat that...Ch. 22 - Prob. 148RQCh. 22 - Prob. 149RQCh. 22 - The compound that causes your eyes to water when...Ch. 22 - Prob. 151RQCh. 22 - Prob. 152RQCh. 22 - Use resonance structures to explain why urea,...Ch. 22 - Prob. 154RQCh. 22 - Prob. 155RQ
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Microphylls are found in which plant group? (A) lycophytes (B) liverworts (C) ferns (D) hornworts
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
61. What is the pH of a solution in which 224 mL of HCl(g), measured at 27.2 °C and 1.02 atm, is dissolved in 1...
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. The fact that we always see the same f...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Why can algae and cyanobacteria be considered indicators of productivity as well as of pollution?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative posi...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ME EX1) Prblm #19-20 I'm so confused with these problems. Can you please help me solve them and explain them? Problems number 19-20, and thanks! step by step and in detail for me please helparrow_forwardCalculate the flux of oxygen between the ocean and the atmosphere, given that: Temp = 18°C Salinity = 35 ppt Density = 1025 kg/m3 Oxygen concentration measured in bulk water = 263.84 mmol/m3 Wind speed = 7.4 m/s Oxygen is observed to be about 10% initially supersaturatedarrow_forward( ME EX1) Prblm 27-28: Can you explain to me both prblms in detail and for prblm 28 what do you mean bi conjugated bi ponds and those structures I'm confused...arrow_forward
- A. Determine the number of electrons in a system of cyclic conjugation (zero if no cyclic conjugation). B. Specify whether the species is "a"-aromatic, "aa"-anti-aromatic, or "na"-non-aromatic (neither aromatic nor anti-aromatic). (Presume rings to be planar unless structure obviously prevents planarity. If there is more than one conjugated ring, count electrons in the largest.) 1. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 18 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) a 2. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 10 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) naarrow_forwardWater is boiling at 1 atm pressure in a stainless steel pan on an electric range. It is observed that 2 kg of liquid water evaporates in 30 min. Find the rate of heat transfer to the water (kW).arrow_forwardCould you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the resonance structures that were given please.arrow_forward
- Could you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the question.arrow_forwardplease solve. If the answer is "no error" and it asks me to type something, and i typed a-helix, its always wrong.arrow_forwardCan you please solve and explain this for me in a simple way? I cant seem to comprehend this problem.arrow_forward
- Part I. Problem solving. Include all necessary calculations 13 provide plots and graphs. Complexation wl diphenyl carbazide (OPC) in acidic media is another type of sensitive photometric method used for the analysis of aqueous. hexavalent chromium. At 540nm the cherry-red complex as a result of DPC reaction w/ chromium can be photometrically measured. at this wavelength. - a 25mL The UV-vis analysis for the determination of nexavalent chromium in ground water sample is given below. The experiment was based on external calibration method w/ each measurement sample prepared are as follows lab sample analysis contained the standard 100 ppb croy cor groundwater sample, volumes used as indicated below), 12.50 mL of 0.02 M H2Soy and 5.50 ml of 100 ppm DPC (wi water to adjust final volume to 25-ml). The main stripping method was square wave voltammetry, following the conditions set in the main ASV experiment. Standard 100 Volumetric Groundwater H2SO4 0.20 M, flask Sample, mL ppb CrO4*, 100…arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardPredict the products of the following reactions. Draw mechanism arrows for each step for a, b, and c. a.) HBr b.) HI H₂O H2SO4 d.) C12 HO H2SO4 1.) BH3 2.) H2O2, NaOHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning




Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 2; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AL_CM_Btef4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 1; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PPIa6EHJMJw;License: Standard Youtube License