
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134074580
Author: Bruice, Paula Yurkanis
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 38P
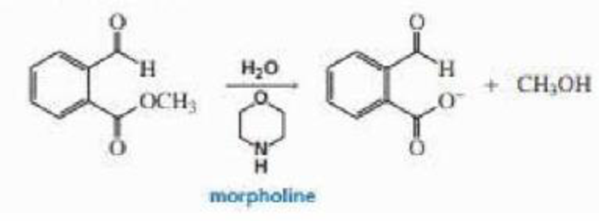
The hydrolysis of the ester shown here is catalyzed by morpholine. Propose a mechanism for the reaction, (Hint: The pKa of the conjugate acid of morpholine is 9.3. so morpholine is too weak a base to function as a base catalyst.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Viscosity of a liquid related to the activation energy.
Vibrational contributions to internal energy and heat capacity1) are temperature independent2) are temperature dependent
The approximation of calculating the partition function by integration instead of the summation of all the energy terms can only be done if the separation of the energy levels is much smaller than the product kT. Explain why.
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
Ch. 22.2 - Compare each of the mechanisms listed here with...Ch. 22.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 22.3 - a. Draw the mechanism for the following reaction...Ch. 22.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 22.5 - Propose a mechanism for the Co2+ catalyzed...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 10PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 22.9 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 22.9 - Which of the following C-terminal peptide bonds is...Ch. 22.9 - Carboxypeptidase A has esterase activity as well...Ch. 22.10 - Arginine and lysine side chains fit into trypsins...Ch. 22.10 - Explain why serine proteases do not catalyze...Ch. 22.11 - If H2 18O is used in the hydrolysis reaction...Ch. 22.11 - Draw the pH-activity profile for an enzyme that...Ch. 22.12 - The pHactivity profile for glucose-6-phosphate...Ch. 22.12 - Prob. 23PCh. 22.13 - Draw the mechanism for the hydroxide ion-catalyzed...Ch. 22.13 - What advantage does the enzyme gain by forming an...Ch. 22.13 - Prob. 26PCh. 22.13 - Prob. 27PCh. 22.13 - Aldolase shows no activity if it is incubated with...Ch. 22 - Which of the following parameters would be...Ch. 22 - Prob. 29PCh. 22 - Prob. 30PCh. 22 - Prob. 31PCh. 22 - Indicate the type of catalysis that is occurring...Ch. 22 - The deuterium kinetic isotope effect (KH2O/KD2O)...Ch. 22 - Prob. 34PCh. 22 - Co2+ catalyzes the hydrolysis of the lactam shown...Ch. 22 - there are two kinds of aldolases. Class I...Ch. 22 - Prob. 37PCh. 22 - The hydrolysis of the ester shown here is...Ch. 22 - Prob. 39PCh. 22 - At pH = 12, the rate of hydrolysis of ester A is...Ch. 22 - 2-Acetoxycyclohexyl tosylate reacts with acetate...Ch. 22 - Proof that an imine was formed between aldolase...Ch. 22 - Prob. 43PCh. 22 - a. Explain why the alkyl halide shown here reacts...Ch. 22 - Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the meaning of: the electron partition function is equal to the degeneracy of the ground state.arrow_forward28. For each of the following species, add charges wherever required to give a complete, correct Lewis structure. All bonds and nonbonded valence electrons are shown. a. b. H H H H H :0-C-H H H H-C-H C. H H d. H-N-0: e. H H-O H-O H B=0 f. H—Ö—Ñ—Ö—H Norton Private Barrow_forwardAt 0oC and 1 atm, the viscosity of hydrogen (gas) is 8.55x10-5 P. Calculate the viscosity of a gas, if possible, consisting of deuterium. Assume that the molecular sizes are equal.arrow_forward
- Indicate the correct option for the velocity distribution function of gas molecules:a) its velocity cannot be measured in any other way due to the small size of the gas moleculesb) it is only used to describe the velocity of particles if their density is very high.c) it describes the probability that a gas particle has a velocity in a given interval of velocitiesd) it describes other magnitudes, such as pressure, energy, etc., but not the velocity of the moleculesarrow_forwardIndicate the correct option for the velocity distribution function of gas molecules:a) its velocity cannot be measured in any other way due to the small size of the gas moleculesb) it is only used to describe the velocity of particles if their density is very high.c) it describes the probability that a gas particle has a velocity in a given interval of velocitiesd) it describes other magnitudes, such as pressure, energy, etc., but not the velocity of the moleculesarrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure of the alkane 4-ethyl-2, 2, 5, 5- tetramethylnonane. How many primary, secondary, tertiary, and quantenary carbons does it have?arrow_forward
- Electronic contribution to the heat capacity at constant volume A) is always zero B) is zero, except for excited levels whose energy is comparable to KT C) equals 3/2 Nk D) equals Nk exp(BE)arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCalculate the packing factor of CaTiO3. It has a perovskite structure. Data: ionic radii Co²+ = 0.106 nm, Ti4+ = 0.064 nm, O² = 0.132 nm; lattice constant is a = 2(rTi4+ + ro2-). Ca2+ 02- T14+ Consider the ions as rigid spheres. 1. 0.581 or 58.1% 2. -0.581 or -58.1 % 3. 0.254 or 25.4%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License