
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134074580
Author: Bruice, Paula Yurkanis
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 44P
a. Explain why the
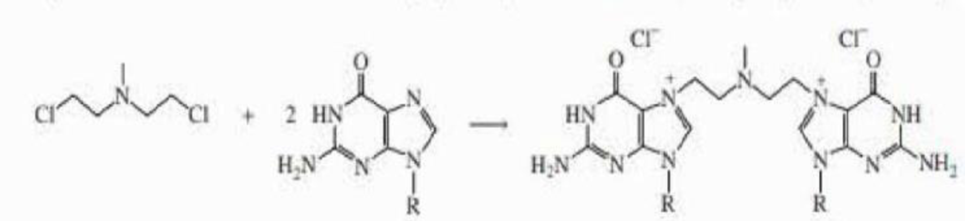
b. The alkyl halide can react with two guanines, each in a different DNA chain, thereby cross-linking the chains. Propose a mechanism for the cross-linking reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2.
CI
The intermediate in the following nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction has at least 5 resonance
structures. For this question, complete the following tasks:
a. Show the mechanistic arrow(s) for the first step.
b. Draw TWO of the many resonance structures of the intermediate, drawing out the -NO₂ groups in each.
c. Draw the neutral product.
NO₂
NO₂ HO
and
others
neutral product
Help
Show the steps of the following
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
Ch. 22.2 - Compare each of the mechanisms listed here with...Ch. 22.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 22.3 - a. Draw the mechanism for the following reaction...Ch. 22.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 22.5 - Propose a mechanism for the Co2+ catalyzed...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 10PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 22.9 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 22.9 - Which of the following C-terminal peptide bonds is...Ch. 22.9 - Carboxypeptidase A has esterase activity as well...Ch. 22.10 - Arginine and lysine side chains fit into trypsins...Ch. 22.10 - Explain why serine proteases do not catalyze...Ch. 22.11 - If H2 18O is used in the hydrolysis reaction...Ch. 22.11 - Draw the pH-activity profile for an enzyme that...Ch. 22.12 - The pHactivity profile for glucose-6-phosphate...Ch. 22.12 - Prob. 23PCh. 22.13 - Draw the mechanism for the hydroxide ion-catalyzed...Ch. 22.13 - What advantage does the enzyme gain by forming an...Ch. 22.13 - Prob. 26PCh. 22.13 - Prob. 27PCh. 22.13 - Aldolase shows no activity if it is incubated with...Ch. 22 - Which of the following parameters would be...Ch. 22 - Prob. 29PCh. 22 - Prob. 30PCh. 22 - Prob. 31PCh. 22 - Indicate the type of catalysis that is occurring...Ch. 22 - The deuterium kinetic isotope effect (KH2O/KD2O)...Ch. 22 - Prob. 34PCh. 22 - Co2+ catalyzes the hydrolysis of the lactam shown...Ch. 22 - there are two kinds of aldolases. Class I...Ch. 22 - Prob. 37PCh. 22 - The hydrolysis of the ester shown here is...Ch. 22 - Prob. 39PCh. 22 - At pH = 12, the rate of hydrolysis of ester A is...Ch. 22 - 2-Acetoxycyclohexyl tosylate reacts with acetate...Ch. 22 - Proof that an imine was formed between aldolase...Ch. 22 - Prob. 43PCh. 22 - a. Explain why the alkyl halide shown here reacts...Ch. 22 - Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can someone explain the slide please, what does it mean Polyalkylation is often oberved?? only disubstituted product can be major product ? can trisubsituted also exist in this reaction? I am confused .arrow_forwardThe hydration reaction of 1-hexene includes the addition of water across the double bond, adding an alcohol group to the more substituted carbon. Sulfuric acid is used as the catalyst for the reaction, which donates a hydrogen. The resulting product is a racemic mixture of 2-hexanol. A. Draw the alkene hydration reaction and its product(s) using information given above. B. Please include reaction mechanism with arrows showing all steps resulting in product formation.arrow_forwardCan someone please help with this.arrow_forward
- Consider the Friedel-Crafts (FC) alkylation of N-phenylacetamide (shown below) in which a reaction with 1-chloropropane and AlCl3 produces two isomers of isopropyl N-phenylacetamide. 1. Draw the complete reaction mechanism for the formation of the ortho product (para is also formed). 2. Is this reaction faster or slower than the similar FC reaction starting with benzene (C6H6)? Explain why. 3. Explain why this reaction produces the ortho and para products (but not meta). Use your mechanism to help explain parts #2 and #3. Use additional drawings and words as needed.arrow_forward5. Which of the following is a true statement? A. Electrophile must be electron deficient. B. Steric effect contributes to the SN1 reactivity of tertiary alkyl halides. C. Retention products could be observed in SN2 reaction. D. The nucleophilicity of a species is equal to its basicity. E. Non-polar solvent is suitable for nucleophilic substitution.arrow_forward2. The intermediate in the following nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction has at least 5 resonance structures. For this question, complete the following tasks: a. Show the mechanistic arrow(s) for the first step. b. Draw TWO of the many resonance structures of the intermediate, drawing out the -NO₂ groups in each. c. Draw the neutral product. يمهم NO₂ NO₂ HO and others neutral productarrow_forward
- What is the rate-determining step in the mechanism of an electrophilic substitution reaction of benzene? Select one: OA. Attachment of the electrophile to benzene ring. OB. Bonding of catalyst to electrophile precursor. O C. Reformation of acid catalyst. OD. Formation of the electrophile. OE. Loss of H+ ion form arenium ion intermediate to reform aromatic ring.arrow_forwardMechanism pleasearrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- Circle the correct bolded word. a. Hydrogenation of an alkyne with palladium on carbon can / cannot be controlled to give an alkene. b. When a reaction becomes more exothermic, the transition state looks more like the substrate / product. C. Addition of two equivalents of HBr to an alkyne results in a vicinal / geminal dibromide. d. An SN2 reaction involves the collision of two alkyl halides to form a new carbon-carbon bond. True / Falsearrow_forward1arrow_forwardGl A. intermediate. alkyl halide is most likely to undergo the reaction mechanism which forms a carbocationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Coenzymes and cofactors; Author: CH15 SWAYAM Prabha IIT Madras;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bubY2Nm7hVM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Aromaticity and Huckel's Rule; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-BguH4_WBQ;License: Standard Youtube License