
(a)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which accept proton. They are also known as proton acceptors. Base accepts a proton and forms conjugate acid. The compound
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
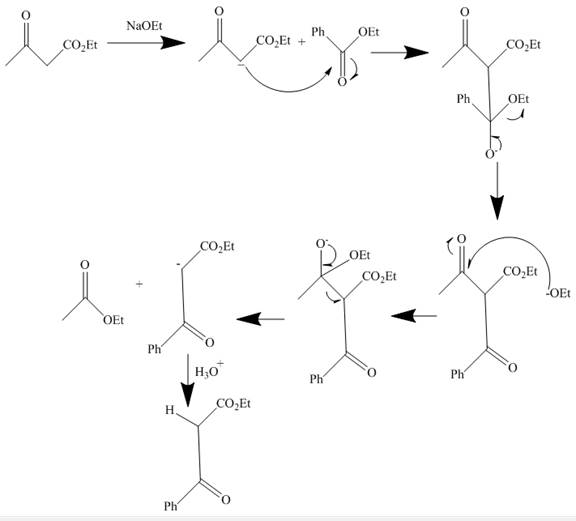
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
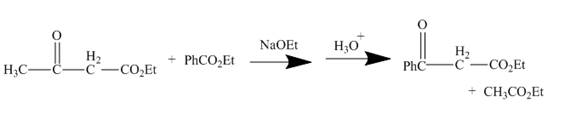
Figure 1
The reaction of given ester with

Figure 2
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which accept proton. They are also known as proton acceptors. Base accepts a proton and forms conjugate acid. The compound
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
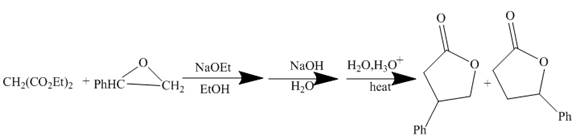
Figure 3
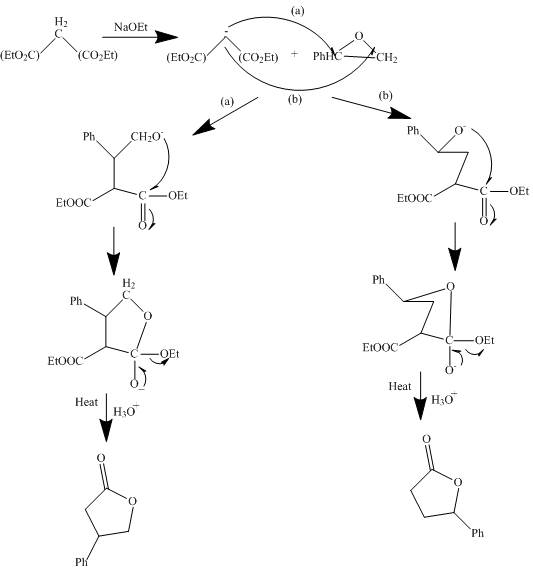
The reaction of a given ester with substituted cyclic ether in the presence of a stong base undergoes ring closure with the help of internal nucleophile to form the desired product.
The complete mechanism is shown below.

Figure 4
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The addition of proton in the chemical reaction is known as protonation. Water acts as a nucleophile due to the presence of lone pair on oxygen atom. Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which accept proton. They are also known as proton acceptors. Base accepts a proton and forms conjugate acid.
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
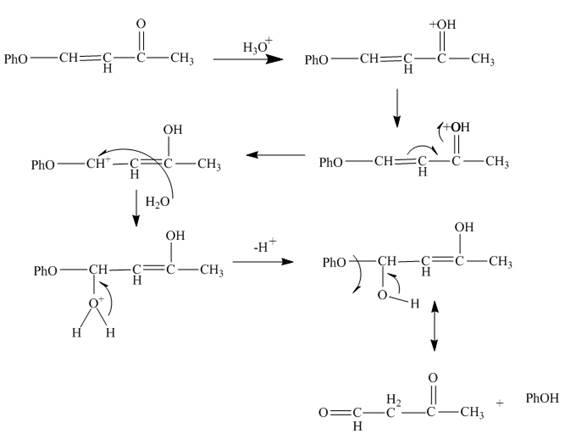
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
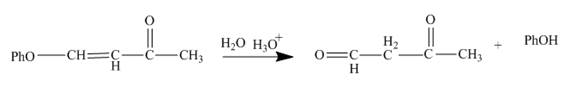
Figure 5
The reaction of given substrate with hydronium ion undergoes electrophilic addition followed by the addition of water molecule to form the desired product.
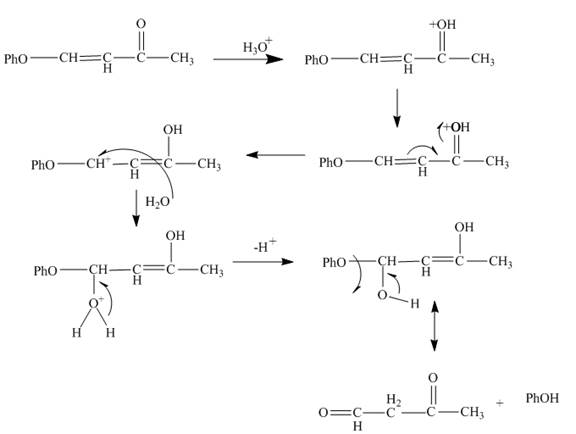
Figure 6
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The addition of proton in the chemical reaction is known as protonation. Water acts as a nucleophile due to the presence of lone pair on oxygen atom. Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which accept proton. They are also known as proton acceptors. Base accepts a proton and forms conjugate acid.
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
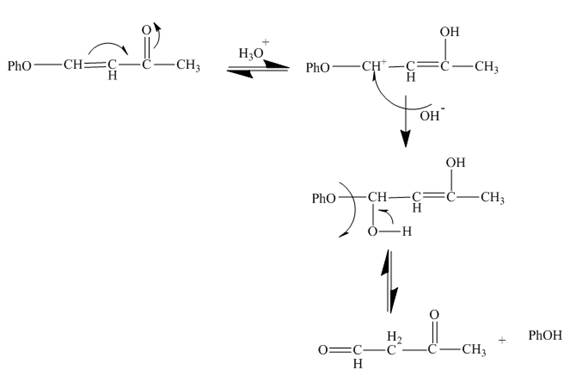
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
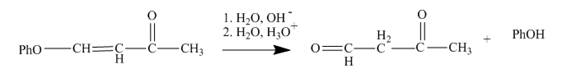
Figure 7
The reaction of given substrate with

Figure 8
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
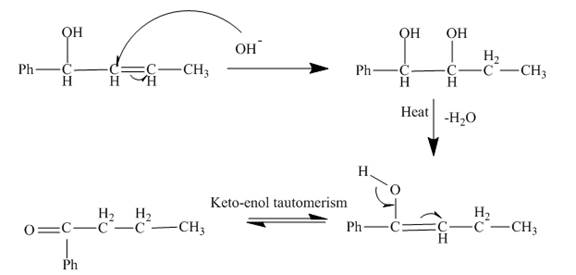
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
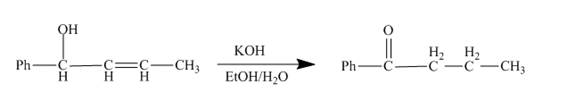
Figure 9
The reaction of given substrate with

Figure 10
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
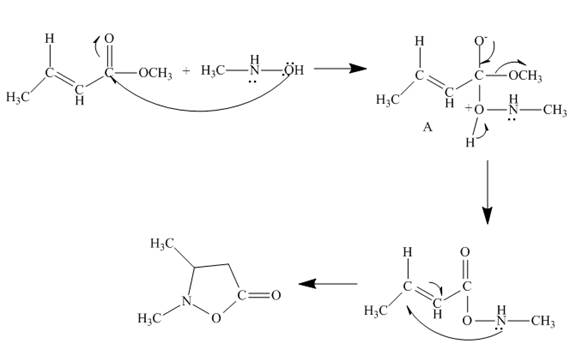
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
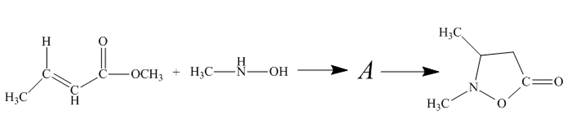
Figure 11
The reaction of given ester with substituted hydroxylamine undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction followed by ring closure with the help of lone pair present on the nitrogen atom to form the desired product. The complete mechanism is shown below.

Figure 12
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Ester undergoes hydrolysis in presence of base in aqueous solution. The ester upon hydrolysis forms the carboxylate salt and alcohol. The presence of
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
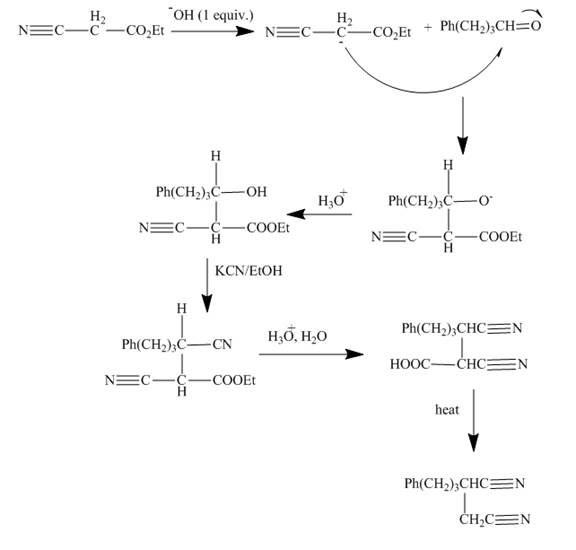
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
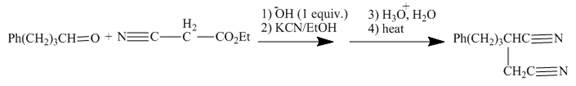
Figure 13
The reaction of given ester with substituted

Figure 14
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
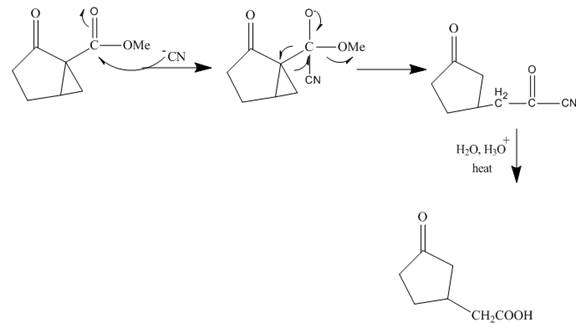
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
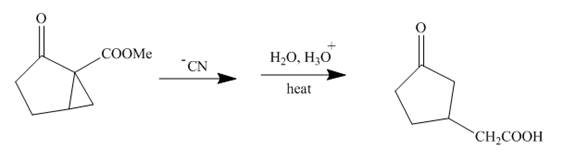
Figure 15
The reaction of given ester with cyanide ion undergoes nucleophilic addition followed by hydrolysis with the removal of carbon dioxide gas to form the desired product. The complete mechanism is shown below.

Figure 16
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In the Wittig reaction, an aldehydes or a
The triphenyl phophonium ylide is termed as Wittig reagent.
Answer to Problem 22.91AP
The curved arrow mechanism is shown below.
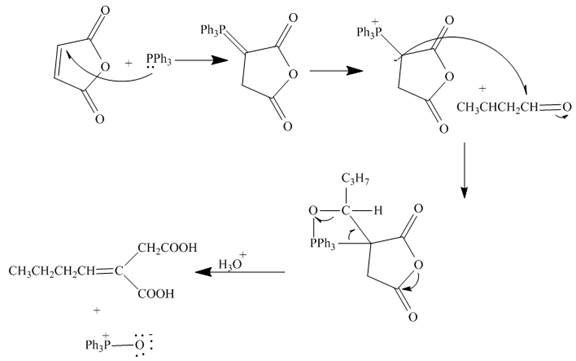
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
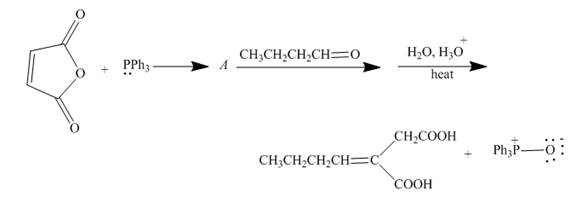
Figure 17
The reaction of given substrate with triphenyl phophine to form ylide which further reacts with carbonyl compound undergoes nucleophilic addition followed by hydrolysis gives the desired product. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 18
The curved arrow mechanism is shown in Figure 18.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw a tetramer if this alternating copolymer pleasearrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward8:44 PM Sun Apr 13 Earn Freecash.com O Measurement and Matter =1 Setting up a unit conversion 110 Eddie says... ✰ www-awu.aleks.com A student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equation. Note: your answer should be in the form of one or more fractions multiplied together. (- 4 J kJ -7.0 × 10 ☐ = ? mmol.°C mol °C x10 μ Explanation Check □·□ torox.io Grey Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forward
- i need help on how to complete the followingarrow_forwardno AI walkthrough current image is wrong answerarrow_forwarda. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

