
Concept explainers
Consider the following sequence of DNA:
- What dipeptide is formed from this DNA after transcription and translation?
- If a mutation converts CGG to CGT in DNA, what dipeptide is formed?
- If a mutation converts CGG to CCG in DNA, what dipeptide is formed?
- If a mutation converts CGG to AGG in DNA, what dipeptide is formed?
(a)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from DNA 3' TTA CGG 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation −Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Ala.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
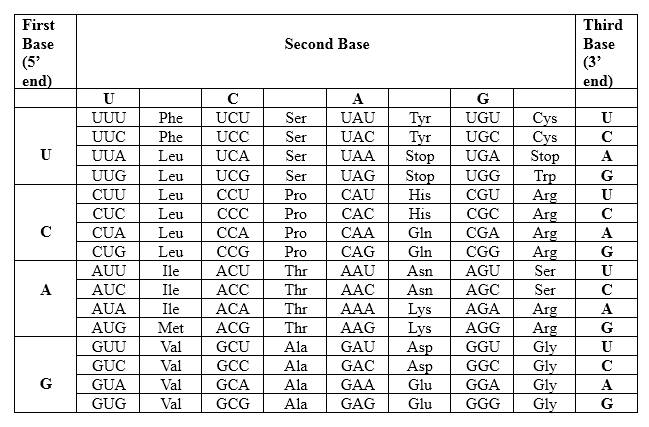
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and GCC is unique for alanine amino acid.
Asn-Ala is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA CGG 5' template DNA strand.
(b)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from mutated DNA 3' TTA CGT 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation − Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Ala.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
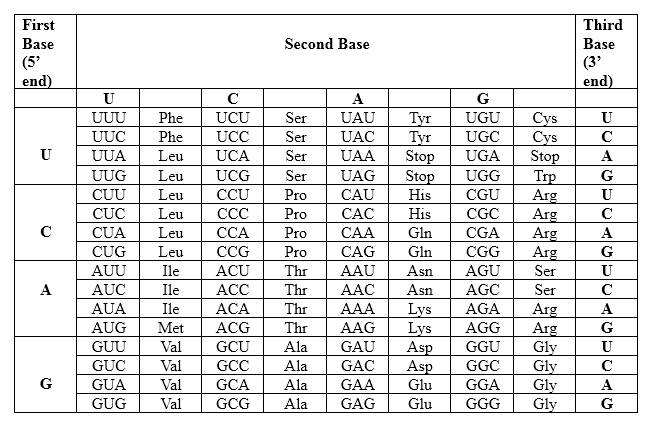
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. For, Alanine (Ala) there are 4 different but unique codons, which are GCU, GCC, GCA and GCG. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and GCA is unique for alanine amino acid. Though there is a mutation in the strand, in this example same peptide is generated as the non-mutated peptide.
Asn-Ala is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA CGT 5' mutated template DNA strand.
(c)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from mutated DNA 3' TTA CCG 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation − Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Gly.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
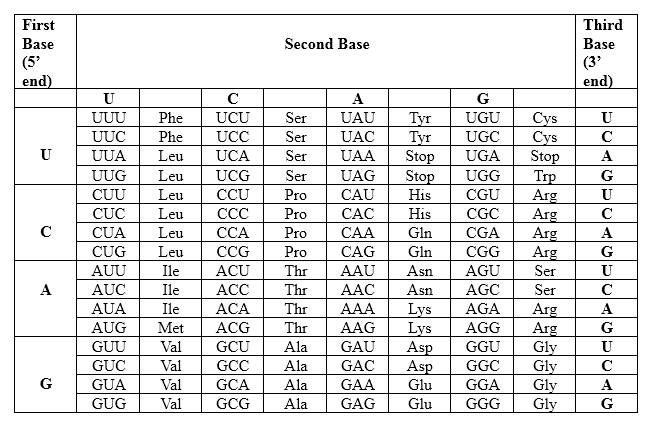
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. For, Glycine (Gly) there are 4 different but unique codons, which are GGU, GGC, GGA and GGG. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and GGC is unique for glycine amino acid. Hence, because of the mutation in the strand, in this example resulting peptide from the mutated template DNA is different from the non-mutated peptide.
Asn-Gly is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA CCG 5' mutated template DNA strand.
(d)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from mutated DNA 3' TTA AGG 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation − Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Ser.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
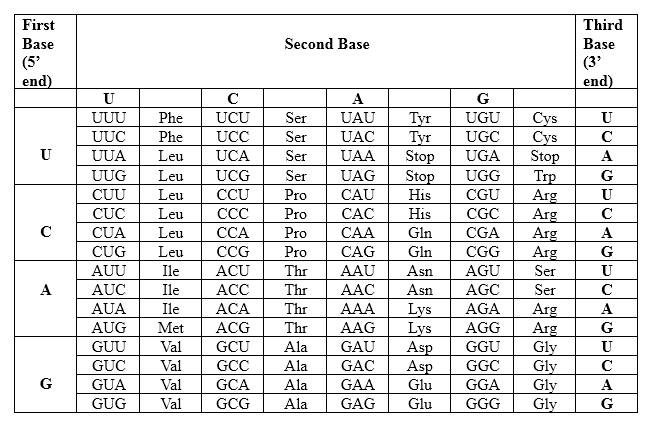
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. For, Serine (Ser) there are 6 different but unique codons, which are UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and UCC is unique for serine amino acid. Hence, because of the mutation in the strand, in this example resulting peptide from the mutated template DNA is different from the non-mutated peptide.
Asn-Ser is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA AGG 5' mutated template DNA strand.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- Identify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. CH3 H₁₂C ○ E ○ z ○ cis transarrow_forwardIdentify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. H₂C- CH3 О Е ○ cis ○ transarrow_forwardThe decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide according to the equation: 50°C 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) follows first-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.0065 s-1. If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.275 M, determine: the final concentration of N2O5 after 180 seconds. ...arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCS2(g) →CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k[CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10−6 s−¹. S What is the concentration of CS2 after 5 hours if the initial concentration is 0.25 M?arrow_forwardCS2(g) → CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k [CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10-6 s−1. S Calculate the half-life.arrow_forward
- The following is a first order reaction where the rate constant, k, is 6.29 x 10-3 min-*** What is the half-life? C2H4 C2H2 + H2arrow_forwardControl Chart Drawing Assignment The table below provides the number of alignment errors observed during the final inspection of a certain model of airplane. Calculate the central, upper, and lower control limits for the c-chart and draw the chart precisely on the graph sheet provided (based on 3-sigma limits). Your chart should include a line for each of the control limits (UCL, CL, and LCL) and the points for each observation. Number the x-axis 1 through 25 and evenly space the numbering for the y-axis. Connect the points by drawing a line as well. Label each line drawn. Airplane Number Number of alignment errors 201 7 202 6 203 6 204 7 205 4 206 7 207 8 208 12 209 9 210 9 211 8 212 5 213 5 214 9 215 8 216 15 217 6 218 4 219 13 220 7 221 8 222 15 223 6 224 6 225 10arrow_forwardCollagen is used to date artifacts. It has a rate constant = 1.20 x 10-4 /years. What is the half life of collagen?arrow_forward
- יווי 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 [ppm] 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 6 [ppm] 1 1.5 -2.5 3.5arrow_forward2H2S(g)+3O2(g)→2SO2(g)+2H2O(g) A 1.2mol sample of H2S(g) is combined with excess O2(g), and the reaction goes to completion. Question Which of the following predicts the theoretical yield of SO2(g) from the reaction? Responses 1.2 g Answer A: 1.2 grams A 41 g Answer B: 41 grams B 77 g Answer C: 77 grams C 154 g Answer D: 154 grams Darrow_forwardPart VII. Below are the 'HNMR, 13 C-NMR, COSY 2D- NMR, and HSQC 2D-NMR (similar with HETCOR but axes are reversed) spectra of an organic compound with molecular formula C6H1003 - Assign chemical shift values to the H and c atoms of the compound. Find the structure. Show complete solutions. Predicted 1H NMR Spectrum 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 f1 (ppm) Predicted 13C NMR Spectrum 100 f1 (ppm) 30 220 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 90 80 70 -26 60 50 40 46 30 20 115 10 1.0 0.9 0.8 0 -10arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





